
The cell division involved in gamete formation is not the same type in different organisms. Justify.
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: All sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy levels may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle.
Step by step answer:Humans are diploid organisms, carrying two complete sets of chromosomes in their somatic cells: one set of 23 chromosomes from their father and one set of 23 chromosomes from their mother. The two sets combined provide a full complement of 46 chromosomes. This total number of individual chromosomes is called the chromosome number. The number of chromosomes found in a single complete set of chromosomes is called the monoploid number (x). The haploid number (n) refers to the total number of chromosomes found in a gamete (a sperm or egg cell produced by meiosis in preparation for sexual reproduction). Under normal conditions, the haploid number is exactly half the total number of chromosomes present in the organism's somatic cells. For diploid organisms, the monoploid number and haploid number are equal; in humans, both are equal to 23. When a human germ cell undergoes meiosis, the diploid 46-chromosome complement is split in half to form haploid gametes. After the fusion of a male and a female gamete during fertilization, the resulting zygote again has the full complement of 46 chromosomes: 2 sets of 23 chromosomes.
An organism whose gametic cells contain a single copy of each chromosome or one set of chromosomes may be considered haploid while the somatic cells, containing two copies of each chromosome are known as diploid. Gametes (sperm and ova) are haploid cells. The haploid gametes produced by most organisms combine to form a zygote with n pairs of chromosomes, i.e. 2n chromosomes in total. The chromosomes in each pair, one of which comes from the sperm and one from the egg, are said to be homologous. Diploid cells have two homologous copies of each chromosome, usually one from the mother and one from the father. All or nearly all mammals are diploid organisms.
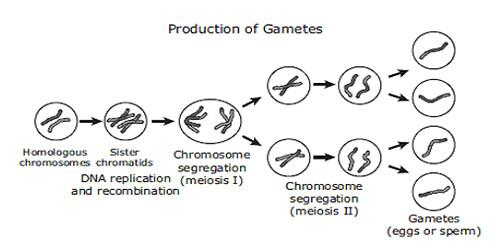
Note: Cells and organisms with pairs of homologous chromosomes are called diploid. For example, most animals are diploid and produce haploid gametes. During meiosis, sex cell precursors have their number of chromosomes halved by randomly "choosing" one member of each pair of chromosomes, resulting in haploid gametes.
Step by step answer:Humans are diploid organisms, carrying two complete sets of chromosomes in their somatic cells: one set of 23 chromosomes from their father and one set of 23 chromosomes from their mother. The two sets combined provide a full complement of 46 chromosomes. This total number of individual chromosomes is called the chromosome number. The number of chromosomes found in a single complete set of chromosomes is called the monoploid number (x). The haploid number (n) refers to the total number of chromosomes found in a gamete (a sperm or egg cell produced by meiosis in preparation for sexual reproduction). Under normal conditions, the haploid number is exactly half the total number of chromosomes present in the organism's somatic cells. For diploid organisms, the monoploid number and haploid number are equal; in humans, both are equal to 23. When a human germ cell undergoes meiosis, the diploid 46-chromosome complement is split in half to form haploid gametes. After the fusion of a male and a female gamete during fertilization, the resulting zygote again has the full complement of 46 chromosomes: 2 sets of 23 chromosomes.
An organism whose gametic cells contain a single copy of each chromosome or one set of chromosomes may be considered haploid while the somatic cells, containing two copies of each chromosome are known as diploid. Gametes (sperm and ova) are haploid cells. The haploid gametes produced by most organisms combine to form a zygote with n pairs of chromosomes, i.e. 2n chromosomes in total. The chromosomes in each pair, one of which comes from the sperm and one from the egg, are said to be homologous. Diploid cells have two homologous copies of each chromosome, usually one from the mother and one from the father. All or nearly all mammals are diploid organisms.

Note: Cells and organisms with pairs of homologous chromosomes are called diploid. For example, most animals are diploid and produce haploid gametes. During meiosis, sex cell precursors have their number of chromosomes halved by randomly "choosing" one member of each pair of chromosomes, resulting in haploid gametes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




