
The compound $\text{ CuCl }$ has a zinc blende structure and the edge length of its unit cell is 500 pm, its density (in $\text{ g c}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}-}}\text{ }$ ) is :
(Given that the atomic weight of $\text{ Cu }$ is $\text{ }63.5\text{ }$ amu and of $\text{ Cl }$ is $\text{ }35.5\text{ }$ amu.)
A) $\text{ }5.24\text{ }$
B) $\text{ }1.14\text{ }$
C) $\text{ }2.99\text{ }$
D) None of the above
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: The density of compound $\text{ CuCl }$ can be calculated by the formula of density in consideration with the cubic lattice. The relation is given as follows:
$\text{ Density = }\dfrac{\text{Mass }\times \text{Z}}{\text{unit cell volume}\times \text{Avogadro }\!\!'\!\!\text{ s No}\text{.}}$
Where , Z is the number of atoms in the crustal structure.
Here, $\text{ CuCl }$ has a zinc blende structure. Thus ,the number of atoms per unit in the $\text{ CuCl }$structure would be equal to the number of units of atoms in the zinc blend structure.
Complete Solution :
We are provided the following data in the problem.
The molar mass of copper chloride $\text{ CuCl }$ is equal to the sum of the molar mass of the copper and chloride.$\text{ Molar mass of CuCl }=\text{ mass of Cu + mass of Cl = 63}\text{.5 + 35}\text{.5 = 99}\text{.0 amu }$
- The edge length ‘a’ of the copper chloride compound is equal to ,
$\text{ a = 500 pm = 500 }\times \text{ 1}{{\text{0}}^{-12}}\text{ m }$
Here ,we wan to determine the density in terms of cm thus ,convert the meters into the cm as ,
$\text{ 1m = 100 cm = 1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{2}}}\text{cm}$
Therefore edge length becomes:
$\text{ a = 500 }\times \text{ 1}{{\text{0}}^{-12}}\text{ m = 500 }\times \text{ 1}{{\text{0}}^{-12}}\times {{10}^{2}}\text{ cm = 500 }\times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-10}}\text{cm }$
- We have to find the Density of the crystal structure.
The density of the crystal structure is related to the edge length .The relation is given as follows:
$\text{ d = }\dfrac{\text{ Z}\times \text{M}}{{{\text{a}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }{{\text{N}}_{\text{A}}}}\text{ }$
Where , d is the density of the crystal structure
Z is the number of atoms per unit structure
M is the molar mass of the compound
‘a’ is the edge length of the crystal structure and
$\text{ }{{\text{N}}_{\text{A}}}\text{ }$ is the avogadro's number .
- We know that the number of units per cell is 4, it means that it has a face-centered cubic (fcc) structure.
Lets substitute the values in the formula of density, then it can be written as:
$\begin{align}
& \text{ d = }\dfrac{\text{ Z}\times \text{M}}{{{\text{a}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }{{\text{N}}_{\text{A}}}}\text{ } \\
& \text{ d = }\dfrac{4\times 99}{{{(500\times {{10}^{-10}})}^{3}}\times 6.02\times {{10}^{23}}} \\
& \text{ d = }\dfrac{396}{75.287}=\text{ 5}\text{.24 g c}{{\text{m}}^{-3}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore , Density of copper chloride is $\text{ 5}\text{.24 g c}{{\text{m}}^{-3}}\text{ }$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: In copper chloride $\text{ CuCl }$structure, the copper is situated at the corners and the center of each face of a cubic structure. The chlorine atoms are placed in between the copper atoms. In copper chloride, the copper and chloride are arranged in ABAB arrangement.It resembles the zinc blend structure.
