
Structure of \[Xe{O_2}{F_2}\] is correctly represented by:
A.

B.
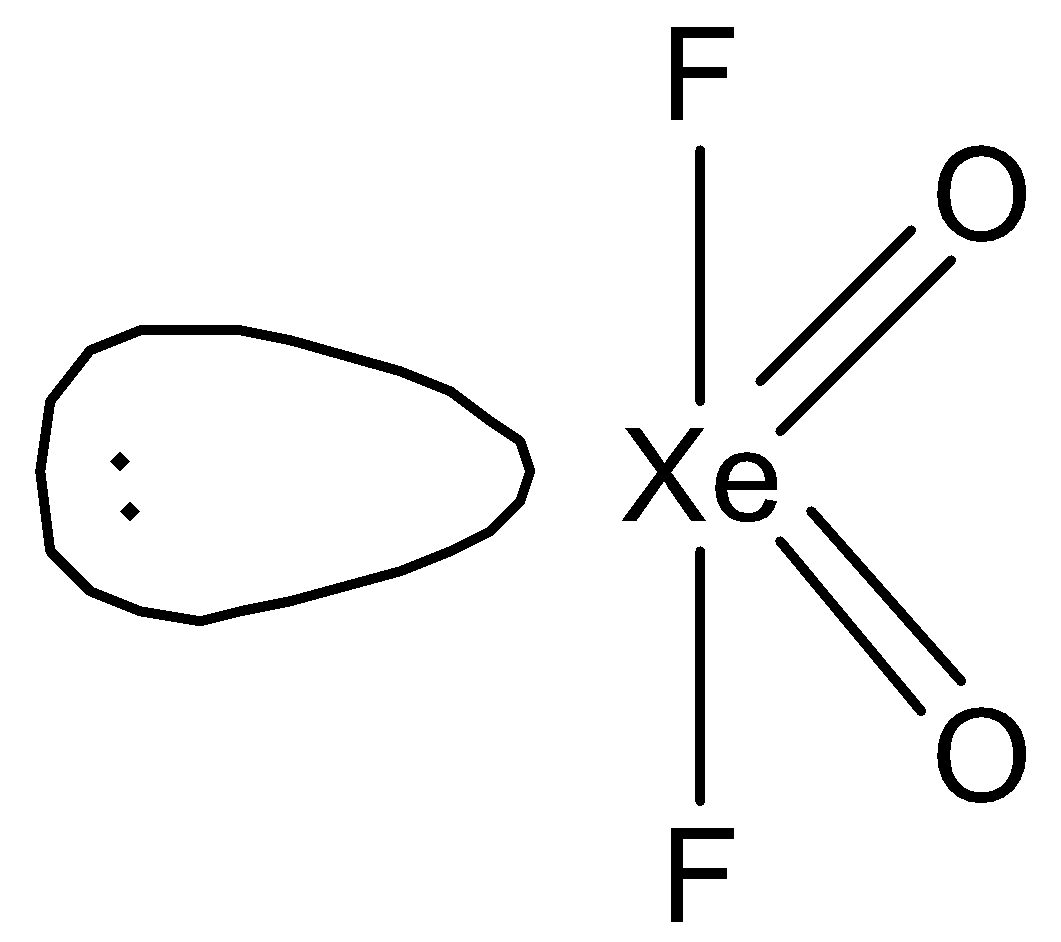

C.
