
Sucrose (cane sugar) is a disaccharide. One molecule of sucrose on hydrolysis gives:
(A) 2 molecules of glucose
(B) 2 molecules of glucose + 1 molecule of fructose
(C) 1 molecule of glucose + 1 molecule of fructose
(D) 2 molecules of fructose
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Sucrose which is a common sugar and also known as table sugar is a disaccharide composed of two monosaccharides whose common names are fruit sugar and blood sugar.
Complete step by step solution:
-Sucrose, also known as cane sugar is produced naturally in plants from which table sugar is refined.
-The molecular formula of sucrose is ${{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}$.
-The sucrose is derived from two French words ‘sucre’ and the generic chemical suffix for sugars –ose. ‘Sucre’ in French means sugar.
-For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined from two sources, either from sugarcane or from sugar beet.
-In sucrose, the two monomer units that are glucose and fructose are linked via an ether bond between C1 on the glucosyl subunit and C2 on the fructose unit, and this bond is called a glycosidic linkage.
-Glucose exists in two isomers, $\alpha $-pyranose and $\beta $-pyranose, but only $\alpha $form links to fructose. Likewise, fructose exists as a mixture of $\alpha $and $\beta $furanose, but only the $\beta $isomer links to glucose.
-Unlike the other disaccharides, the glycosidic bond in sucrose is formed in between the reducing ends of both glucose and fructose.
-Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar as it contains no anomeric hydroxyl groups.
-The hydrolysis of sucrose breaks the glycosidic bond converting sucrose into glucose and fructose. Hydrolysis of sucrose is so slow that it can go years with negligible change. However, the enzyme sucrase is added to fasten the hydrolysis process.
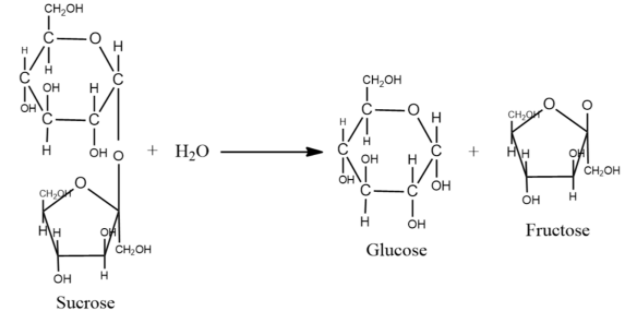
-Hence, the hydrolysis of sucrose gives one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose.
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Sucrose present in plants is consumed by many mammals, birds, insects, and bacteria. It is a key component of soft drinks and other beverages. This compound is used in many medicines. The sucrose acts as a chemical intermediate for many emulsifying agents and detergents. It also acts as an agent for food thickening and as a nutrient stabilizer. The use of sucrose in baking results in the baked products being brown. Sucrose also serves as an antioxidant and is widely used as a preservative in foods.
Complete step by step solution:
-Sucrose, also known as cane sugar is produced naturally in plants from which table sugar is refined.
-The molecular formula of sucrose is ${{C}_{12}}{{H}_{22}}{{O}_{11}}$.
-The sucrose is derived from two French words ‘sucre’ and the generic chemical suffix for sugars –ose. ‘Sucre’ in French means sugar.
-For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined from two sources, either from sugarcane or from sugar beet.
-In sucrose, the two monomer units that are glucose and fructose are linked via an ether bond between C1 on the glucosyl subunit and C2 on the fructose unit, and this bond is called a glycosidic linkage.
-Glucose exists in two isomers, $\alpha $-pyranose and $\beta $-pyranose, but only $\alpha $form links to fructose. Likewise, fructose exists as a mixture of $\alpha $and $\beta $furanose, but only the $\beta $isomer links to glucose.
-Unlike the other disaccharides, the glycosidic bond in sucrose is formed in between the reducing ends of both glucose and fructose.
-Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar as it contains no anomeric hydroxyl groups.
-The hydrolysis of sucrose breaks the glycosidic bond converting sucrose into glucose and fructose. Hydrolysis of sucrose is so slow that it can go years with negligible change. However, the enzyme sucrase is added to fasten the hydrolysis process.

-Hence, the hydrolysis of sucrose gives one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose.
So, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: Sucrose present in plants is consumed by many mammals, birds, insects, and bacteria. It is a key component of soft drinks and other beverages. This compound is used in many medicines. The sucrose acts as a chemical intermediate for many emulsifying agents and detergents. It also acts as an agent for food thickening and as a nutrient stabilizer. The use of sucrose in baking results in the baked products being brown. Sucrose also serves as an antioxidant and is widely used as a preservative in foods.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




