
The area under acceleration – time graph gives
A. Change in acceleration.
B. Change in velocity.
C. Change in displacement.
D. Change in deceleration.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Acceleration is defined as change in velocity (\[\vec v\]) per unit time. To find out instantaneous acceleration ( \[\vec a\] ) we differentiate the velocity (\[\vec v\]) with respect to time (\[t\]). In graphs in order to find the change in velocity we find the area under acceleration – time graph.
Formulae Used:
\[\vec a = \dfrac{{d\vec v}}{{dt}}\]
Where \[\vec a\]= acceleration of the particle
\[d\vec v\]= infinitesimal change in velocity.
\[dt\]= time take for making that infinitesimal change in velocity
Complete step-by-step solution:
Since instantaneous acceleration is given by
\[\vec a = \dfrac{{d\vec v}}{{dt}}\]
Rearranging the terms
\[d\vec v = \vec a.dt\]
Integrating both sides , we get
\[\int {d\vec v = \int {\vec a.dt} } \] we know that the term \[\int\limits_{{t_1}}^{{t_2}} {\vec a.dt} \]gives the area between the acceleration – time graph between time \[{t_1}\]to \[{t_2}\] and the term \[\int {d\vec v} \], represents the total change in velocity between the same interval of time.
Since, the area of the curve between acceleration – time graph shows the change in velocity of the moving object.
Hence, option ( B ) is the correct answer.
In case of uniform motion velocity remains constant , and displacement is the linear function of velocity as \[s = vt\], where \[s\] is the displacement of any object and \[v\] is the constant velocity with which the particle is moving & \[t\] is the time taken to cover the displacement or the time for which the particle is moving with constant velocity \[v\].
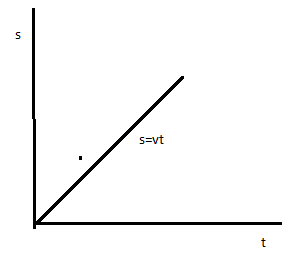
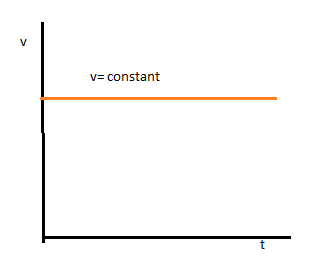
In case of uniformly accelerated motion the velocity is increasing with respect to time. The velocity is increasing with respect to time and the displacement is also increasing with respect to time.
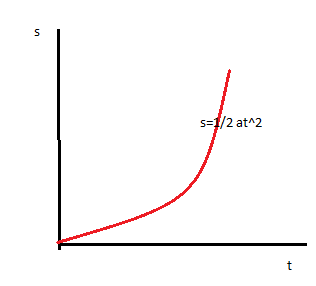
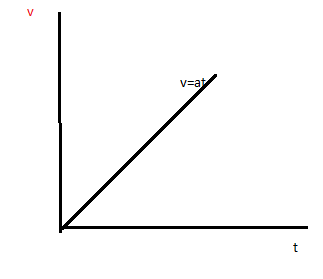
Note:- Here is a diagram that shows the relation between displacement, velocity & acceleration.
Slope of velocity - time curve gives the value of instantaneous acceleration & the slope of displacement - time curve gives the value of instantaneous velocity.
Formulae Used:
\[\vec a = \dfrac{{d\vec v}}{{dt}}\]
Where \[\vec a\]= acceleration of the particle
\[d\vec v\]= infinitesimal change in velocity.
\[dt\]= time take for making that infinitesimal change in velocity
Complete step-by-step solution:
Since instantaneous acceleration is given by
\[\vec a = \dfrac{{d\vec v}}{{dt}}\]
Rearranging the terms
\[d\vec v = \vec a.dt\]
Integrating both sides , we get
\[\int {d\vec v = \int {\vec a.dt} } \] we know that the term \[\int\limits_{{t_1}}^{{t_2}} {\vec a.dt} \]gives the area between the acceleration – time graph between time \[{t_1}\]to \[{t_2}\] and the term \[\int {d\vec v} \], represents the total change in velocity between the same interval of time.
Since, the area of the curve between acceleration – time graph shows the change in velocity of the moving object.
Hence, option ( B ) is the correct answer.
In case of uniform motion velocity remains constant , and displacement is the linear function of velocity as \[s = vt\], where \[s\] is the displacement of any object and \[v\] is the constant velocity with which the particle is moving & \[t\] is the time taken to cover the displacement or the time for which the particle is moving with constant velocity \[v\].


In case of uniformly accelerated motion the velocity is increasing with respect to time. The velocity is increasing with respect to time and the displacement is also increasing with respect to time.


Note:- Here is a diagram that shows the relation between displacement, velocity & acceleration.
Slope of velocity - time curve gives the value of instantaneous acceleration & the slope of displacement - time curve gives the value of instantaneous velocity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




