
The banana bond in diborane is constituted by?
(A) 2 Atoms and 2 electrons
(B) 2 Atoms and 3 electrons
(C) 3 Atoms and 2 electrons
(D) 3 Atoms and 3 electrons
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Diborane forms 4 normal covalent bonds with 4 H atoms. The banana bonds are formed in between the B atoms. There are a total of 2 banana bonds in diborane.
Complete-step- by- step answer:
Diborane is a chemical compound with the formula-${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ .
It is a colourless, highly flammable gas with a repulsive sweet odour. It is extremely toxic.
Combustion of diborane is extremely exothermic.
To understand what is meant by a banana bond, let us look into the structure of diborane.
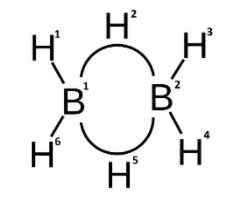
In diborane, first we need to know that the B with atomic number 5, has the electronic configuration- $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}$. While hybridising, one of the 2s valence electrons is excited to a 2p orbital and we get 4 $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised orbitals. Among these 4 hybrid orbitals, 3 of them have one electron each. And, one of them is an empty orbital.
Each B atom in ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ forms 2 normal covalent bonds with the 1s orbitals of the H atoms. Hence, in total the 2 B atoms form 4 normal covalent bonds. These bonds are 2 centre – 2 electron bonds named according to the atoms and number of electrons.
The 2 B atoms are now left with one orbital with an unpaired electron and one empty orbital each. These are the orbitals that form the two bridging B-H-B bonds with the two 1s orbitals of the H atoms. These bonds are commonly known as the banana bonds.
Now, let us look at the number of atoms and electrons in the banana bonds.
Each banana bond has contributions of 2 B atoms and 1 H atom. Hence, there are 3 atoms.
The number of electrons in each bond will be, one electron from H atom, and a total of one electron from both the B atoms. Hence, the number of electrons is 2.
Therefore we can conclude that the banana bond in diborane consists of 3 atoms and 2 electrons.
So, the correct answer is (C).
Additional Information:
Diborane is a chemical compound with many applications in various fields.
i) Diborane and some of its variants are used as reagents for hydroboration.
ii) It is also used as a reducing agent and can readily reduce carboxylic acids to corresponding alcohols.
iii) Diborane has been tested as a rocket propellant as its combustion is extremely exothermic.
iv) It is used as a rubber vulcaniser and as a catalyst for polymerisation reactions.
v) It is used as a doping agent for semiconductor production.
Note: Banana bonds are also called as 3-centre 2-electron bonds. It signifies that the bond is constituted by 3 atoms and 2 electrons. While drawing the structure of diborane, it is advised to use curved lines to show the banana bonds.
Complete-step- by- step answer:
Diborane is a chemical compound with the formula-${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ .
It is a colourless, highly flammable gas with a repulsive sweet odour. It is extremely toxic.
Combustion of diborane is extremely exothermic.
To understand what is meant by a banana bond, let us look into the structure of diborane.

In diborane, first we need to know that the B with atomic number 5, has the electronic configuration- $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}$. While hybridising, one of the 2s valence electrons is excited to a 2p orbital and we get 4 $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised orbitals. Among these 4 hybrid orbitals, 3 of them have one electron each. And, one of them is an empty orbital.
Each B atom in ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ forms 2 normal covalent bonds with the 1s orbitals of the H atoms. Hence, in total the 2 B atoms form 4 normal covalent bonds. These bonds are 2 centre – 2 electron bonds named according to the atoms and number of electrons.
The 2 B atoms are now left with one orbital with an unpaired electron and one empty orbital each. These are the orbitals that form the two bridging B-H-B bonds with the two 1s orbitals of the H atoms. These bonds are commonly known as the banana bonds.
Now, let us look at the number of atoms and electrons in the banana bonds.
Each banana bond has contributions of 2 B atoms and 1 H atom. Hence, there are 3 atoms.
The number of electrons in each bond will be, one electron from H atom, and a total of one electron from both the B atoms. Hence, the number of electrons is 2.
Therefore we can conclude that the banana bond in diborane consists of 3 atoms and 2 electrons.
So, the correct answer is (C).
Additional Information:
Diborane is a chemical compound with many applications in various fields.
i) Diborane and some of its variants are used as reagents for hydroboration.
ii) It is also used as a reducing agent and can readily reduce carboxylic acids to corresponding alcohols.
iii) Diborane has been tested as a rocket propellant as its combustion is extremely exothermic.
iv) It is used as a rubber vulcaniser and as a catalyst for polymerisation reactions.
v) It is used as a doping agent for semiconductor production.
Note: Banana bonds are also called as 3-centre 2-electron bonds. It signifies that the bond is constituted by 3 atoms and 2 electrons. While drawing the structure of diborane, it is advised to use curved lines to show the banana bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




