
The angle between magnetic meridian and geographical meridian is known as:
A). Magnetic dip
B). Magnetic latitude
C). Magnetic declination
D). Magnetic longitude
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: To answer this question we need to find the definitions of all the options that are mentioned. Once, we know what every option includes, we can write the answer, on the basis of the criteria mentioned in the question.
Complete step by step answer:
To answer this question, we have to elaborate on each and every option that is mentioned. The first option that is given is the Magnetic Dip.
Magnetic Dip is defined as the angle which is made between the horizontal and the Earth’s magnetic field lines. The angle is not constant and depends on the different points that are taken into consideration, on the Earth’s surface. So, this cannot be the answer to the required question.
The second option is the Magnetic latitude. By magnetic latitude, we mean the parameter which is analogous to that of the geographic latitude. The only exception is that it does not include the consideration of geographic poles. Rather, it is defined with respect to the geomagnetic dipole. This geomagnetic dipole is extracted from the International Geomagnetic Reference Field. So, this cannot be the answer.
The third option that is given is known as the Magnetic Declination. The Magnetic Declination is defined as the angle present on the horizontal plane and occurs between the magnetic north and the true north. This can also be written as an angle between the magnetic meridian and that of the geographical meridian. So, this is the required answer.
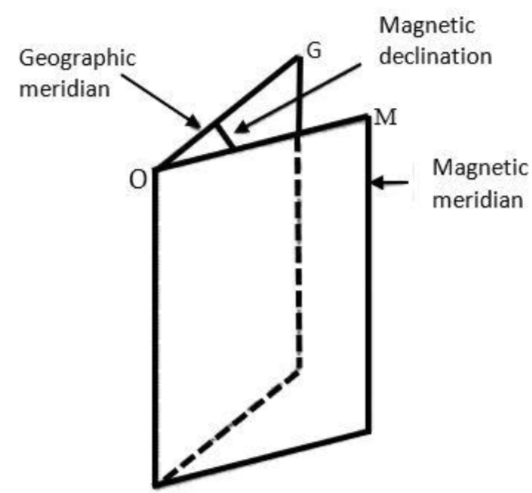
The last option is the Magnetic longitude. By Magnetic longitude, we mean the parameter which is analogous to that of the geographic longitude. So, this cannot be the answer.
Hence, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: The magnetic declination is considered to be important because it helps in navigation. For navigation, the compass that we use will always point towards the lines of magnetic force. This means that it will converge at the magnetic poles. The angle occurring between the direction of the force and that of the geographic north pole will give us the declination.
Complete step by step answer:
To answer this question, we have to elaborate on each and every option that is mentioned. The first option that is given is the Magnetic Dip.
Magnetic Dip is defined as the angle which is made between the horizontal and the Earth’s magnetic field lines. The angle is not constant and depends on the different points that are taken into consideration, on the Earth’s surface. So, this cannot be the answer to the required question.
The second option is the Magnetic latitude. By magnetic latitude, we mean the parameter which is analogous to that of the geographic latitude. The only exception is that it does not include the consideration of geographic poles. Rather, it is defined with respect to the geomagnetic dipole. This geomagnetic dipole is extracted from the International Geomagnetic Reference Field. So, this cannot be the answer.
The third option that is given is known as the Magnetic Declination. The Magnetic Declination is defined as the angle present on the horizontal plane and occurs between the magnetic north and the true north. This can also be written as an angle between the magnetic meridian and that of the geographical meridian. So, this is the required answer.

The last option is the Magnetic longitude. By Magnetic longitude, we mean the parameter which is analogous to that of the geographic longitude. So, this cannot be the answer.
Hence, the correct answer is Option C.
Note: The magnetic declination is considered to be important because it helps in navigation. For navigation, the compass that we use will always point towards the lines of magnetic force. This means that it will converge at the magnetic poles. The angle occurring between the direction of the force and that of the geographic north pole will give us the declination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




