
The cisternae that makes up the Golgi Complex are:
A. Rough
B. Polarized
C. Reticulata
D. Both B and C
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint:-To solve this question, we need to understand the structure of the cisternae.
Cisternae are the sacs like flat disc shaped structures that form the major portion of Golgi complex.
Complete step-by-step solution:-Golgi bodies help in the modification of the proteins and lipids by the process of glycosylation.
Golgi body is made up of three parts:
(I) Cisternae:
These are flat disc shaped, sac like structure. Many cisternae are arranged in a stack parallel to each other. The dense opaque material inside the cisternae is called Nodes.
In a Golgi complex, variable numbers of cisternae are present which are concentrically arranged near the nucleus.
Cisternae are polarized i.e. it has two poles:
The convex surface of the cisternae which is towards the nucleus is called cis or forming face while the concave surface of the cisternae which is towards the membrane is called trans or maturing face.
Both the poles, cis and trans faces, of the organelle are entirely different but are interconnected.
They are found in diffused form and are thus reticulated.
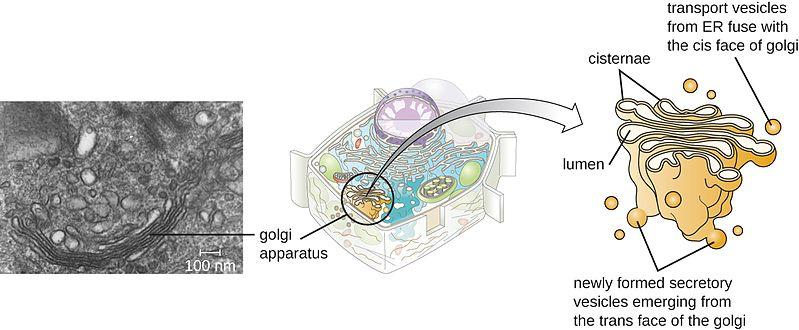
(II) Tubules:
Tubules are the branched and irregular, associated with the cisternae.
(III) Vesicles:
Vesicles help in the transportation of packaged material.
Thus, the correct option is (d) Both B ab C.
Option (a) is incorrect because Cisternae are smooth as there is absence of ribosome on these.
Note:-
Golgi bodies are also known as “the director of macro-molecular traffic in the cell” or “middleman of the cell “ because they perform the function to send the macromolecules in or out of the cell. Their chief function is the secretion of macromolecules and their further modification.
In plant cells, Golgi bodies are known as Dictyosomes.
Cisternae are the sacs like flat disc shaped structures that form the major portion of Golgi complex.
Complete step-by-step solution:-Golgi bodies help in the modification of the proteins and lipids by the process of glycosylation.
Golgi body is made up of three parts:
(I) Cisternae:
These are flat disc shaped, sac like structure. Many cisternae are arranged in a stack parallel to each other. The dense opaque material inside the cisternae is called Nodes.
In a Golgi complex, variable numbers of cisternae are present which are concentrically arranged near the nucleus.
Cisternae are polarized i.e. it has two poles:
The convex surface of the cisternae which is towards the nucleus is called cis or forming face while the concave surface of the cisternae which is towards the membrane is called trans or maturing face.
Both the poles, cis and trans faces, of the organelle are entirely different but are interconnected.
They are found in diffused form and are thus reticulated.

(II) Tubules:
Tubules are the branched and irregular, associated with the cisternae.
(III) Vesicles:
Vesicles help in the transportation of packaged material.
Thus, the correct option is (d) Both B ab C.
Option (a) is incorrect because Cisternae are smooth as there is absence of ribosome on these.
Note:-
Golgi bodies are also known as “the director of macro-molecular traffic in the cell” or “middleman of the cell “ because they perform the function to send the macromolecules in or out of the cell. Their chief function is the secretion of macromolecules and their further modification.
In plant cells, Golgi bodies are known as Dictyosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




