
What statement is correct for keto-enol tautomerism?
(A) Tautomerism can be catalyzed by acid and base both.
(B) Tautomers are present in a dynamic equilibrium state.
(C) Generally keto form is more stable than enol form in simple ketone.
(D) All of the above.
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: Because of the acidity of alpha hydrogens in carbonyl compounds, they show keto-enol tautomerism. The keto and enol forms are called Tautomers. They are rapidly interconvertible between keto and enol forms.
Complete step by step answer:
The equilibrium between tautomers ( keto and enol forms) is rapid under normal conditions and it strongly favors one of the isomers (keto form-99.99%).
For example take a simple ketone like Acetone.
Acetone shows the keto-enol tautomerism as follows.
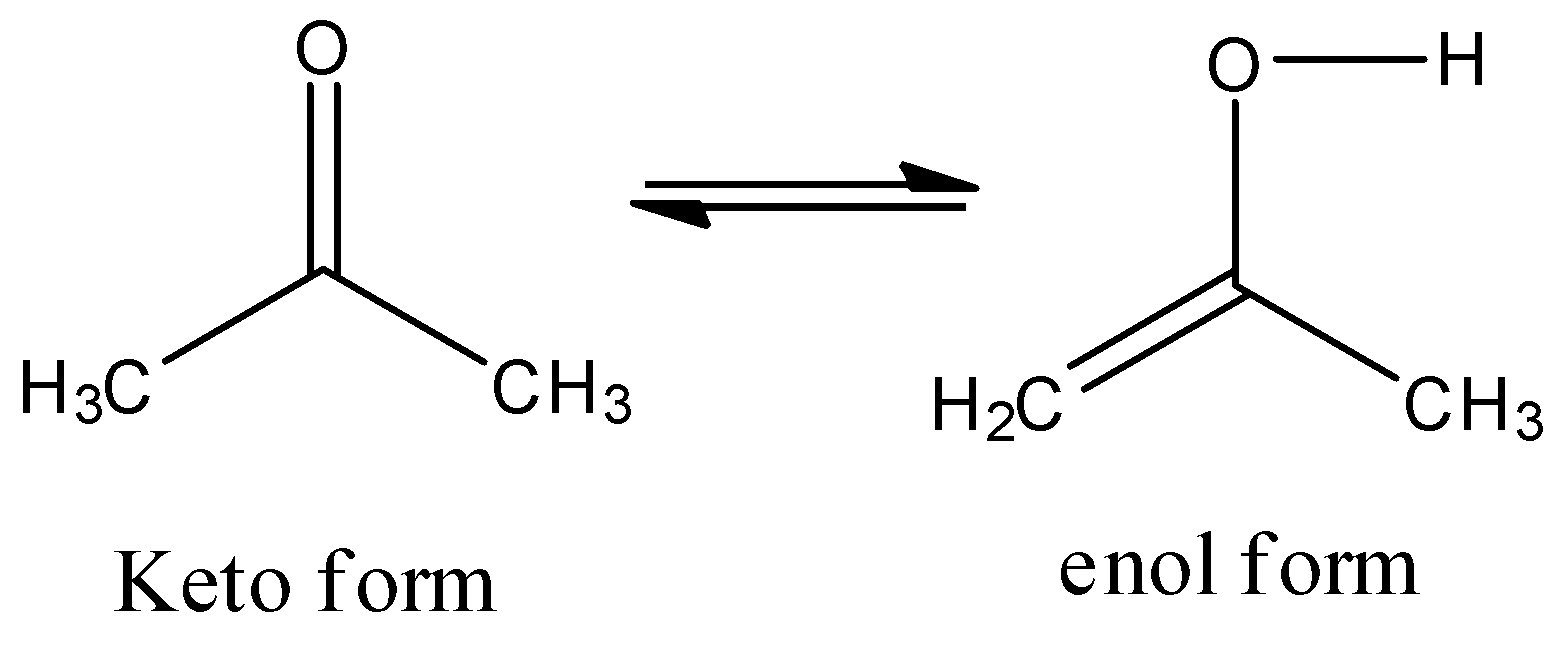
-Due to the presence of alpha hydrogens reasonable for the formation of this type of isomerism in carbonyl compounds.
