
Stomata on the surface of the leaf open by
(a) Decreasing the solute concentration in the guard cells
(b) Increasing the solute concentration in the guard cells
(c) Increasing the water potential in the guard cells
(d) Both b and c
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: A proton pump pushes protons ${ \left( { H }^{ + } \right) }$ from the guard cells when conditions are conducive to stomatal opening (e.g: high light intensity and high moisture) . This means the electrical potential of the cells is becoming increasingly negative.
Complete answer:
When, due to the transport of ions in the cell, the solute concentration of the guard cells is increased, the water concentration is decreased. In the guard cells, this results in an increase in the water potential. The strain causes the cells in the guard to become turgid. Owing to the stretching of the guard cells' inner walls, the stomatal pore opens.
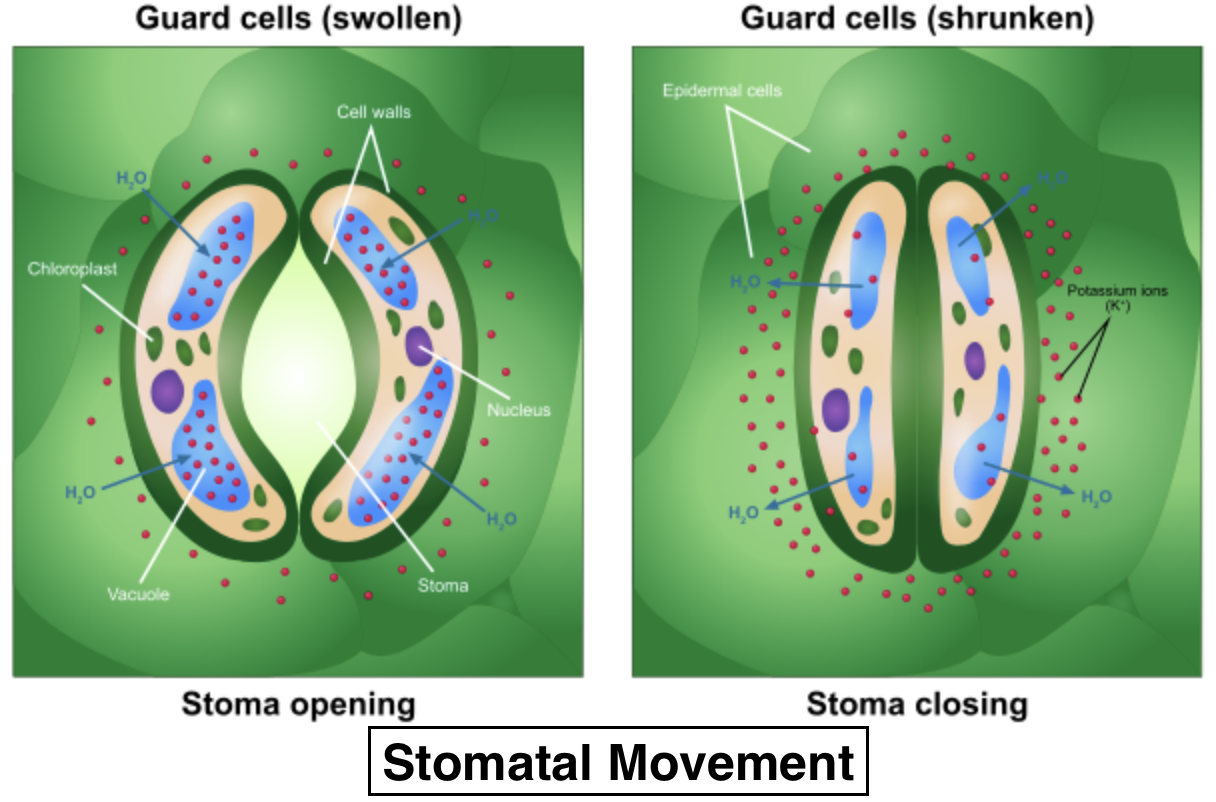
Potassium voltage-gated channels are opened by the negative potential in the cell and so there is an absorption of potassium ions ${ \left( { K }^{ + } \right) }$. Negative ions balance the influx of potassium in order to retain this internal negative voltage such that the entry of potassium ions does not stop. In some cases, chloride ions enter, whereas in other plants, in guard cells, organic ion malate is formed. This increase in solvent concentration decreases the capacity of water within the cell, resulting in water being diffused into the cell via the process of osmosis.
Abscisic acid (ABA) is released when the roots begin to feel a water shortage in the soil. It prevents the absorption into the cells of anymore ${ K }^{ + }$ and, consequently, the loss of ${ K }^{ + }$. The lack of these solutes creates a rise in the potential for water, which results in osmosis to diffuse water back out of the cell. This allows the cell to plasmolyze, resulting in the closure of the stomatal pores.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(d) Both b and c’.
Note: A stoma (plural 'stomata') in botany is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs that regulates the rate of exchange of gas. Pair of specialised parenchyma cells known as guard cells that are responsible for controlling the size of the stomatal opening are bordered by the pore.
There are more chloroplasts in guard cells than the other epidermal cells that guard cells are derived from. Their role is controversial.
Complete answer:
When, due to the transport of ions in the cell, the solute concentration of the guard cells is increased, the water concentration is decreased. In the guard cells, this results in an increase in the water potential. The strain causes the cells in the guard to become turgid. Owing to the stretching of the guard cells' inner walls, the stomatal pore opens.

Potassium voltage-gated channels are opened by the negative potential in the cell and so there is an absorption of potassium ions ${ \left( { K }^{ + } \right) }$. Negative ions balance the influx of potassium in order to retain this internal negative voltage such that the entry of potassium ions does not stop. In some cases, chloride ions enter, whereas in other plants, in guard cells, organic ion malate is formed. This increase in solvent concentration decreases the capacity of water within the cell, resulting in water being diffused into the cell via the process of osmosis.
Abscisic acid (ABA) is released when the roots begin to feel a water shortage in the soil. It prevents the absorption into the cells of anymore ${ K }^{ + }$ and, consequently, the loss of ${ K }^{ + }$. The lack of these solutes creates a rise in the potential for water, which results in osmosis to diffuse water back out of the cell. This allows the cell to plasmolyze, resulting in the closure of the stomatal pores.
So, the correct answer is, ‘(d) Both b and c’.
Note: A stoma (plural 'stomata') in botany is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs that regulates the rate of exchange of gas. Pair of specialised parenchyma cells known as guard cells that are responsible for controlling the size of the stomatal opening are bordered by the pore.
There are more chloroplasts in guard cells than the other epidermal cells that guard cells are derived from. Their role is controversial.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




