
What structural and functional characteristics do cilia, flagella and centrioles have in common?
Answer
478.2k+ views
Hint: Cilia and flagella are cell extensions. They are composed of microtubules and covered by an extension of the plasma membrane, as depicted in this animation. Flagella and centrioles are motile and are designed to move the cell or substances over or around it. The microtubules that make up centrioles and flagella are similar. Two rings of nine microtubule "triplets" are positioned at right angles to one another in centrioles. Flagella do not have this configuration.
Complete solution:
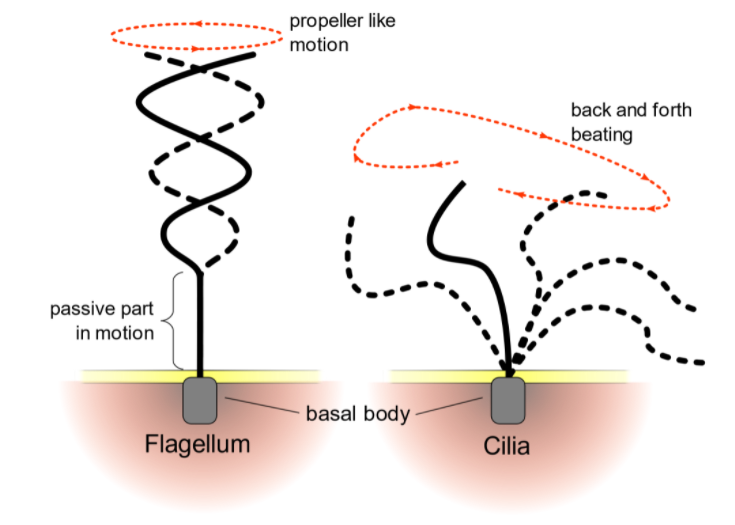
Cilia in mammalian cells serve to transfer fluid, mucus, or cells over their surface. The internal structure of cilia and flagella is identical. The main distinction is in their length. Cilia and flagella move because of the interactions of a set of microtubules inside. Collectively, these are called an "axoneme".
Flagella and cilia have the same axoneme structure, with nine doublet microtubules organized in a circle around two central singlet microtubules, despite their differing names. Centrioles, like cilia and flagella, are made up of microtubules. Centrioles are microtubule-based hollow cylinders.
Centrioles assist in the organization of the microtubules that transport chromosomes during cell division, ensuring that each daughter cell receives the correct number of chromosomes.
The primary function of cilia and flagella is movement. They are the means by which many microscopic unicellular and multicellular organisms move from place to place. Many of these organisms are found in aqueous environments, where they are propelled along by the beating of cilia or the whip-like action of flagella.re also necessary for the production of cilia and flagella, which are cell structures.
Note:
Centrioles, which travel to the cell's edge, organize cilia and flagella. The direction of movement is governed by basal bodies. The cilia or flagella movement is controlled by centrioles. The mother centriole, which becomes the basal body in flagellates and ciliates, determines the position of the flagellum or cilium. A number of hereditary and developmental illnesses have been connected to cells' failure to employ centrioles to create functional flagella and cilia.
Complete solution:
Cilia in mammalian cells serve to transfer fluid, mucus, or cells over their surface. The internal structure of cilia and flagella is identical. The main distinction is in their length. Cilia and flagella move because of the interactions of a set of microtubules inside. Collectively, these are called an "axoneme".
Flagella and cilia have the same axoneme structure, with nine doublet microtubules organized in a circle around two central singlet microtubules, despite their differing names. Centrioles, like cilia and flagella, are made up of microtubules. Centrioles are microtubule-based hollow cylinders.

Centrioles assist in the organization of the microtubules that transport chromosomes during cell division, ensuring that each daughter cell receives the correct number of chromosomes.
The primary function of cilia and flagella is movement. They are the means by which many microscopic unicellular and multicellular organisms move from place to place. Many of these organisms are found in aqueous environments, where they are propelled along by the beating of cilia or the whip-like action of flagella.re also necessary for the production of cilia and flagella, which are cell structures.
Note:
Centrioles, which travel to the cell's edge, organize cilia and flagella. The direction of movement is governed by basal bodies. The cilia or flagella movement is controlled by centrioles. The mother centriole, which becomes the basal body in flagellates and ciliates, determines the position of the flagellum or cilium. A number of hereditary and developmental illnesses have been connected to cells' failure to employ centrioles to create functional flagella and cilia.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