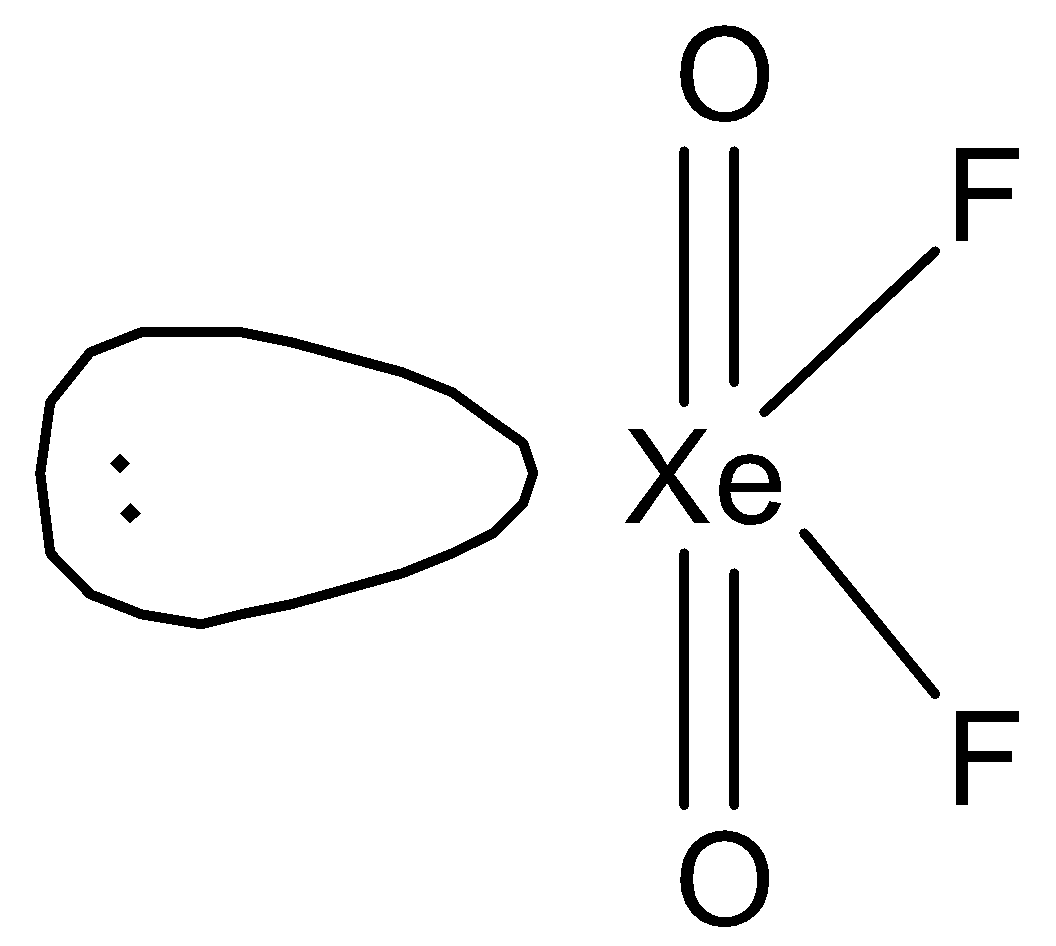

D.Both (B) and (C)



Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint:We know that valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory is used to determine the geometry of molecules from the electron pairs surrounding the central atom. Geometry of a molecule can be decided by considering both bond pairs and lone pairs of the molecules, but shape is decided by considering only the bonded pair of molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find the hybridization of \[{\text{Xe}}\] in \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\] to find its structure. We know that that the electronic configuration of \[{\text{Xe}}\] is \[\left[ {{\text{Kr}}} \right]{\text{4}}{{\text{d}}^{{\text{10}}}}{\text{5}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{5}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}\], oxygen is \[\left[ {{\text{He}}} \right]{\text{2}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{4}}}\] and fluorine is \[\left[ {{\text{He}}} \right]{\text{2}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}^5}\]. So, Xe has 8 valence electrons, oxygen and fluorine is monovalent. The \[{\text{5s}}\],\[{\text{5p}}\] and \[{\text{5d}}\] orbitals take part in hybridisation in the following way.
