
The alkaline hydrolysis of oil or fat gives soap and:
A.Glycerol
B.Ethanol
C.Glycol
D.Ethanoic acid
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint:The alkaline hydrolysis is also called saponification in which oils or fats are converted to produce soap. This process is carried out in the presence of aqueous alkaline solution. For example: $NaOH$ .
Complete step by step answer:
The process in which the oils or fats are converted to produce soap is called saponification.
Here, the ester is treated in the presence of aqueous $NaOH$ or $KOH$ to give alcohol or sodium/potassium salt of the acid.
It mostly occurs when triglycerides react with potassium to give glycerol and fatty acids.
Reaction of Saponification:
Basically triglycerides are the animal fats and vegetable oils.
These when reacted with $NaOH$ , a hard form soap is produced.
General equation of soap: ester $ + $ base $ = $ soap $ + $ alcohol
Here is an example of Saponification given below:
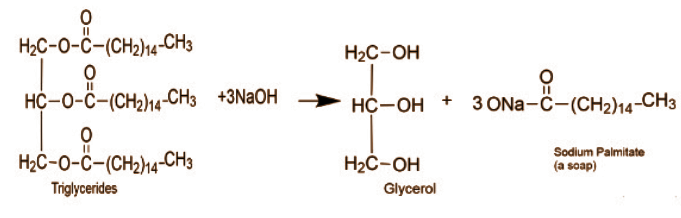
In the above reaction triglycerides react with $NaOH$ . which is a strong base, glycerol is produced which is an acid, along with the soap (sodium palmitate).
In the same way, we can use potassium with an ester to produce soap and alcohol. The reaction is given below as follows:
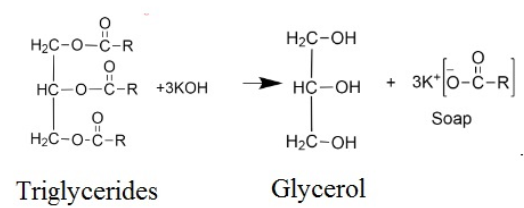
In the above reaction also, potassium palmitate (soap) and glycerol (alcohol) are formed.
So the correct answer will be option A) Glycerol.
Note:
Sodium soaps and potassium soaps are only used for cleaning purposes. Soaps can be of two types: hard soaps or soft soaps. Sodium soaps are hard while the potassium soaps are soft.
Glycerol is also known as glycerin is a natural byproduct which is separated during the saponification process.
Complete step by step answer:
The process in which the oils or fats are converted to produce soap is called saponification.
Here, the ester is treated in the presence of aqueous $NaOH$ or $KOH$ to give alcohol or sodium/potassium salt of the acid.
It mostly occurs when triglycerides react with potassium to give glycerol and fatty acids.
Reaction of Saponification:
Basically triglycerides are the animal fats and vegetable oils.
These when reacted with $NaOH$ , a hard form soap is produced.
General equation of soap: ester $ + $ base $ = $ soap $ + $ alcohol
Here is an example of Saponification given below:

In the above reaction triglycerides react with $NaOH$ . which is a strong base, glycerol is produced which is an acid, along with the soap (sodium palmitate).
In the same way, we can use potassium with an ester to produce soap and alcohol. The reaction is given below as follows:

In the above reaction also, potassium palmitate (soap) and glycerol (alcohol) are formed.
So the correct answer will be option A) Glycerol.
Note:
Sodium soaps and potassium soaps are only used for cleaning purposes. Soaps can be of two types: hard soaps or soft soaps. Sodium soaps are hard while the potassium soaps are soft.
Glycerol is also known as glycerin is a natural byproduct which is separated during the saponification process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