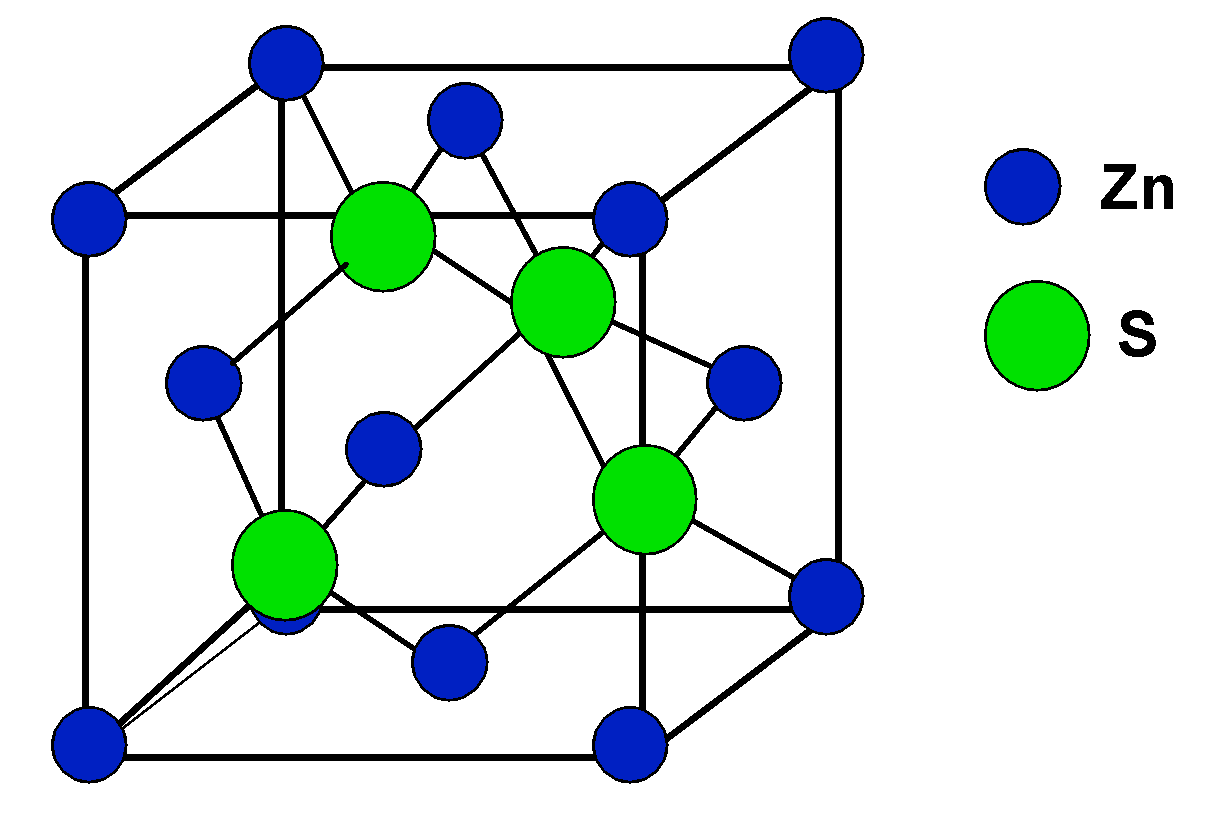
There is no need to get confused by the zinc blende structure, it is just a trick. The structure of the zinc blend $\text{ ZnS }$ is given as follows,
It relates to the fcc structure of the unit cell, and that will help in identifying the value of Z, i.e. the number of units per cell, which is 4.
$\text{ Density = }\dfrac{\text{Mass }\times \text{Z}}{\text{unit cell volume}\times \text{Avogadro }\!\!'\!\!\text{ s No}\text{.}}$
Where , Z is the number of atoms in the crustal structure.
Here, $\text{ CuCl }$ has a zinc blende structure. Thus ,the number of atoms per unit in the $\text{ CuCl }$structure would be equal to the number of units of atoms in the zinc blend structure.
Complete Solution :
We are provided the following data in the problem.
The molar mass of copper chloride $\text{ CuCl }$ is equal to the sum of the molar mass of the copper and chloride.$\text{ Molar mass of CuCl }=\text{ mass of Cu + mass of Cl = 63}\text{.5 + 35}\text{.5 = 99}\text{.0 amu }$
- The edge length ‘a’ of the copper chloride compound is equal to ,
$\text{ a = 500 pm = 500 }\times \text{ 1}{{\text{0}}^{-12}}\text{ m }$
Here ,we wan to determine the density in terms of cm thus ,convert the meters into the cm as ,
$\text{ 1m = 100 cm = 1}{{\text{0}}^{\text{2}}}\text{cm}$
Therefore edge length becomes:
$\text{ a = 500 }\times \text{ 1}{{\text{0}}^{-12}}\text{ m = 500 }\times \text{ 1}{{\text{0}}^{-12}}\times {{10}^{2}}\text{ cm = 500 }\times \text{1}{{\text{0}}^{-10}}\text{cm }$
- We have to find the Density of the crystal structure.
The density of the crystal structure is related to the edge length .The relation is given as follows:
$\text{ d = }\dfrac{\text{ Z}\times \text{M}}{{{\text{a}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }{{\text{N}}_{\text{A}}}}\text{ }$
Where , d is the density of the crystal structure
Z is the number of atoms per unit structure
M is the molar mass of the compound
‘a’ is the edge length of the crystal structure and
$\text{ }{{\text{N}}_{\text{A}}}\text{ }$ is the avogadro's number .
- We know that the number of units per cell is 4, it means that it has a face-centered cubic (fcc) structure.
Lets substitute the values in the formula of density, then it can be written as:
$\begin{align}
& \text{ d = }\dfrac{\text{ Z}\times \text{M}}{{{\text{a}}^{\text{3}}}\text{ }\!\!\times\!\!\text{ }{{\text{N}}_{\text{A}}}}\text{ } \\
& \text{ d = }\dfrac{4\times 99}{{{(500\times {{10}^{-10}})}^{3}}\times 6.02\times {{10}^{23}}} \\
& \text{ d = }\dfrac{396}{75.287}=\text{ 5}\text{.24 g c}{{\text{m}}^{-3}} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore , Density of copper chloride is $\text{ 5}\text{.24 g c}{{\text{m}}^{-3}}\text{ }$
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: In copper chloride $\text{ CuCl }$structure, the copper is situated at the corners and the center of each face of a cubic structure. The chlorine atoms are placed in between the copper atoms. In copper chloride, the copper and chloride are arranged in ABAB arrangement.It resembles the zinc blend structure.

There is no need to get confused by the zinc blende structure, it is just a trick. The structure of the zinc blend $\text{ ZnS }$ is given as follows,
It relates to the fcc structure of the unit cell, and that will help in identifying the value of Z, i.e. the number of units per cell, which is 4.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




