
The area enclosed between the ${y^2} = x$ and $y = |x|$ is
A) $\dfrac{1}{3}$
B) $\dfrac{2}{3}$
C) $1$
D) $\dfrac{1}{6}$
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: The area between two curves can be found using definite integral. Since the curves are expressed in terms of $y =
f(x)$, we can integrate with respect to $x$. No specific interval is given. So we can take the unit interval $(0,1)$.
Formula used: If we have two curves $y = f(x)$ and $y = g(x)$ such that $f(x) > g(x)$ then the area between them bounded by the horizontal lines $x = a,x = b$ is given by
$A = \int\limits_a^b {(f(x) - g(x))dx} $
Complete step-by-step solution:
We are given the curves ${y^2} = x$ and $y = |x|$.
We have to find the area enclosed between them.
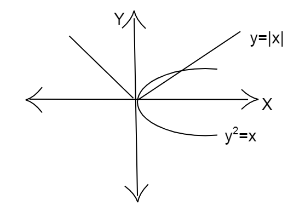
We can rewrite them as follows.
${y^2} = x \Rightarrow y = \sqrt x $
And we have,
$|x|$ takes the value $x$ for $x > 0$ and $ - x$ for $x < 0$.
To find the area between the curves,
Consider the interval $(0,1)$.
If we have two curves $y = f(x)$ and $y = g(x)$ such that $f(x) > g(x)$ then the area between them bounded by the
horizontal lines $x = a,x = b$ is given by
$A = \int\limits_a^b {(f(x) - g(x))dx} $
So let $f(x) = \sqrt x $ and $g(x) = |x|$.
In the interval $(0,1)$, we have $\sqrt x > |x| = x$
So substituting we get the area as,
$\Rightarrow$$A = \int\limits_0^1 {(\sqrt x - x)dx} $
This gives,
$\Rightarrow$$A = \int\limits_0^1 {({x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} - x)dx} $
We know that $\int\limits_0^1 {{x^n}dx} = [\dfrac{{{x^{n + 1}}}}{{n + 1}}]_0^1$
We get,
$\Rightarrow$$A = [\dfrac{{{x^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{{\dfrac{3}{2}}} - \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2}]_0^1$
Simplifying we have,
$\Rightarrow$$A = [\dfrac{{2{x^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{3} - \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2}]_0^1$
Substituting the limits we get,
$\Rightarrow$$A = [\dfrac{{2 \times {1^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{3} - \dfrac{{{1^2}}}{2} - (\dfrac{{2 \times {0^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{3} -\dfrac{{{0^2}}}{2})]$
Simplifying we get,
$\Rightarrow$$A = [\dfrac{2}{3} - \dfrac{1}{2} - (0 - 0)]$
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{4 - 3}}{6}$
So we get,
$\Rightarrow$$A = \dfrac{1}{6}$
That is the area enclosed between the two curves is $\dfrac{1}{6}$.
Therefore the answer is option D.
Note: We took the value of $|x|$ as $x$ since the values are positive in the unit interval. Also, we have for positive numbers less than one, its root exceeds the number. So, we get the function $f(x)$ greater than the function $g(x)$. If in the question any interval is specified, we have to change the range of $x$.
f(x)$, we can integrate with respect to $x$. No specific interval is given. So we can take the unit interval $(0,1)$.
Formula used: If we have two curves $y = f(x)$ and $y = g(x)$ such that $f(x) > g(x)$ then the area between them bounded by the horizontal lines $x = a,x = b$ is given by
$A = \int\limits_a^b {(f(x) - g(x))dx} $
Complete step-by-step solution:
We are given the curves ${y^2} = x$ and $y = |x|$.
We have to find the area enclosed between them.

We can rewrite them as follows.
${y^2} = x \Rightarrow y = \sqrt x $
And we have,
$|x|$ takes the value $x$ for $x > 0$ and $ - x$ for $x < 0$.
To find the area between the curves,
Consider the interval $(0,1)$.
If we have two curves $y = f(x)$ and $y = g(x)$ such that $f(x) > g(x)$ then the area between them bounded by the
horizontal lines $x = a,x = b$ is given by
$A = \int\limits_a^b {(f(x) - g(x))dx} $
So let $f(x) = \sqrt x $ and $g(x) = |x|$.
In the interval $(0,1)$, we have $\sqrt x > |x| = x$
So substituting we get the area as,
$\Rightarrow$$A = \int\limits_0^1 {(\sqrt x - x)dx} $
This gives,
$\Rightarrow$$A = \int\limits_0^1 {({x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}} - x)dx} $
We know that $\int\limits_0^1 {{x^n}dx} = [\dfrac{{{x^{n + 1}}}}{{n + 1}}]_0^1$
We get,
$\Rightarrow$$A = [\dfrac{{{x^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{{\dfrac{3}{2}}} - \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2}]_0^1$
Simplifying we have,
$\Rightarrow$$A = [\dfrac{{2{x^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{3} - \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2}]_0^1$
Substituting the limits we get,
$\Rightarrow$$A = [\dfrac{{2 \times {1^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{3} - \dfrac{{{1^2}}}{2} - (\dfrac{{2 \times {0^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}}}{3} -\dfrac{{{0^2}}}{2})]$
Simplifying we get,
$\Rightarrow$$A = [\dfrac{2}{3} - \dfrac{1}{2} - (0 - 0)]$
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{{4 - 3}}{6}$
So we get,
$\Rightarrow$$A = \dfrac{1}{6}$
That is the area enclosed between the two curves is $\dfrac{1}{6}$.
Therefore the answer is option D.
Note: We took the value of $|x|$ as $x$ since the values are positive in the unit interval. Also, we have for positive numbers less than one, its root exceeds the number. So, we get the function $f(x)$ greater than the function $g(x)$. If in the question any interval is specified, we have to change the range of $x$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




