
What is the sum of all the angles of a Hexagon?
Answer
501.3k+ views
Hint: The word “Polygon” is the combination of two words, i.e. “poly” (means many) and “gon” (means sides). We need to find the sum of all angles of a Hexagon. We know that, sum of all angles of a $n$ sided polygon is \[(n - 2) \times {180^\circ }\]. Here, we know that a Hexagon has 6 sides. So substitute this value of $n$ in the formula to get the final output. Or we can divide the hexagon in triangles such that no triangles overlap each other. Since, we know that, the sum of the interior angles of the triangle is \[{180^\circ }\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that,
A hexagon is a polygon with six sides.
An interior angle is an angle measured between the two sides of a polygon.
The sum of the interior angles of a hexagon can be calculated in two ways:
1) Dividing hexagon into triangles
2) Interior angle sum formula
First, We are going to divide the Hexagon into four triangles as shown below:
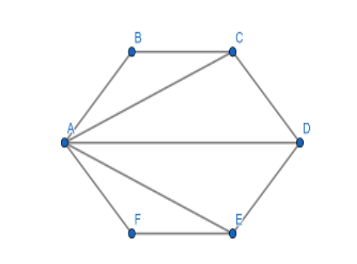
The given Hexagon is divided into 4 triangles (do not overlap) namely,
\[\;\Delta BCA,{\text{ }}\Delta CDA,{\text{ }}\Delta DEA,{\text{ }}\Delta EFA\]
So, the sum of the angles (interior) is
\[ = \angle A + \angle B + \angle C + \angle D + \angle E + \angle F\]
\[ = \left( {\angle BAC + \angle CAD + \;\angle DAE + \;\angle FAE} \right) + \;\angle B + \left( {\angle BCA + \angle DCA} \right) + \left( {\angle CDA + \angle EDA} \right) + \left( {\angle AEF + \angle AED} \right) + \;\angle F\]Rearranging the terms, we will get,
\[ = \left( {\angle BAC + \;\angle B + \;\angle BCA} \right) + \left( {\angle CAD + \;\angle DCA + \;\angle CDA\;} \right) + \left( {\angle EDA + \;\angle DAE + \;\angle AED} \right)\; + \left( {\;\angle AEF + \;\angle FAE + \;\angle F} \right)\]
=Sum of the interior angle of \[\;\Delta BCA\] + Sum of the interior angles of \[\Delta CDA\] + Sum of the interior angles of \[\Delta DEA\] + Sum of the interior angles of \[\Delta EFA\].
Since, the sum of the interior angles of the triangle is \[{180^\circ }\].
\[ = {180^\circ } + {180^\circ } + {180^\circ } + {180^\circ }\]
\[ = {720^\circ }\]
Therefore, the sum of the angles of a hexagon is \[{720^\circ }\].
Note:
Method 2: Using interior angle sum formula:
We know that,
Sum of the interior angles of a n-gon is
\[ = (n - 2) \times {180^\circ }\] where n means number of sides.
For a hexagon, n = 6.
So, substituting this value of n in the above formula, we will get,
\[ = (6 - 2) \times {180^\circ }\]
Simply this, we will get,
\[ = 4 \times {180^\circ }\]
\[ = {720^\circ }\]
Hence, the sum of the angles of a hexagon is \[{720^\circ }\].
For irregular hexagons also, it is true.
Method 3:
The sum of the interior angles of a hexagon = 4 times the sum of the interior angles of a triangle
\[ = 4 \times {180^\circ }\]
\[ = {720^\circ }\]
So, the correct answer is “\[ {720^\circ }\]”.
A polygon is a two-dimensional geometric figure that has a finite number of sides. The sides of a polygon are made of straight line segments connected to each other end to end. A circle is also a plane figure but it is not considered as a polygon, because it is a curved shape and does not have sides or angles. A minimum of three line segments is required to connect end to end, to make a closed figure. Thus a polygon with a minimum of three sides is known as Triangle and it is also called 3-gon. An n-sided polygon is called n-gon.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that,
A hexagon is a polygon with six sides.
An interior angle is an angle measured between the two sides of a polygon.
The sum of the interior angles of a hexagon can be calculated in two ways:
1) Dividing hexagon into triangles
2) Interior angle sum formula
First, We are going to divide the Hexagon into four triangles as shown below:

The given Hexagon is divided into 4 triangles (do not overlap) namely,
\[\;\Delta BCA,{\text{ }}\Delta CDA,{\text{ }}\Delta DEA,{\text{ }}\Delta EFA\]
So, the sum of the angles (interior) is
\[ = \angle A + \angle B + \angle C + \angle D + \angle E + \angle F\]
\[ = \left( {\angle BAC + \angle CAD + \;\angle DAE + \;\angle FAE} \right) + \;\angle B + \left( {\angle BCA + \angle DCA} \right) + \left( {\angle CDA + \angle EDA} \right) + \left( {\angle AEF + \angle AED} \right) + \;\angle F\]Rearranging the terms, we will get,
\[ = \left( {\angle BAC + \;\angle B + \;\angle BCA} \right) + \left( {\angle CAD + \;\angle DCA + \;\angle CDA\;} \right) + \left( {\angle EDA + \;\angle DAE + \;\angle AED} \right)\; + \left( {\;\angle AEF + \;\angle FAE + \;\angle F} \right)\]
=Sum of the interior angle of \[\;\Delta BCA\] + Sum of the interior angles of \[\Delta CDA\] + Sum of the interior angles of \[\Delta DEA\] + Sum of the interior angles of \[\Delta EFA\].
Since, the sum of the interior angles of the triangle is \[{180^\circ }\].
\[ = {180^\circ } + {180^\circ } + {180^\circ } + {180^\circ }\]
\[ = {720^\circ }\]
Therefore, the sum of the angles of a hexagon is \[{720^\circ }\].
Note:
Method 2: Using interior angle sum formula:
We know that,
Sum of the interior angles of a n-gon is
\[ = (n - 2) \times {180^\circ }\] where n means number of sides.
For a hexagon, n = 6.
So, substituting this value of n in the above formula, we will get,
\[ = (6 - 2) \times {180^\circ }\]
Simply this, we will get,
\[ = 4 \times {180^\circ }\]
\[ = {720^\circ }\]
Hence, the sum of the angles of a hexagon is \[{720^\circ }\].
For irregular hexagons also, it is true.
Method 3:
The sum of the interior angles of a hexagon = 4 times the sum of the interior angles of a triangle
\[ = 4 \times {180^\circ }\]
\[ = {720^\circ }\]
So, the correct answer is “\[ {720^\circ }\]”.
A polygon is a two-dimensional geometric figure that has a finite number of sides. The sides of a polygon are made of straight line segments connected to each other end to end. A circle is also a plane figure but it is not considered as a polygon, because it is a curved shape and does not have sides or angles. A minimum of three line segments is required to connect end to end, to make a closed figure. Thus a polygon with a minimum of three sides is known as Triangle and it is also called 3-gon. An n-sided polygon is called n-gon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




