
The basic building unit of protein is
(A) Polypeptide
(B) Amino acids
(C) Amines
(D) Carboxylic acids
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Proteins are polypeptide chains made up of these building blocks. These chains are wrapped around each other in various forms. This building block contains two functional groups: amino group and carboxylic acid group and depending on their number it can be acidic, basic or neutral.
Complete step by step answer:
-First of all we will see what proteins are.
Those large, complex molecules which play many critical roles in our body are known as proteins. Proteins form 60% of the dry weight of the dry weight of the cells and thus are also known as “building blocks of life”. Not just cells, but many enzymes, regulatory and structural parts of the body are made of proteins. Hence, proteins are highly essential for the growth and development of any body.
-All the proteins are α-amino acids which means that they are polymeric chains of amino acid residues. Every protein has different properties due to the presence of different types of amino acids.
Amino acids are compounds which contain both amino ($ - N{H_2}$)and carboxylic acid functional groups (-COOH). The amino acids can be α, β, γ, δ and so on depending on the position of the amino group relative to the position of the carboxyl group.
Amino acids are basically substituted methane, in which the 4 valencies of the α-carbon are occupied by: an amino group, a carboxyl group, hydrogen and 4th by different R groups. There are 20 different amino acids of which 9 are essential amino acids.
The general representation of an amino acid is like:
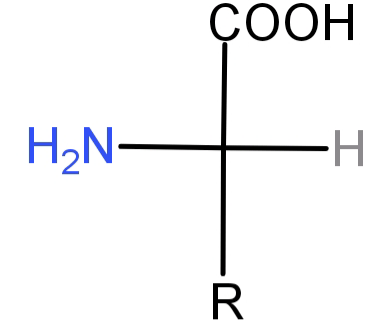
-Different amino acids are linked to each other via peptide bonds or peptide linkages to form long chain polypeptides. A peptide bond is an amide (-CO-NH-) formed between a (–COOH) group of 1 amino acid with ($N{H_2}$) group of another amino acid. Either one or more such polypeptide chains fold around each other in various manners to form proteins. This can be generally represented as:
$N{H_2} - CH(R) - COOH + N{H_2} - CH(R') - COOH \to N{H_2} - CH(R) - [CO - NH] - CH(R') - COOH$
A polypeptide chain may look like:
$\left\{ { - NH - CH({R_1}) - CO - NH - CH({R_2}) - CO - NH - CH({R_3}) - CO - } \right\}$
Hence we can say that amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
So, the correct option will be: (B) Amino acids.
Note: The amino acids can be acidic, basic or neutral depending on the number of amino and carboxyl groups present in it. The amino acids are of 2 types: essential amino acids and non-essential amino acids. The amino acids which can be synthesized in our body are non-essential. Those which cannot be synthesized and need to be taken in via diet are essential amino acids.
Complete step by step answer:
-First of all we will see what proteins are.
Those large, complex molecules which play many critical roles in our body are known as proteins. Proteins form 60% of the dry weight of the dry weight of the cells and thus are also known as “building blocks of life”. Not just cells, but many enzymes, regulatory and structural parts of the body are made of proteins. Hence, proteins are highly essential for the growth and development of any body.
-All the proteins are α-amino acids which means that they are polymeric chains of amino acid residues. Every protein has different properties due to the presence of different types of amino acids.
Amino acids are compounds which contain both amino ($ - N{H_2}$)and carboxylic acid functional groups (-COOH). The amino acids can be α, β, γ, δ and so on depending on the position of the amino group relative to the position of the carboxyl group.
Amino acids are basically substituted methane, in which the 4 valencies of the α-carbon are occupied by: an amino group, a carboxyl group, hydrogen and 4th by different R groups. There are 20 different amino acids of which 9 are essential amino acids.
The general representation of an amino acid is like:

-Different amino acids are linked to each other via peptide bonds or peptide linkages to form long chain polypeptides. A peptide bond is an amide (-CO-NH-) formed between a (–COOH) group of 1 amino acid with ($N{H_2}$) group of another amino acid. Either one or more such polypeptide chains fold around each other in various manners to form proteins. This can be generally represented as:
$N{H_2} - CH(R) - COOH + N{H_2} - CH(R') - COOH \to N{H_2} - CH(R) - [CO - NH] - CH(R') - COOH$
A polypeptide chain may look like:
$\left\{ { - NH - CH({R_1}) - CO - NH - CH({R_2}) - CO - NH - CH({R_3}) - CO - } \right\}$
Hence we can say that amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
So, the correct option will be: (B) Amino acids.
Note: The amino acids can be acidic, basic or neutral depending on the number of amino and carboxyl groups present in it. The amino acids are of 2 types: essential amino acids and non-essential amino acids. The amino acids which can be synthesized in our body are non-essential. Those which cannot be synthesized and need to be taken in via diet are essential amino acids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




