
The cilia and flagella arise from
(A)Basal bodies
(B)Basal granules
(C)Blepharoplasts
(D)All of the above
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: The cilia and flagella arise from one part and that one part has its three different names and all are starting with the same letter and the term is related to the base.
Complete answer:
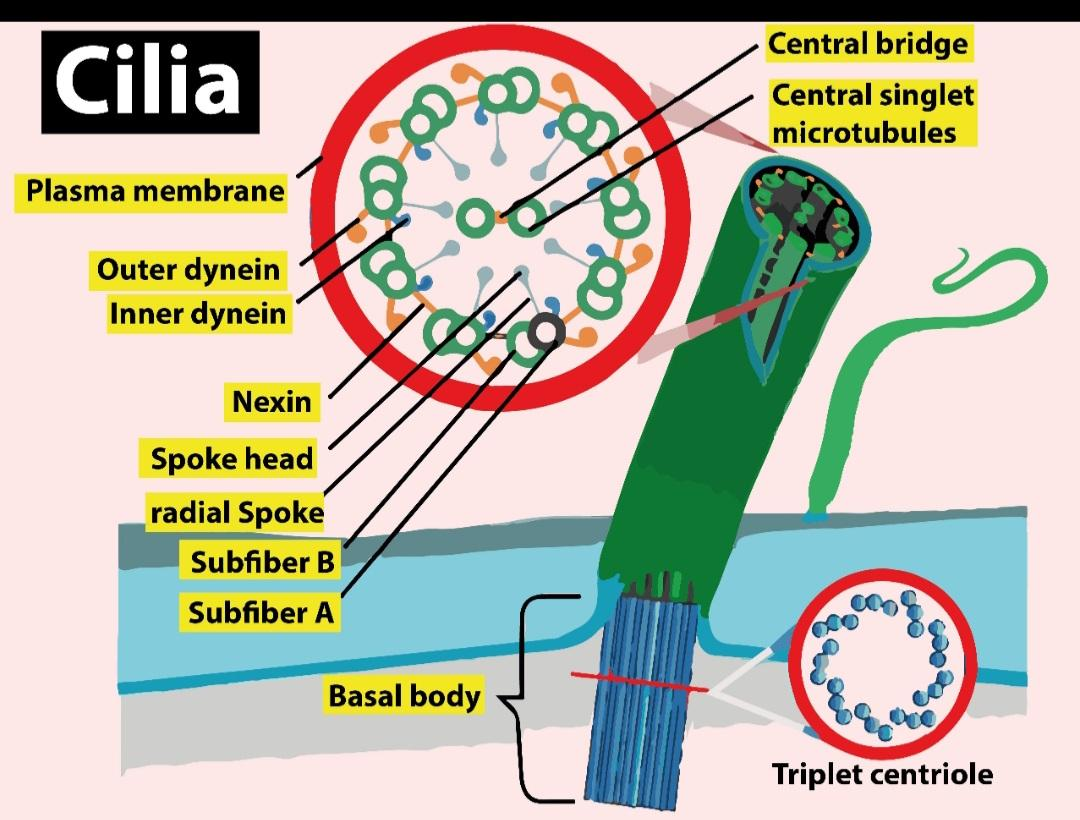
The cilia and flagella arise from the basal body. Another name of the basal body is basal granule, kinetosome, and in older cytological literature it is also known as blepharoplast. The basal body is a protein structure found at the base of a eukaryotic cilium or flagellum. The basal body serves as a site for the growth of the axoneme microtubules.
Additional Information: Cilia and flagella are the projections that come out from the cell. They're made from microtubules and are covered by an extension of the cell wall. they're motile and designed either to move the cell itself or to move substances over or around the cell. The first purpose of cilia in mammalian cells is to move fluid, mucous, or cells over their surface. Cilia and flagella have an equivalent internal structure. The main difference is in their length. Cilia and flagella can move just because of the interactions of a set of microtubules inside. These sets of microtubules are called an "axoneme".Two of these microtubules join to form one doublet in the cilia or flagella This is shown in the middle panel. It was seen that one of the tubules is incomplete.
So, the correct answer is ‘All of the above’.
Note: Like the Cilia and Flagella, Centrioles are also made of microtubules. The basic difference is that they contain 9 sets of triplets and no doublet in the center. Centrioles come in pairs and each of them is organized at right angles to the other.
Complete answer:
The cilia and flagella arise from the basal body. Another name of the basal body is basal granule, kinetosome, and in older cytological literature it is also known as blepharoplast. The basal body is a protein structure found at the base of a eukaryotic cilium or flagellum. The basal body serves as a site for the growth of the axoneme microtubules.
Additional Information: Cilia and flagella are the projections that come out from the cell. They're made from microtubules and are covered by an extension of the cell wall. they're motile and designed either to move the cell itself or to move substances over or around the cell. The first purpose of cilia in mammalian cells is to move fluid, mucous, or cells over their surface. Cilia and flagella have an equivalent internal structure. The main difference is in their length. Cilia and flagella can move just because of the interactions of a set of microtubules inside. These sets of microtubules are called an "axoneme".Two of these microtubules join to form one doublet in the cilia or flagella This is shown in the middle panel. It was seen that one of the tubules is incomplete.
So, the correct answer is ‘All of the above’.
Note: Like the Cilia and Flagella, Centrioles are also made of microtubules. The basic difference is that they contain 9 sets of triplets and no doublet in the center. Centrioles come in pairs and each of them is organized at right angles to the other.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




