
Study the food chain below, correct it and convert into a pyramid of energy.
Mulberry→ Sparrow→ Caterpillar→ Kite
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint:An energy pyramid is a model that shows the flow of energy from one trophic, or feeding, level to the next in an ecosystem. The pyramid model is a diagram that compares the energy used by organisms at each trophic level.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we have to know about the food chain. A food chain is a continuous sequence of organisms via which energy and nutrients transfer as one individual organism feed on another. In a food chain, every individual organism lives in a different trophic level, referred by how much energy transfers separate it from the base input of the chain. At the bottom of the food chain relies on the primary producers. The primary producers are autotrophs, they produce their food by photosynthesis process, some of them are- plants, algae, or cyanobacteria.
The organisms that eat the primary producers are known as primary consumers. Primary consumers are commonly herbivores, they eat plants, and they may also eat algae or bacteria. The organisms that feed on the primary consumers are known as secondary consumers. Secondary consumers generally are carnivores. The organisms that eat the secondary consumers are known as tertiary consumers. They are like eagles or big fish.
Mulberry → Caterpillar → Sparrow → Kite
Mulberry is an autotrophic plant. The caterpillar eats mulberry which is the primary consumer. The sparrow is a bird which eats the caterpillar and functions as the secondary consumer. The kite feeds on the sparrow and it is the tertiary consumer.
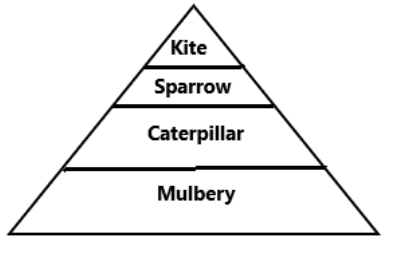
Fig –Pyramid of energy.
Note:Each group of food chain is known as a trophic level, and it displays how much energy and nutrients passes, how many consumption steps divide an organism from the food chain's original energy source, like light. Humans are omnivores because they can feed on both animals and plants.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we have to know about the food chain. A food chain is a continuous sequence of organisms via which energy and nutrients transfer as one individual organism feed on another. In a food chain, every individual organism lives in a different trophic level, referred by how much energy transfers separate it from the base input of the chain. At the bottom of the food chain relies on the primary producers. The primary producers are autotrophs, they produce their food by photosynthesis process, some of them are- plants, algae, or cyanobacteria.
The organisms that eat the primary producers are known as primary consumers. Primary consumers are commonly herbivores, they eat plants, and they may also eat algae or bacteria. The organisms that feed on the primary consumers are known as secondary consumers. Secondary consumers generally are carnivores. The organisms that eat the secondary consumers are known as tertiary consumers. They are like eagles or big fish.
Mulberry → Caterpillar → Sparrow → Kite
Mulberry is an autotrophic plant. The caterpillar eats mulberry which is the primary consumer. The sparrow is a bird which eats the caterpillar and functions as the secondary consumer. The kite feeds on the sparrow and it is the tertiary consumer.

Fig –Pyramid of energy.
Note:Each group of food chain is known as a trophic level, and it displays how much energy and nutrients passes, how many consumption steps divide an organism from the food chain's original energy source, like light. Humans are omnivores because they can feed on both animals and plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




