
The cell membranes of adjacent cells are fused at this cell junction.
(A) Macula adherens
(B) Zonula adherens
(C) Zonula occludens
(D) Nexus
Answer
580.2k+ views
Hint: The cell membranes of adjacent cells are fused at the tight junction. They are multiprotein junctional complexes. They provide a general function such as in the prevention of leakage of transported solutes and water molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
The cell membranes of adjacent cells are fused at the cell junction which is known as Zonula occludens. Zonula occludens is also known as Tight Junction. Tight junctions are present mostly in all vertebrates. The junctions that occur in invertebrates are separate junctions.
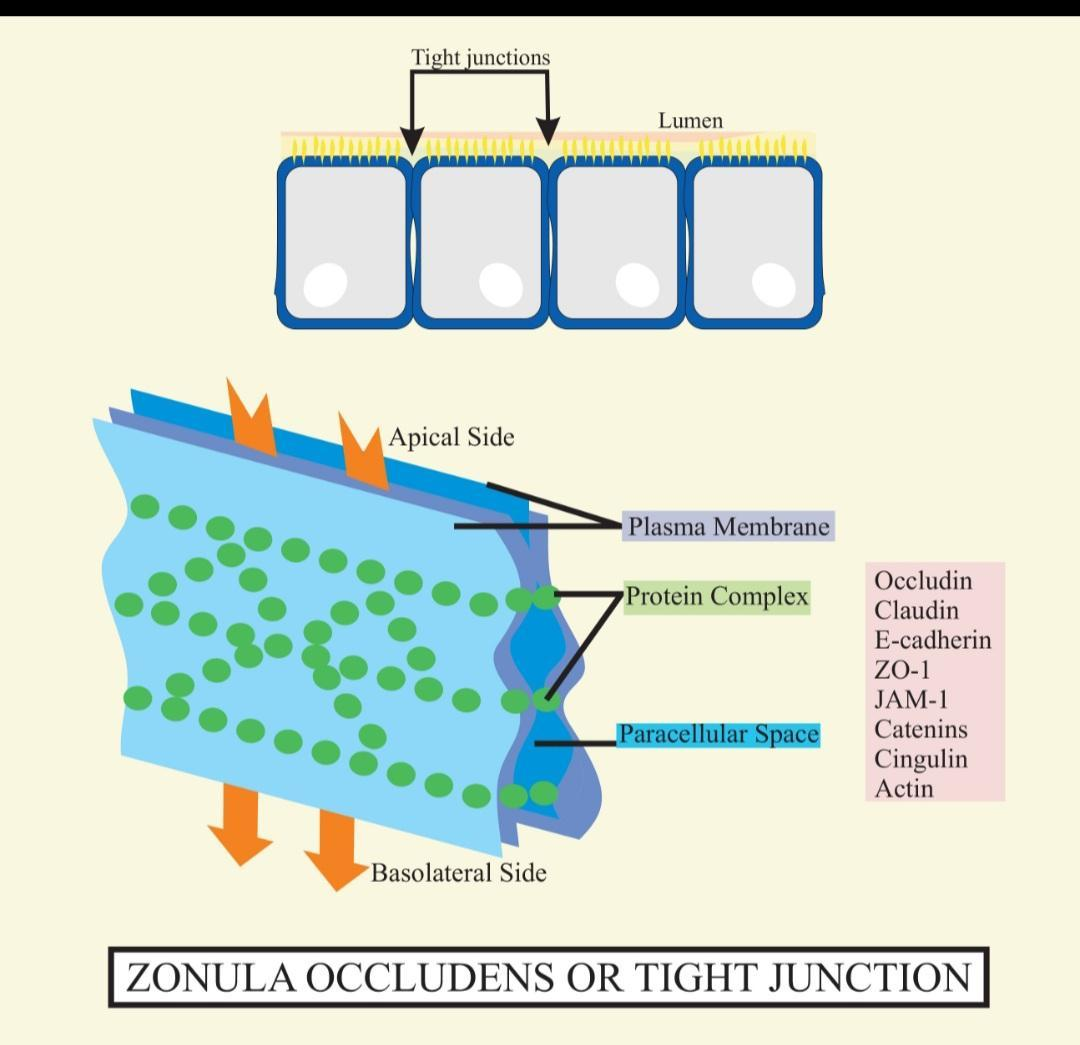
So, the correct answer is ‘Zonula occludens’.
Additional Information: Tight junctions are mainly composed of a branching network of sealing strands, each strand acting independently from the others. The efficiency of this junction in preventing ion passage increases exponentially with the number of strands. Each strand is made up of a row of transmembrane proteins that are embedded in both plasma membranes, with extracellular domains joining each other directly. There is a minimum of 40 different proteins composing the tight junctions. These proteins contain both transmembrane and cytoplasmic proteins. The three major transmembrane proteins which are present are occludin, claudins, and junction adhesion molecule (JAM) proteins. In human physiology, there are two main sorts of epithelia using distinct kinds of barrier mechanisms. Epidermal structures like skin form a barrier from many layers of keratinized squamous cells. Internal epithelia on the opposite hand more often believe tight junctions for their barrier function. This type of barrier is usually formed by just one or two layers of cells.
Note: Epithelia are classified in two ways:
- Tight epithelia: They have tight junctions that prevent most movement between cells. samples of tight epithelia include the distal convoluted tubule, the collecting duct of the nephron within the kidney, and therefore the bile ducts ramifying through liver tissue.
- Leaky epithelia: They don't have these tight junctions, or if present have less complex tight junctions. As an example, the tight junction within the kidney proximal tubule, a really leaky epithelium, has only two to 3 junctional strands, and these strands exhibit infrequent large slit breaks.
Complete step by step answer:
The cell membranes of adjacent cells are fused at the cell junction which is known as Zonula occludens. Zonula occludens is also known as Tight Junction. Tight junctions are present mostly in all vertebrates. The junctions that occur in invertebrates are separate junctions.

So, the correct answer is ‘Zonula occludens’.
Additional Information: Tight junctions are mainly composed of a branching network of sealing strands, each strand acting independently from the others. The efficiency of this junction in preventing ion passage increases exponentially with the number of strands. Each strand is made up of a row of transmembrane proteins that are embedded in both plasma membranes, with extracellular domains joining each other directly. There is a minimum of 40 different proteins composing the tight junctions. These proteins contain both transmembrane and cytoplasmic proteins. The three major transmembrane proteins which are present are occludin, claudins, and junction adhesion molecule (JAM) proteins. In human physiology, there are two main sorts of epithelia using distinct kinds of barrier mechanisms. Epidermal structures like skin form a barrier from many layers of keratinized squamous cells. Internal epithelia on the opposite hand more often believe tight junctions for their barrier function. This type of barrier is usually formed by just one or two layers of cells.
Note: Epithelia are classified in two ways:
- Tight epithelia: They have tight junctions that prevent most movement between cells. samples of tight epithelia include the distal convoluted tubule, the collecting duct of the nephron within the kidney, and therefore the bile ducts ramifying through liver tissue.
- Leaky epithelia: They don't have these tight junctions, or if present have less complex tight junctions. As an example, the tight junction within the kidney proximal tubule, a really leaky epithelium, has only two to 3 junctional strands, and these strands exhibit infrequent large slit breaks.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




