
How many structures of X is possible?
(A) 4
(B) 5
(C) 6
(D) 3

Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: The intermediate structures for any given reaction give some basic reaction rules that would be vital and sensible.
Some of these rules are resonance effect, inductive effect, etc.
Complete step by step solution:
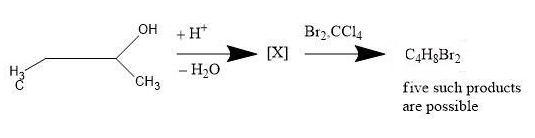
The given reaction is about the dehydrogenation of Butan-2-ol. Let us see the mechanism and conditions for the reaction.
There are 2 steps for the given reaction i.e.
1. The positive ion removes a water molecule from the butan-2-ol and carbocation is formed.
2. The carbocation loses the hydrogen ion to form a double bond.
The structures arising from the second step will be the answer for the given problem.
When the carbocation loses the hydrogen ion (from adjacent carbon atom of the carbon atom already having positive charge) to form double bond, it has two choices i.e.
1. Lose the hydrogen ion from the adjacent $C{{H}_{3}}$ group.
-Due to this move, But-1-ene ($C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$) is formed.
2. Loss the hydrogen ion from the adjacent $C{{H}_{2}}$ group.
-Due to this move, But-2-ene ($C{{H}_{3}}-CH=CH-C{{H}_{3}}$) is formed.
-But, here the effect of resonance will take place as But-2-ene has a geometrical isomer. We get a mixture of two isomers i.e. cis-but-2-ene and trans-but-2-ene.
Thus,
Dehydration of Butan-2-ol leads to mixture containing,
a. But-1-ene
b. cis-but-2-ene
c. trans-but-2-ene
Therefore, three types of intermediates or structures would be formed for the given dehydration of the But-2-ol.
Hence, option (D) is correct.
Note: Do note to consider the phenomenon of resonance when we see the possibilities of having geometrical isomers.The loss of hydrogen ion from a carbocation always takes place from the alpha carbon atom of carbon holding the positive charge. Thus, the number of alpha carbons decides the basic number of intermediate structures having double bonds within themselves.
Some of these rules are resonance effect, inductive effect, etc.
Complete step by step solution:
The given reaction is about the dehydrogenation of Butan-2-ol. Let us see the mechanism and conditions for the reaction.
There are 2 steps for the given reaction i.e.
1. The positive ion removes a water molecule from the butan-2-ol and carbocation is formed.
2. The carbocation loses the hydrogen ion to form a double bond.
The structures arising from the second step will be the answer for the given problem.
When the carbocation loses the hydrogen ion (from adjacent carbon atom of the carbon atom already having positive charge) to form double bond, it has two choices i.e.
1. Lose the hydrogen ion from the adjacent $C{{H}_{3}}$ group.
-Due to this move, But-1-ene ($C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$) is formed.
2. Loss the hydrogen ion from the adjacent $C{{H}_{2}}$ group.
-Due to this move, But-2-ene ($C{{H}_{3}}-CH=CH-C{{H}_{3}}$) is formed.
-But, here the effect of resonance will take place as But-2-ene has a geometrical isomer. We get a mixture of two isomers i.e. cis-but-2-ene and trans-but-2-ene.
Thus,
Dehydration of Butan-2-ol leads to mixture containing,
a. But-1-ene
b. cis-but-2-ene
c. trans-but-2-ene
Therefore, three types of intermediates or structures would be formed for the given dehydration of the But-2-ol.
Hence, option (D) is correct.
Note: Do note to consider the phenomenon of resonance when we see the possibilities of having geometrical isomers.The loss of hydrogen ion from a carbocation always takes place from the alpha carbon atom of carbon holding the positive charge. Thus, the number of alpha carbons decides the basic number of intermediate structures having double bonds within themselves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