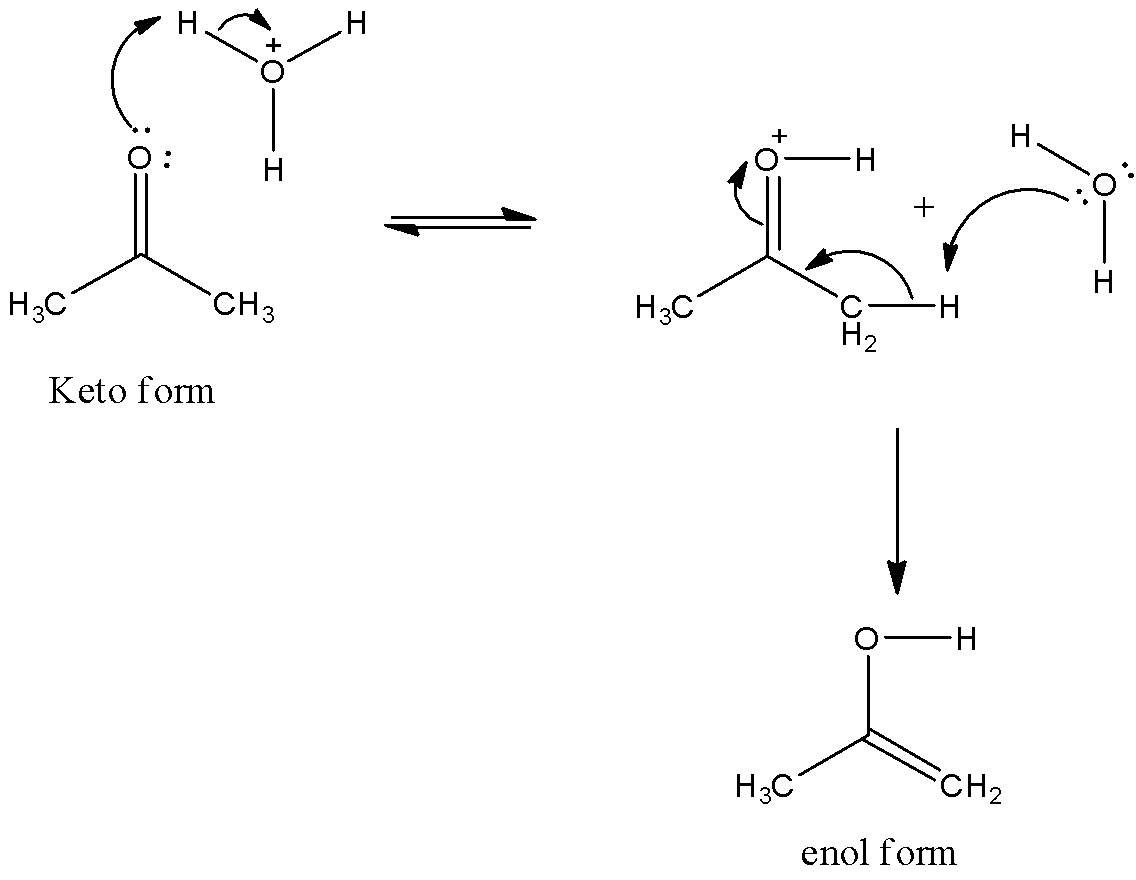
-Coming to the given options, option A, Tautomerism can be catalyzed by acid and base both. Yes it is correct by adding a small amount of acid and base we can increase the chances of showing keto-enol tautomerism. Because acid or base catalyze the tautomerism by proton transfer. We can see the mechanism of addition of acid to keto form as follows. So, option A is correct.
-Coming to option B, Tautomers are present in dynamic equilibrium state. Generally, the chemical equilibrium in keto-enol tautomerism is extremely thermodynamically driven. Generally at room temperature equilibrium heavily favors the existence of the keto form. If we increase the temperature a little bit more then keto converts into enol form. So, option B is also correct.
-Coming to option C, Generally keto form is more stable than enol form in simple ketone. Yes at room temperature the equilibrium between keto and enol form greatly favors the formation of the keto form. Because at room temperature keto form is more stable than enol form. So, option C is also correct.
Therefore all the options A, B and C are correct.
So, the correct option is D, all of the above.
Note: Tautomers of a compound which differ only in the position of the hydrogen atom. Due to the presence of alpha hydrogen the keto-enol tautomerism exists. Alpha hydrogens mean the hydrogens which are attached to the carbon that is directly attached to electron withdrawing groups like carbonyl functional groups.
Complete step by step answer:
The equilibrium between tautomers ( keto and enol forms) is rapid under normal conditions and it strongly favors one of the isomers (keto form-99.99%).
For example take a simple ketone like Acetone.
Acetone shows the keto-enol tautomerism as follows.

-Due to the presence of alpha hydrogens reasonable for the formation of this type of isomerism in carbonyl compounds.
-Coming to the given options, option A, Tautomerism can be catalyzed by acid and base both. Yes it is correct by adding a small amount of acid and base we can increase the chances of showing keto-enol tautomerism. Because acid or base catalyze the tautomerism by proton transfer. We can see the mechanism of addition of acid to keto form as follows. So, option A is correct.

-Coming to option B, Tautomers are present in dynamic equilibrium state. Generally, the chemical equilibrium in keto-enol tautomerism is extremely thermodynamically driven. Generally at room temperature equilibrium heavily favors the existence of the keto form. If we increase the temperature a little bit more then keto converts into enol form. So, option B is also correct.
-Coming to option C, Generally keto form is more stable than enol form in simple ketone. Yes at room temperature the equilibrium between keto and enol form greatly favors the formation of the keto form. Because at room temperature keto form is more stable than enol form. So, option C is also correct.
Therefore all the options A, B and C are correct.
So, the correct option is D, all of the above.
Note: Tautomers of a compound which differ only in the position of the hydrogen atom. Due to the presence of alpha hydrogen the keto-enol tautomerism exists. Alpha hydrogens mean the hydrogens which are attached to the carbon that is directly attached to electron withdrawing groups like carbonyl functional groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