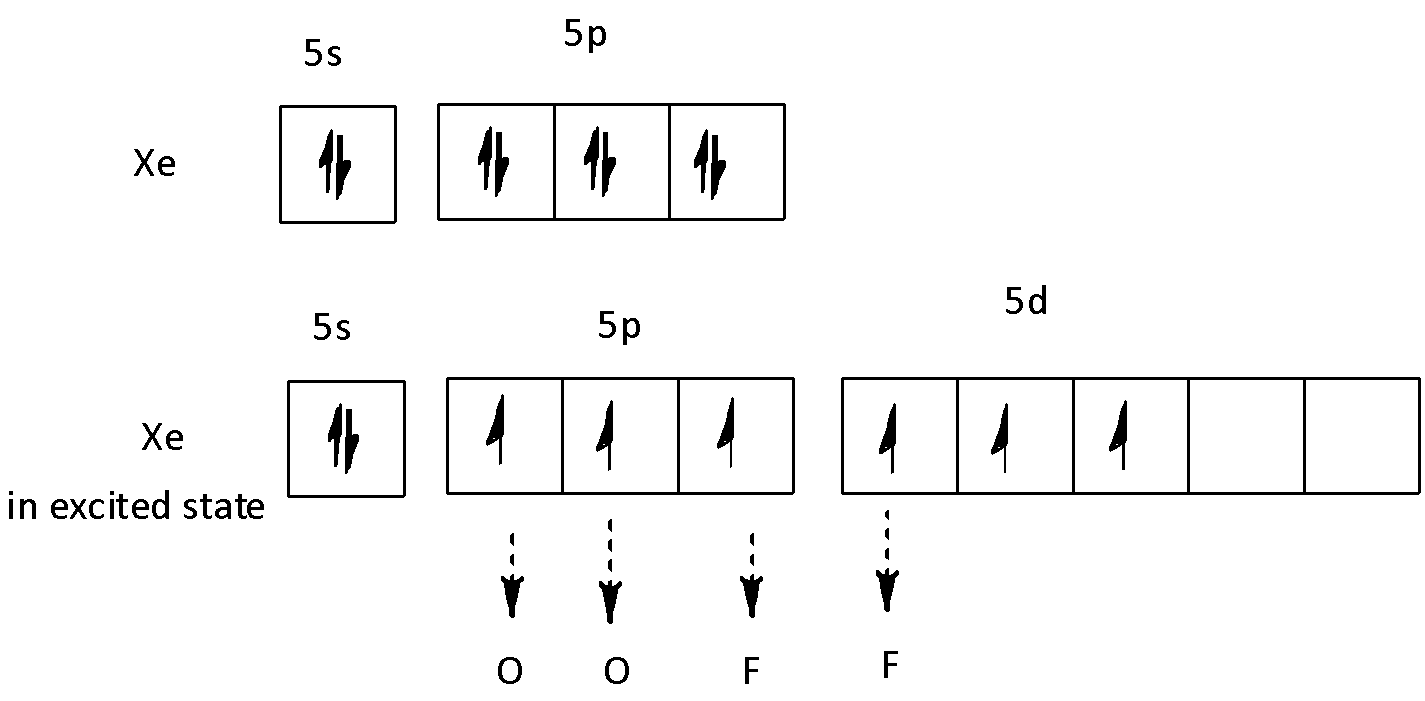
So, hybridisation of \[{\text{Xe}}\] in \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\] will be \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{d}}\]. Therefore, \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\] will have a see-saw structure. We can draw the structure of this compound in the following way.
