
The angle between the incident and emergent ray when the ray is passing through an equilateral prism is called the angle of:
A.)Refraction
B.)Base
C.)Dispersion
D.)Deviation
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: When a ray of light is incident on an equilateral prism surface, the light ray will bend towards the normal, since the light is passing from a rarer medium to a denser medium. When the same ray hits the other side and comes out of the prism, the emergent ray will bend away from the normal.
Complete step by step answer:
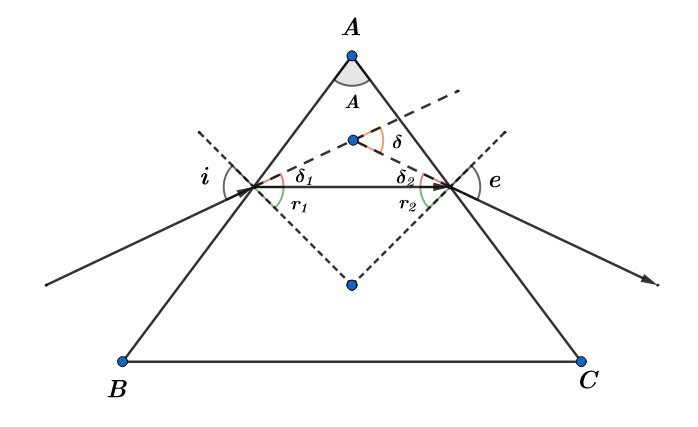
Suppose a ray of light hits on the surface AB of a prism. The light passing into the prism will bend towards the normal since the light passes through a rarer medium to a denser medium. If ${{i}_{1}}$is the angle of incidence, then ${{r}_{1}}$ is the angle of refraction, where ${{i}_{1}}>{{r}_{1}}$ . ${{\delta }_{1}}$ is the angle of deviation made by the ray of light when it passes into the prism.
So the ray of light hits on the surface AC after travelling through the prism. The light passing out of the prism will bend away from the normal since the light passes through a denser medium to a rarer medium. If ${{r}_{2}}$is the angle of incidence, then $e$ is the angle of refraction or emergence, where $e>{{r}_{2}}$ . ${{\delta }_{2}}$ is the angle of deviation made by the ray of light when it passes out of the prism.
If you extend the incident ray on the face AB and extend the emergent ray backwards, both of these will meet a point, and the angle formed by these two lines is called the angle of deviation of the prism. We can write the angle of deviation of the prism as the sum of deviation produced by the incident ray at the face AB and the emergent ray at the face AC. So we can write,
$\delta ={{\delta }_{1}}+{{\delta }_{2}}$. The angle is called Deviation angle so option D is correct.
Note:
The refractive index of a material is a function of wavelength. So for each wavelength of light, there will be a refractive index for each of them. So, when white light passes through a prism, it gets split into its constituent colours because each wavelength will have a refractive index and as a result of different speeds while passing through the same medium. This phenomenon is called the dispersion of light.
The angle of minimum deviation (${{\delta }_{m}}$) is the angle of deviation between the incident and emergent ray of the prism when the refracted ray passes parallel to the prism base.
The refractive index of an equilateral prism can be found using the formula,
$\mu =\dfrac{\sin \left[ \dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right]}{\sin \left[ \dfrac{A}{2} \right]}$
Where,
$\mu $ is the refractive index of the prism.
A is the prism angle.
${{\delta }_{m}}$ is the angle of minimum deviation.
Complete step by step answer:

Suppose a ray of light hits on the surface AB of a prism. The light passing into the prism will bend towards the normal since the light passes through a rarer medium to a denser medium. If ${{i}_{1}}$is the angle of incidence, then ${{r}_{1}}$ is the angle of refraction, where ${{i}_{1}}>{{r}_{1}}$ . ${{\delta }_{1}}$ is the angle of deviation made by the ray of light when it passes into the prism.
So the ray of light hits on the surface AC after travelling through the prism. The light passing out of the prism will bend away from the normal since the light passes through a denser medium to a rarer medium. If ${{r}_{2}}$is the angle of incidence, then $e$ is the angle of refraction or emergence, where $e>{{r}_{2}}$ . ${{\delta }_{2}}$ is the angle of deviation made by the ray of light when it passes out of the prism.
If you extend the incident ray on the face AB and extend the emergent ray backwards, both of these will meet a point, and the angle formed by these two lines is called the angle of deviation of the prism. We can write the angle of deviation of the prism as the sum of deviation produced by the incident ray at the face AB and the emergent ray at the face AC. So we can write,
$\delta ={{\delta }_{1}}+{{\delta }_{2}}$. The angle is called Deviation angle so option D is correct.
Note:
The refractive index of a material is a function of wavelength. So for each wavelength of light, there will be a refractive index for each of them. So, when white light passes through a prism, it gets split into its constituent colours because each wavelength will have a refractive index and as a result of different speeds while passing through the same medium. This phenomenon is called the dispersion of light.
The angle of minimum deviation (${{\delta }_{m}}$) is the angle of deviation between the incident and emergent ray of the prism when the refracted ray passes parallel to the prism base.
The refractive index of an equilateral prism can be found using the formula,
$\mu =\dfrac{\sin \left[ \dfrac{A+{{\delta }_{m}}}{2} \right]}{\sin \left[ \dfrac{A}{2} \right]}$
Where,
$\mu $ is the refractive index of the prism.
A is the prism angle.
${{\delta }_{m}}$ is the angle of minimum deviation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




