
State what is meant by the refraction of light. State Snell’s law for the refraction of light and also express it mathematically.
The refractive index of air with respect to glass is $\dfrac{2}{3}$, and the refractive index of water with respect to air is $\dfrac{4}{3}$. If the speed of the light in glass is $2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$, find the speed of the light in (a) air, (b) water.
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: Define refraction and the properties of refraction. The change in the direction of propagation of refracted ray at the junction two medium depends on the refractive index of the two media. Obtain the formula for refractive index in terms of the velocity of light in the two media.
Snell’s law: $\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{n}_{2}}}{{{n}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{{{v}_{2}}}\text{ = constant}$. Use Snell’s law to solve the problem.
Complete step by step answer:
When a light ray travels from one medium to another at the interface of the two medium a part of the light ray will be reflected back to the first medium and the other part will enter the second medium. The direction of propagation of the obliquely incident light ray that will enter the second medium, changes at the interface of the two media. This is called the refraction. The speed of light depends on the medium in which it is travelling. So, when it enters from one medium to another, there will be a change in its speed. So, it will change its direction to keep the time constant.
When a light ray enters from a rarer medium to denser medium, the light rays will bend towards the normal. And when the light ray travels from a denser to a rarer medium, it will bend away from the normal as shown below.
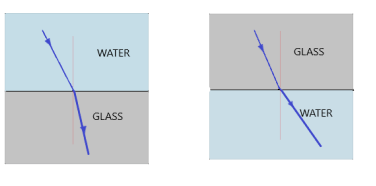
Snell’s law of refraction:
For a given pair of medium and colour of light, sin of the angle of incident to the sin of the angle of the refraction is a constant.
The mathematical expression is
$\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\text{ constant}$
$\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{n}_{2}}}{{{n}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{{{v}_{2}}}\text{ }\to \text{ 1}$
In the problem,
The velocity of light in the glass, ${{v}_{g}}=2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$
The refractive index of air with respect to glass,
$\dfrac{{{n}_{a}}}{{{n}_{g}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{{{v}_{g}}}{{{v}_{a}}}\text{ }\to \text{ 2}$
The refractive index of water with respect to air,
$\dfrac{{{n}_{w}}}{{{n}_{a}}}=\dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{{{v}_{a}}}{{{v}_{w}}}\text{ }\to \text{ 3}$
In equation (2),
$\dfrac{{{v}_{g}}}{{{v}_{a}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}$, substituting the value of ${{v}_{g}}$
$\dfrac{2\times {{10}^{8}}}{{{v}_{a}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}$, then we will get
${{v}_{a}}=\dfrac{3\times 2\times {{10}^{8}}}{2}=3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$
Now in equation (3),
$\dfrac{{{v}_{a}}}{{{v}_{w}}}=\dfrac{4}{3}$
${{v}_{w}}=\dfrac{3\times {{10}^{8}}\times 3}{4}=2.25\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$
Therefore, the velocity of light in air and water are $3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$ and $2.25\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$ respectively.
Note: So far, light is the fastest moving wave. Its velocity is $3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$, which means it travels about 3 lakh km in just one second. The speed of the light reduces as it moves through solids and liquids due to the collision with the particles in the medium. It can be described as, with the increase in refractive index of the medium the velocity of light decreases.
Snell’s law: $\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{n}_{2}}}{{{n}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{{{v}_{2}}}\text{ = constant}$. Use Snell’s law to solve the problem.
Complete step by step answer:
When a light ray travels from one medium to another at the interface of the two medium a part of the light ray will be reflected back to the first medium and the other part will enter the second medium. The direction of propagation of the obliquely incident light ray that will enter the second medium, changes at the interface of the two media. This is called the refraction. The speed of light depends on the medium in which it is travelling. So, when it enters from one medium to another, there will be a change in its speed. So, it will change its direction to keep the time constant.
When a light ray enters from a rarer medium to denser medium, the light rays will bend towards the normal. And when the light ray travels from a denser to a rarer medium, it will bend away from the normal as shown below.

Snell’s law of refraction:
For a given pair of medium and colour of light, sin of the angle of incident to the sin of the angle of the refraction is a constant.
The mathematical expression is
$\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\text{ constant}$
$\dfrac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{{{n}_{2}}}{{{n}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{v}_{1}}}{{{v}_{2}}}\text{ }\to \text{ 1}$
In the problem,
The velocity of light in the glass, ${{v}_{g}}=2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$
The refractive index of air with respect to glass,
$\dfrac{{{n}_{a}}}{{{n}_{g}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{{{v}_{g}}}{{{v}_{a}}}\text{ }\to \text{ 2}$
The refractive index of water with respect to air,
$\dfrac{{{n}_{w}}}{{{n}_{a}}}=\dfrac{4}{3}=\dfrac{{{v}_{a}}}{{{v}_{w}}}\text{ }\to \text{ 3}$
In equation (2),
$\dfrac{{{v}_{g}}}{{{v}_{a}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}$, substituting the value of ${{v}_{g}}$
$\dfrac{2\times {{10}^{8}}}{{{v}_{a}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}$, then we will get
${{v}_{a}}=\dfrac{3\times 2\times {{10}^{8}}}{2}=3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$
Now in equation (3),
$\dfrac{{{v}_{a}}}{{{v}_{w}}}=\dfrac{4}{3}$
${{v}_{w}}=\dfrac{3\times {{10}^{8}}\times 3}{4}=2.25\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$
Therefore, the velocity of light in air and water are $3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$ and $2.25\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$ respectively.
Note: So far, light is the fastest moving wave. Its velocity is $3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s$, which means it travels about 3 lakh km in just one second. The speed of the light reduces as it moves through solids and liquids due to the collision with the particles in the medium. It can be described as, with the increase in refractive index of the medium the velocity of light decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