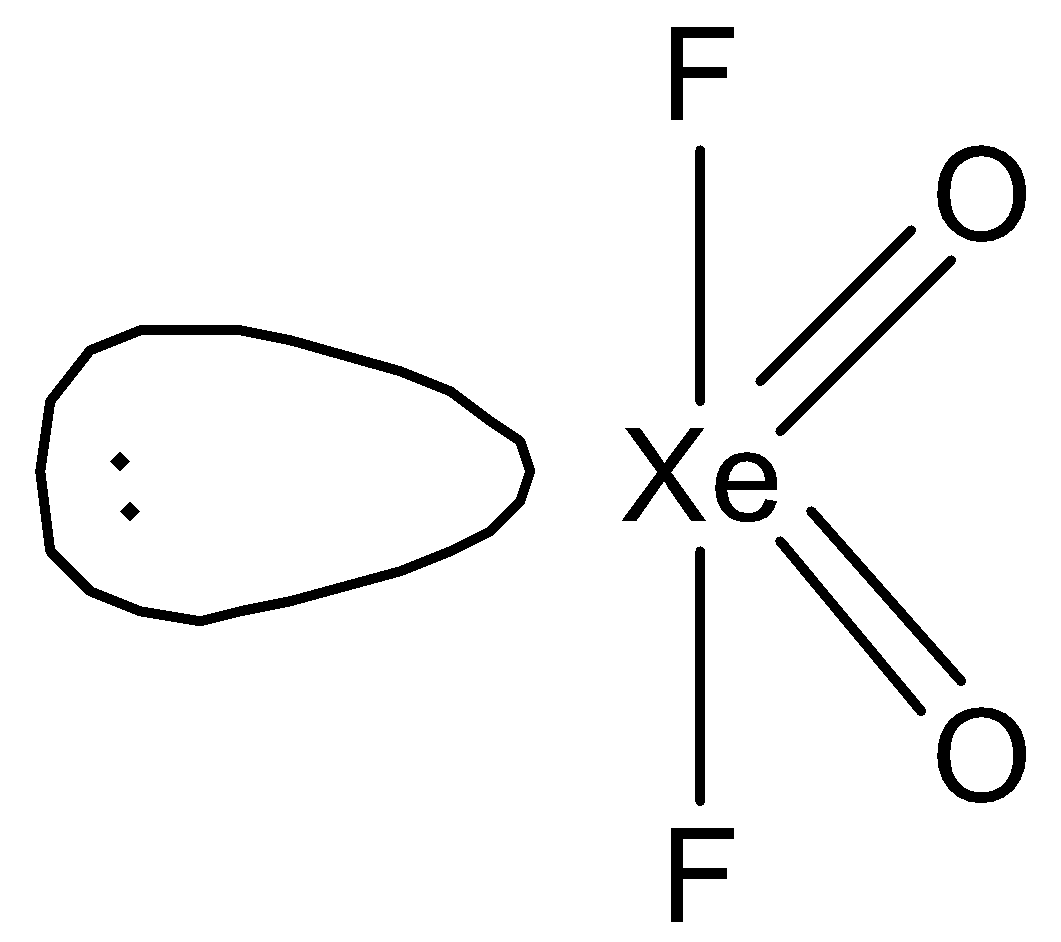
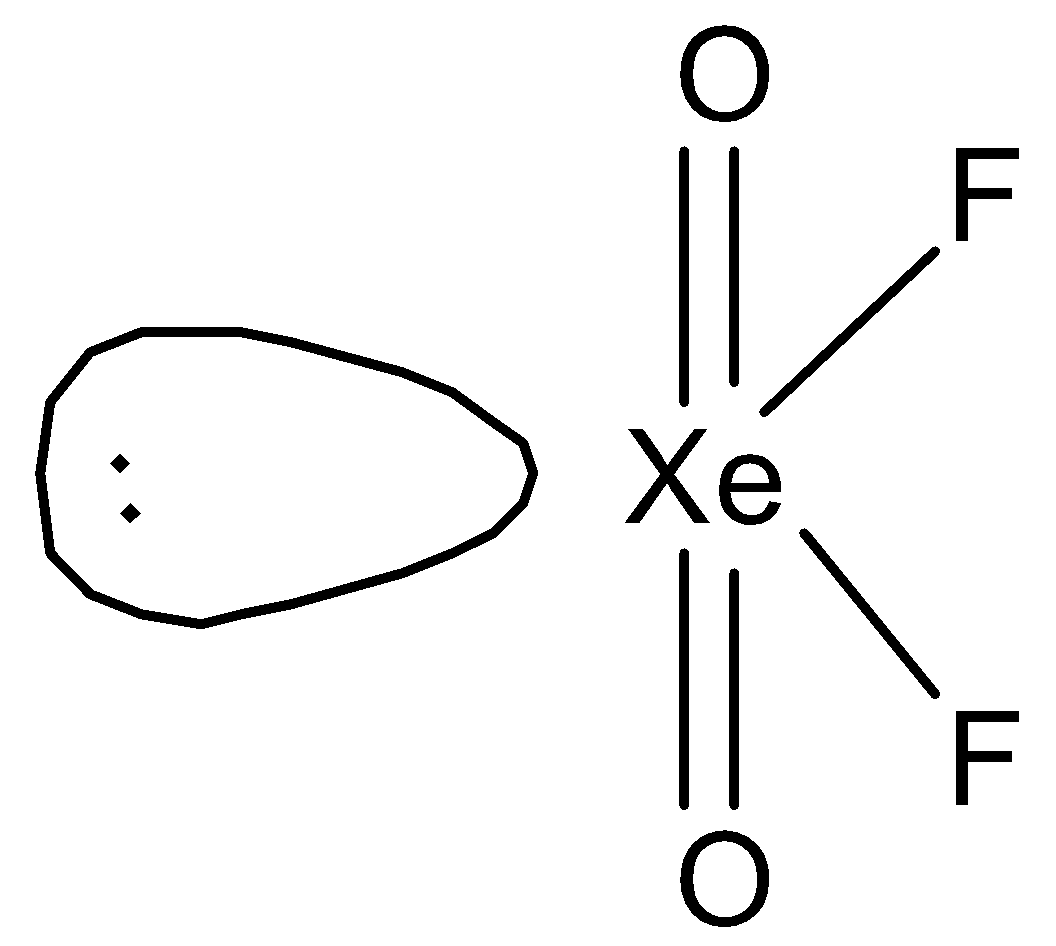


Therefore, we can say that D is the correct option.
Additional information:
VSEPR helps in predicting the geometry of a compound taking in account the arrangement of electron pairs. VSEPR theory states that the electrons present in and around repel each other, and it tends to take up an arrangement that will have minimum repulsion. The number of the valence shell present in the central metal atom is determined by drawing a Lewis structure of that atom. The number of electrons in the valence shell determined how and how many numbers of other atoms can find it and construct a structure. VSEPR theory states that the repulsion by the lone pair is greater than the repulsion by the bonding pair.
Note:
The steric number of the central atom in the molecule is defined as the number of the atoms which are bonded to the central atom. It is the summation of the coordination number and the number of lone pairs of valence electrons on the central atom.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find the hybridization of \[{\text{Xe}}\] in \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\] to find its structure. We know that that the electronic configuration of \[{\text{Xe}}\] is \[\left[ {{\text{Kr}}} \right]{\text{4}}{{\text{d}}^{{\text{10}}}}{\text{5}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{5}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{6}}}\], oxygen is \[\left[ {{\text{He}}} \right]{\text{2}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{4}}}\] and fluorine is \[\left[ {{\text{He}}} \right]{\text{2}}{{\text{s}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{2}}{{\text{p}}^5}\]. So, Xe has 8 valence electrons, oxygen and fluorine is monovalent. The \[{\text{5s}}\],\[{\text{5p}}\] and \[{\text{5d}}\] orbitals take part in hybridisation in the following way.

So, hybridisation of \[{\text{Xe}}\] in \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\] will be \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{d}}\]. Therefore, \[{\text{Xe}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}\] will have a see-saw structure. We can draw the structure of this compound in the following way.


Therefore, we can say that D is the correct option.
Additional information:
VSEPR helps in predicting the geometry of a compound taking in account the arrangement of electron pairs. VSEPR theory states that the electrons present in and around repel each other, and it tends to take up an arrangement that will have minimum repulsion. The number of the valence shell present in the central metal atom is determined by drawing a Lewis structure of that atom. The number of electrons in the valence shell determined how and how many numbers of other atoms can find it and construct a structure. VSEPR theory states that the repulsion by the lone pair is greater than the repulsion by the bonding pair.
Note:
The steric number of the central atom in the molecule is defined as the number of the atoms which are bonded to the central atom. It is the summation of the coordination number and the number of lone pairs of valence electrons on the central atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




