
Statement: In the ZnS (zinc blend) structure, the coordination number of each ion is 4.
State whether the given statement is true or false.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Zinc blend is also known as Sphalerite. It has a face-centered cubic structure. Each atom in the zinc blende or Sphalerite is surrounded by 4 atoms. ZnS also occurs in the Wurtzite form.
Complete step by step answer:
There are two common forms of ZnS. These are zinc blend, also known as Sphalerite and Wurtzite form.
Both of them have some common features:
i)- Both of them have a stoichiometry of 1:1 of Zn: S.
ii)- Each ion in both structures is surrounded by 4 atoms. They have coordination number 4.
iii)- Both of them have tetrahedral coordination.
The structure of the zinc blende (Sphalerite) is based on a face-centered cubic structure whereas the structure of Wurtzite is hexagonal cubic centered.
In both the structures there are 2 types of tetrahedral holes, in which half of them are occupied by the cations.
In both structures the bonding to the nearest neighbor atom is similar but with farther atoms the distance and bond angles are different.
There are 4 asymmetric units in zinc blende and 2 asymmetric units in Wurtzite.
Zinc blend has its own antitype i.e. both the cations and anions can switch their places and it does not affect the shape of the structure.
Hence it is a 4 coordinate ion and has a tetrahedral geometry.
The structure of the zinc blende is given below:
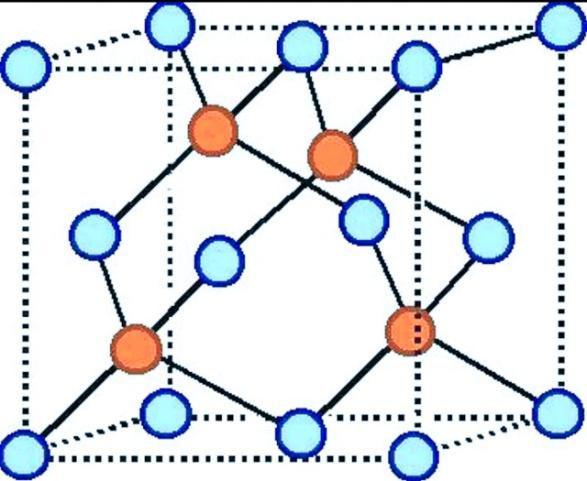
Where blue circles represent the sulfur ions and orange circles represent the zinc ions.
Hence, the statement ZnS (zinc blend) structure, the coordination number of each ion is 4 is true.
Note: The cations and anions can switch their places in the structure of zinc blend the same as in the structure of NaCl. In the zinc blende structure, if we replace all the zinc and sulfur ions with carbon atoms we get the same structure of diamond.
Complete step by step answer:
There are two common forms of ZnS. These are zinc blend, also known as Sphalerite and Wurtzite form.
Both of them have some common features:
i)- Both of them have a stoichiometry of 1:1 of Zn: S.
ii)- Each ion in both structures is surrounded by 4 atoms. They have coordination number 4.
iii)- Both of them have tetrahedral coordination.
The structure of the zinc blende (Sphalerite) is based on a face-centered cubic structure whereas the structure of Wurtzite is hexagonal cubic centered.
In both the structures there are 2 types of tetrahedral holes, in which half of them are occupied by the cations.
In both structures the bonding to the nearest neighbor atom is similar but with farther atoms the distance and bond angles are different.
There are 4 asymmetric units in zinc blende and 2 asymmetric units in Wurtzite.
Zinc blend has its own antitype i.e. both the cations and anions can switch their places and it does not affect the shape of the structure.
Hence it is a 4 coordinate ion and has a tetrahedral geometry.
The structure of the zinc blende is given below:

Where blue circles represent the sulfur ions and orange circles represent the zinc ions.
Hence, the statement ZnS (zinc blend) structure, the coordination number of each ion is 4 is true.
Note: The cations and anions can switch their places in the structure of zinc blend the same as in the structure of NaCl. In the zinc blende structure, if we replace all the zinc and sulfur ions with carbon atoms we get the same structure of diamond.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




