
The bacteria present in root nodules of leguminous plants that fix the atmospheric nitrogen is
A. Rhizobium
B. Blue-green algae
C. Nitrifying bacteria
D. Paramecium
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: Leguminous plants are those that have nodular or bed like structures in their roots called legumes. These plants live in a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria. As plants cannot degrade the atmospheric nitrogen on their own they give shelter to these bacteria to do the tough work. A diazotroph gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium lives in the nodules of leguminous plants.
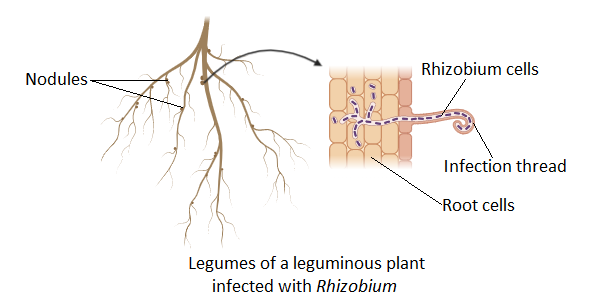
Complete answer:The leguminous plants like soybean, chickpea, etc. have bead-like structures present on their roots. Thus, their roots are given a special name that is legumes. So, the leguminous plant term is derived from the legumes of these plants. The legumes enclose nitrogen-fixing bacteria that help in degrading atmospheric nitrogen and provide it to plants. The nitrogen converts into ammonium which is used by plants for their growth and development.
Rhizobium is a diazotroph which is gram-negative and is rod-shaped bacteria found in association with roots of leguminous plants, packed in nodular structures attached to the roots. It is approximately 1 micron in length. It can fix atmospheric nitrogen in a symbiotic relationship with host legumes. It converts the atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium for plants and gets nutrients for its own metabolic processes from the host. Generally, it is found in chickpea, black gram, soybean, etc. Rhizobium can be classified as Rhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, Sinorhizobium, and Photo Rhizobium. It gives pink color to the nodules in which it lives in its most active stage.
Blue-green algae are an alga species. It also acts as a nitrogen-fixing microbe and helps in plant development. Nitrifying bacteria are those that fix atmospheric ammonium or ammonia into nitrate. They are found abundantly in sewage water areas. Paramecium is a unicellular ciliated microbe that is present in stagnant waters majorly.
Thus, Rhizobium is the bacterium that is present in the root nodules of leguminous plants that fix the atmospheric nitrogen.
So, option A) Rhizobium is the correct answer.
Note: Rhizobium is a slow-growing microbe which can fix atmospheric nitrogen and this happens in 5 steps, which are, Attraction by flavonoids produced by legumes and multiplication of rhizobium, Attachment by exopolysaccharide produced by Rhizobium interaction with lectin produced from plants to the root surface, Root hair curling caused by indole acetic acid produced by Rhizobium, Formation of infection thread and at last nodule formation.
Complete answer:The leguminous plants like soybean, chickpea, etc. have bead-like structures present on their roots. Thus, their roots are given a special name that is legumes. So, the leguminous plant term is derived from the legumes of these plants. The legumes enclose nitrogen-fixing bacteria that help in degrading atmospheric nitrogen and provide it to plants. The nitrogen converts into ammonium which is used by plants for their growth and development.
Rhizobium is a diazotroph which is gram-negative and is rod-shaped bacteria found in association with roots of leguminous plants, packed in nodular structures attached to the roots. It is approximately 1 micron in length. It can fix atmospheric nitrogen in a symbiotic relationship with host legumes. It converts the atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium for plants and gets nutrients for its own metabolic processes from the host. Generally, it is found in chickpea, black gram, soybean, etc. Rhizobium can be classified as Rhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, Sinorhizobium, and Photo Rhizobium. It gives pink color to the nodules in which it lives in its most active stage.

Blue-green algae are an alga species. It also acts as a nitrogen-fixing microbe and helps in plant development. Nitrifying bacteria are those that fix atmospheric ammonium or ammonia into nitrate. They are found abundantly in sewage water areas. Paramecium is a unicellular ciliated microbe that is present in stagnant waters majorly.
Thus, Rhizobium is the bacterium that is present in the root nodules of leguminous plants that fix the atmospheric nitrogen.
So, option A) Rhizobium is the correct answer.
Note: Rhizobium is a slow-growing microbe which can fix atmospheric nitrogen and this happens in 5 steps, which are, Attraction by flavonoids produced by legumes and multiplication of rhizobium, Attachment by exopolysaccharide produced by Rhizobium interaction with lectin produced from plants to the root surface, Root hair curling caused by indole acetic acid produced by Rhizobium, Formation of infection thread and at last nodule formation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




