
State whether true or false.
A concave lens is commonly called a converging lens.
$
{\text{A}}{\text{. True}} \\
{\text{B}}{\text{. False}} \\
$
Answer
598.5k+ views
- Hint: To do this question, we should know about the focusing property of a concave lens, when parallel light beams fall on it.
Complete step-by-step solution -
A converging lens is the one which converges all the parallel beams of light on the focus point of the lens whereas a diverging lens diverges the beam of light falling parallel on it.
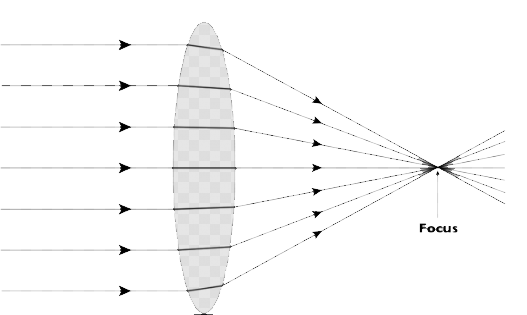
A convex lens is a converging lens, since it focuses the parallel beams of light at the real focus. For a convex lens:
For a concave lens,
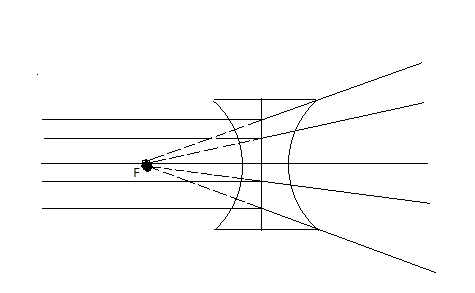
The parallel beams diverge and appear to meet at the focus.
A concave lens possesses at least one surface curved inwards. It spreads out light rays that have been refracted through it, therefore it is called a diverging lens. A concave lens is thinner at its centre than at its edges, and its this property makes the light waves diverge after passing through it. So, the concave lens is a diverging lens. After light rays (parallel) have passed through the lens, they appear to come from a point called the principal focus ( the point at which the light from a distant source that moves parallel to the axis of the lens is focused).
The image formed by a concave lens:
Virtual i.e. can not be obtained on a screen and so is not a real image.
Appears to be farther than it actually is.
Is smaller than the real scale of the object.
The properties of the image formed by a concave lens, makes it useful as a corrective lens for treating short-sightedness or myopia.
So, a concave lens diverges the beam of light coming to it.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: The converging and diverging nature of a lens depends on the thickness of the lens and also on the refractive index of the lens and the surrounding medium.
A concave lens can also act as a converging lens when the surrounding medium has a refractive index more than that of the material of the lens.
Complete step-by-step solution -
A converging lens is the one which converges all the parallel beams of light on the focus point of the lens whereas a diverging lens diverges the beam of light falling parallel on it.
A convex lens is a converging lens, since it focuses the parallel beams of light at the real focus. For a convex lens:

For a concave lens,

The parallel beams diverge and appear to meet at the focus.
A concave lens possesses at least one surface curved inwards. It spreads out light rays that have been refracted through it, therefore it is called a diverging lens. A concave lens is thinner at its centre than at its edges, and its this property makes the light waves diverge after passing through it. So, the concave lens is a diverging lens. After light rays (parallel) have passed through the lens, they appear to come from a point called the principal focus ( the point at which the light from a distant source that moves parallel to the axis of the lens is focused).
The image formed by a concave lens:
Virtual i.e. can not be obtained on a screen and so is not a real image.
Appears to be farther than it actually is.
Is smaller than the real scale of the object.
The properties of the image formed by a concave lens, makes it useful as a corrective lens for treating short-sightedness or myopia.
So, a concave lens diverges the beam of light coming to it.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: The converging and diverging nature of a lens depends on the thickness of the lens and also on the refractive index of the lens and the surrounding medium.
A concave lens can also act as a converging lens when the surrounding medium has a refractive index more than that of the material of the lens.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




