
Study the diagram given and answer the question.
Identify the anode end in the diagram.

Answer
570.3k+ views
Hint: Genetic engineering leads to the development of a new combination of genetic material which is recombinant DNA. This experiment takes place in the laboratory and requires restriction enzymes, source of donor DNA, polymerase enzymes, ligase, vectors, and host organisms.
Complete answer:
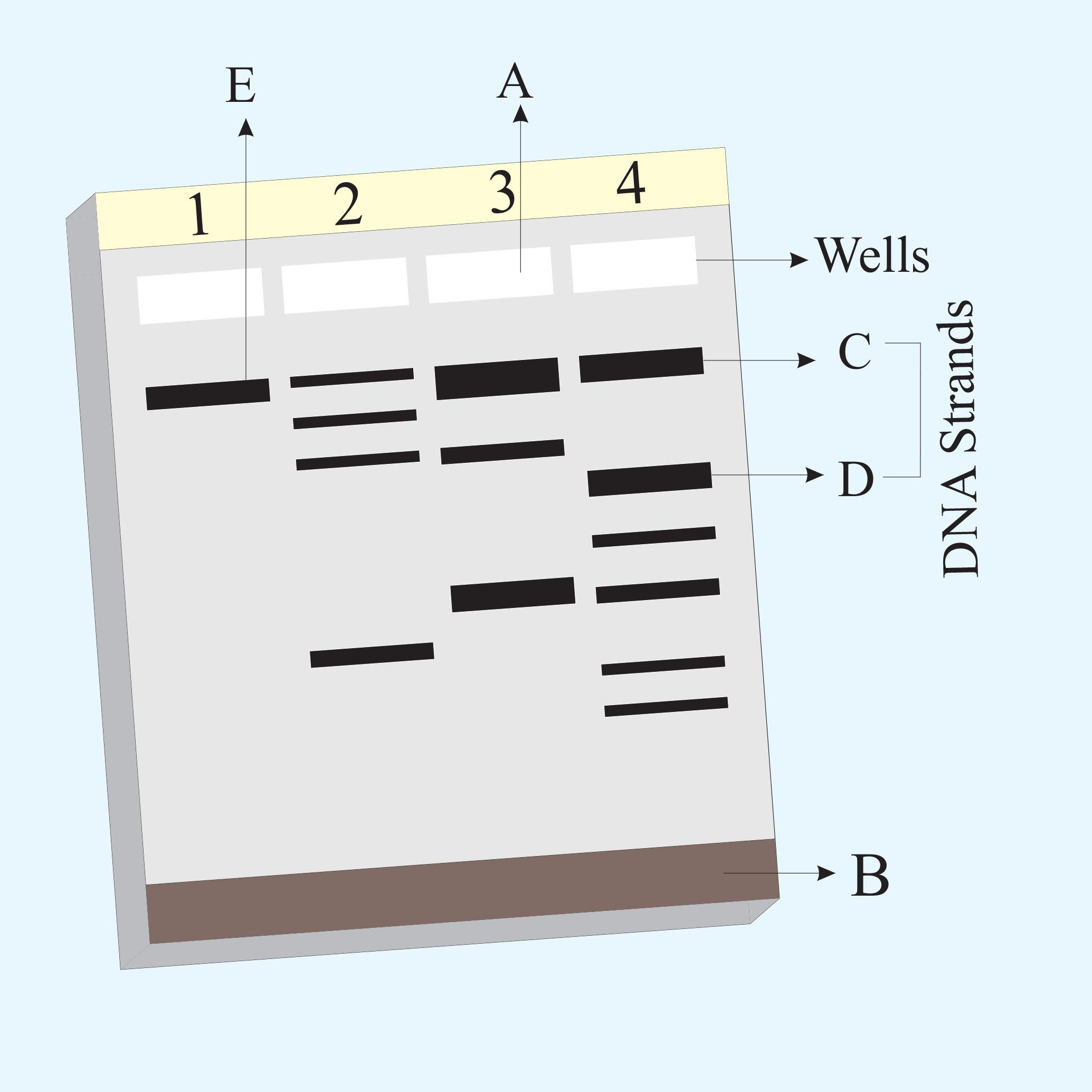
The diagram is of gel electrophoresis where A is cathode half and B is anode half. C and E represent the largest undigested DNA fragments and D represents smaller digested DNA fragments.
In genetic engineering tools, restriction enzymes recognize the palindromic DNA sequence and degrade it. The first restriction endonuclease was Hind II which used to cut DNA at particular points. Till now 900 restriction enzymes were isolated with 230 strains of bacteria. Restriction endonuclease is of two types of exonuclease which cleave DNA/RNA from the end and endonuclease cuts DNA at a specific site. Separation and isolation is the technique to separate variable length of DNA by gel electrophoresis. Cathode and anode represent both ends of the instrument, DNA placed at the cathode and when electric field generated negatively charged DNA starts to move towards a positive end cathode. Larger fragments show slow movement while shorter fragments show fast movement. The DNA fragment is visible with the help of ethidium bromide, the later the band gets extracted from agarose gel. After that cloning of vectors takes place with the initiation of replication which needs a selectable marker for transformation. Transformation leads to the transfer of foreign DNA or a plasmid containing passenger DNA into host cells. Later DNA is inserted on the given site.
Note: In Agrobacterium tumefaciens, the cut has taken place in the DNA of tumor-inducing bacteria and a new plasmid gets ligated which is infection-free. Genetic engineering leads to the formation of disease-resistant genes.
Complete answer:
The diagram is of gel electrophoresis where A is cathode half and B is anode half. C and E represent the largest undigested DNA fragments and D represents smaller digested DNA fragments.
In genetic engineering tools, restriction enzymes recognize the palindromic DNA sequence and degrade it. The first restriction endonuclease was Hind II which used to cut DNA at particular points. Till now 900 restriction enzymes were isolated with 230 strains of bacteria. Restriction endonuclease is of two types of exonuclease which cleave DNA/RNA from the end and endonuclease cuts DNA at a specific site. Separation and isolation is the technique to separate variable length of DNA by gel electrophoresis. Cathode and anode represent both ends of the instrument, DNA placed at the cathode and when electric field generated negatively charged DNA starts to move towards a positive end cathode. Larger fragments show slow movement while shorter fragments show fast movement. The DNA fragment is visible with the help of ethidium bromide, the later the band gets extracted from agarose gel. After that cloning of vectors takes place with the initiation of replication which needs a selectable marker for transformation. Transformation leads to the transfer of foreign DNA or a plasmid containing passenger DNA into host cells. Later DNA is inserted on the given site.
Note: In Agrobacterium tumefaciens, the cut has taken place in the DNA of tumor-inducing bacteria and a new plasmid gets ligated which is infection-free. Genetic engineering leads to the formation of disease-resistant genes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




