
The bulk of histone proteins are synthesized in
A. \[{G_1}\] phase
B. ${G_2}$ phase
C. S phase
D. ${G_0}$ phase
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: Histones are proteins that are components of chromatin. These proteins remain associated with the DNA and help to condense the long chromosomes into smaller volumes. Histones are made during one of the phases of the cell cycle.
Complete answer:
The cell cycle is a cyclical process that is responsible for cell division. This cycle comprises four phases – ${G_1}$ or Gap 1, the S or Synthetic phase, in which the chromosome in the cell doubles, ${G_2}$ or Gap 2 comes after the S-phase and the M-phase or Mitotic phase in which the cell divides into daughter cells.
${G_1}$ is the first phase of cell division. It is in this phase that all the proteins required for DNA replication are formed. Some of the histone proteins are formed in this phase of cell cycle. Also, during this phase the cell decides whether to enter the S-phase or the dormant ${G_0}$ phase.
${G_2}$ phase of the cell cycle involves protein synthesis in bulk in order to prepare the cell for the upcoming M-phase or Mitotic phase. This phase also contains a checkpoint called the ${G_2}$ checkpoint that checks for any DNA damage that might have occurred during the DNA replication in the S-phase. If damages are found, the cell will either repair it or if irreparable, the checkpoint activates a mechanism called apoptosis that involves the death of the cell.
Synthetic phase or the S-phase is the phase when duplication of DNA occurs. During this phase, the amount of DNA in a cell is doubled. However, the number of chromosomes remain unchanged. Generally, transcription and protein synthesis occur at low rates. The only exception to this is the histone proteins. Most of the histone present in a cell is formed during the S-phase of cell division.
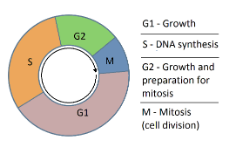
${G_0}$ phase is the resting phase. Cells in ${G_0}$ phase are considered to be out of the cell cycle. A cell can enter the ${G_0}$ phase from ${G_1}$ phase due to factors such as lack of nutrients. A cell can remain in the ${G_0}$ phase for a long period of time or they may never enter this phase at all. Or there are certain cells that remain in ${G_0}$ throughout their life. For example, epithelial cells do not enter ${G_0}$ at all, while nerve cells or neurons reside in this phase through their life.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
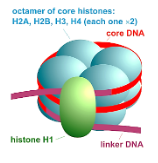
Note: Histone proteins are synthesized in bulk in the S-phase of cell division. Histones help in condensation of chromosome structure which will otherwise be very long and difficult to put in the nucleus of a tiny cell. The histones are closely involved in genetic regulation. There are five types of histones – H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3, H4. Among these, H1/H5 are known as linker histones and the rest are core histones. These core histones are present in dimers. Four such dimers interact to form an octamer around which the chromosome is wound. This structure is known as the nucleosome. Linker histones link two such nucleosomes.
Complete answer:
The cell cycle is a cyclical process that is responsible for cell division. This cycle comprises four phases – ${G_1}$ or Gap 1, the S or Synthetic phase, in which the chromosome in the cell doubles, ${G_2}$ or Gap 2 comes after the S-phase and the M-phase or Mitotic phase in which the cell divides into daughter cells.
${G_1}$ is the first phase of cell division. It is in this phase that all the proteins required for DNA replication are formed. Some of the histone proteins are formed in this phase of cell cycle. Also, during this phase the cell decides whether to enter the S-phase or the dormant ${G_0}$ phase.
${G_2}$ phase of the cell cycle involves protein synthesis in bulk in order to prepare the cell for the upcoming M-phase or Mitotic phase. This phase also contains a checkpoint called the ${G_2}$ checkpoint that checks for any DNA damage that might have occurred during the DNA replication in the S-phase. If damages are found, the cell will either repair it or if irreparable, the checkpoint activates a mechanism called apoptosis that involves the death of the cell.
Synthetic phase or the S-phase is the phase when duplication of DNA occurs. During this phase, the amount of DNA in a cell is doubled. However, the number of chromosomes remain unchanged. Generally, transcription and protein synthesis occur at low rates. The only exception to this is the histone proteins. Most of the histone present in a cell is formed during the S-phase of cell division.

${G_0}$ phase is the resting phase. Cells in ${G_0}$ phase are considered to be out of the cell cycle. A cell can enter the ${G_0}$ phase from ${G_1}$ phase due to factors such as lack of nutrients. A cell can remain in the ${G_0}$ phase for a long period of time or they may never enter this phase at all. Or there are certain cells that remain in ${G_0}$ throughout their life. For example, epithelial cells do not enter ${G_0}$ at all, while nerve cells or neurons reside in this phase through their life.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: Histone proteins are synthesized in bulk in the S-phase of cell division. Histones help in condensation of chromosome structure which will otherwise be very long and difficult to put in the nucleus of a tiny cell. The histones are closely involved in genetic regulation. There are five types of histones – H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3, H4. Among these, H1/H5 are known as linker histones and the rest are core histones. These core histones are present in dimers. Four such dimers interact to form an octamer around which the chromosome is wound. This structure is known as the nucleosome. Linker histones link two such nucleosomes.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




