
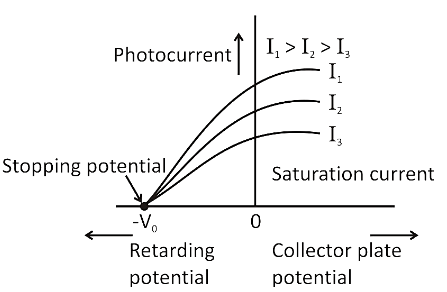
What is stopping voltage (or cut voltage)? Plot a graph of variation of photoelectric current with collector plate potential for two incident radiations of same frequency and different intensities.
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: We know that the stopping voltage is a reference of voltage difference to stop electrons from moving plates and creating a current, from that we plot a graph of variation of photoelectric current with collector plate potential.
Complete answer:
In the photoelectric experiment, the stopping voltage (or stopping potential) refers to the voltage difference needed to stop electrons from moving between plates and producing a current. Photoelectrons are released from a metal, when illuminated with light, above the threshold frequency of the metal, with a spectrum of kinetic energies. The stopping potential is the voltage between the metal surface and a cathode, positioned near to the surface, in a vacuum, which only prevents them from creating a current.
Additional information:
Stopping voltage: Stopping voltage (or stopping potential) refers to the voltage difference needed to stop electrons from travelling between plates and generating a current in the photoelectric experiment. Recall that light is focused onto a metal plate in the photoelectric experiment, and if the frequency of light is high enough, electrons are expelled from the surface. Then these electrons pass directly through a second metal plate. The work function is defined as the minimum amount of energy that is needed to eject an electron from the metal surface. By subtracting the work function from the energy contained in one photon of light, the maximum kinetic energy that the ejected electron has is given.
Note:The negative voltage on the collector plate at which the photoelectric current simply becomes is the stopping potential or voltage. The volt is the unit of stopping potential. Light is focused on a metal plate in the photoelectric experiment and if the frequency of light is sufficient, electrons are ejected from the surface.
Complete answer:
In the photoelectric experiment, the stopping voltage (or stopping potential) refers to the voltage difference needed to stop electrons from moving between plates and producing a current. Photoelectrons are released from a metal, when illuminated with light, above the threshold frequency of the metal, with a spectrum of kinetic energies. The stopping potential is the voltage between the metal surface and a cathode, positioned near to the surface, in a vacuum, which only prevents them from creating a current.

Additional information:
Stopping voltage: Stopping voltage (or stopping potential) refers to the voltage difference needed to stop electrons from travelling between plates and generating a current in the photoelectric experiment. Recall that light is focused onto a metal plate in the photoelectric experiment, and if the frequency of light is high enough, electrons are expelled from the surface. Then these electrons pass directly through a second metal plate. The work function is defined as the minimum amount of energy that is needed to eject an electron from the metal surface. By subtracting the work function from the energy contained in one photon of light, the maximum kinetic energy that the ejected electron has is given.
Note:The negative voltage on the collector plate at which the photoelectric current simply becomes is the stopping potential or voltage. The volt is the unit of stopping potential. Light is focused on a metal plate in the photoelectric experiment and if the frequency of light is sufficient, electrons are ejected from the surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




