
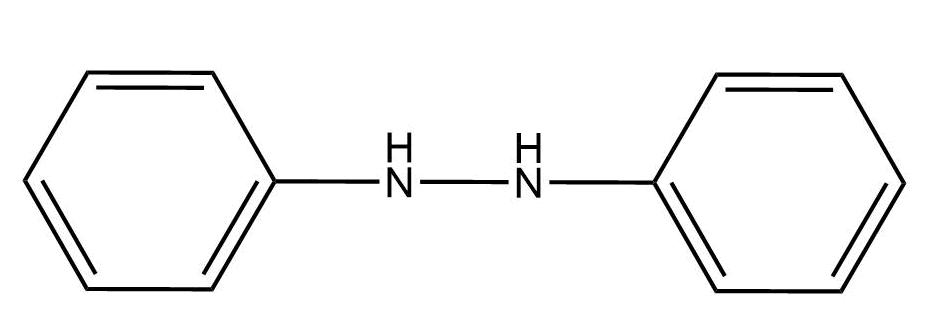
The compound I is:
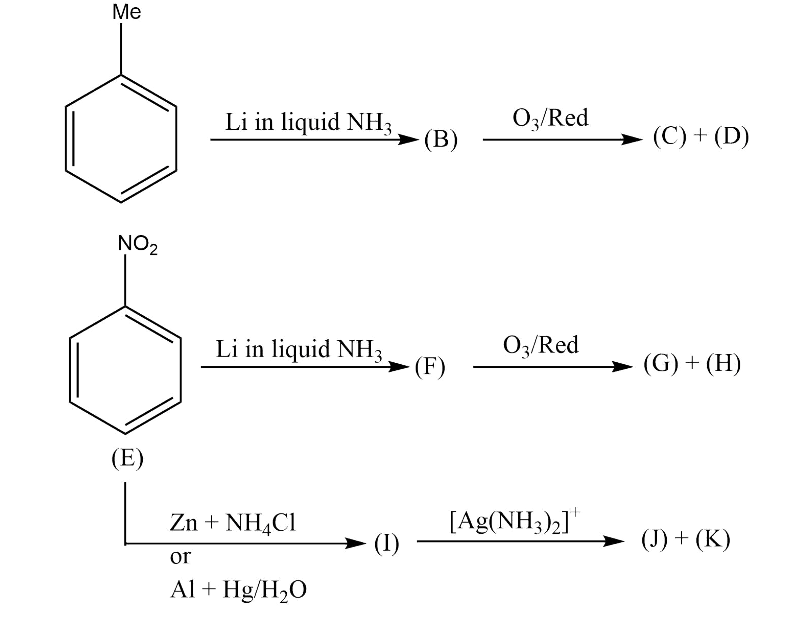
A.
B.
C.
D.





Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: To answer this question you must recall the reactions of nitrobenzene. For the formation of product I, nitrobenzene is treated with zinc in presence of ammonium chloride. Zinc dust in the presence of ammonium chloride acts as a mild reducing agent.
Complete step by step solution:
Zinc in the presence of ammonium chloride reduces a double bonded oxygen group to a hydroxyl group (in this case from nitro to oxime group). The ammonium chloride salt acts as a promoter of the zinc reduction. It serves as an electrolyte and complex forming agent to enable the reduction to occur at ambient temperatures. The zinc molecule acts as an electron pair donor to get converted into its bivalent cation.
The reduction reaction occurring between nitrobenzene and zinc can be written as:
$Ph - N{O_2}\xrightarrow[{}]{{Z{n^{2 + }}}}Ph - N = O\xrightarrow[{}]{{Z{n^{2 + }}}}Ph - NH(OH)$
In the nitro group, nitrogen atom is bonded to two more electronegative oxygen atoms and thus carries a partial positive charge. The zinc atom donates one electron to this electrophilic nitrogen atom and the pi electrons of the nitrogen oxygen double bond move to the oxygen atom.
Now the oxygen atom is carrying a negative charge and it attacks the second molecule of nitrobenzene resulting in the formation of N,N- dihydroxy benzene which undergoes dehydration and forms the intermediate nitrobenzene. Nitrosobenzene further accepts two electrons from zinc dust and results in the formation of N-phenyl hydroxylamine.
Hence, the correct answer is A.
Note: Under mildly acidic conditions, the reaction stops at the formation of N- phenyl hydroxylamine. But when the reaction with zinc dust is carried out under acidic conditions, aniline is obtained as the product.
Complete step by step solution:
Zinc in the presence of ammonium chloride reduces a double bonded oxygen group to a hydroxyl group (in this case from nitro to oxime group). The ammonium chloride salt acts as a promoter of the zinc reduction. It serves as an electrolyte and complex forming agent to enable the reduction to occur at ambient temperatures. The zinc molecule acts as an electron pair donor to get converted into its bivalent cation.
The reduction reaction occurring between nitrobenzene and zinc can be written as:
$Ph - N{O_2}\xrightarrow[{}]{{Z{n^{2 + }}}}Ph - N = O\xrightarrow[{}]{{Z{n^{2 + }}}}Ph - NH(OH)$
In the nitro group, nitrogen atom is bonded to two more electronegative oxygen atoms and thus carries a partial positive charge. The zinc atom donates one electron to this electrophilic nitrogen atom and the pi electrons of the nitrogen oxygen double bond move to the oxygen atom.
Now the oxygen atom is carrying a negative charge and it attacks the second molecule of nitrobenzene resulting in the formation of N,N- dihydroxy benzene which undergoes dehydration and forms the intermediate nitrobenzene. Nitrosobenzene further accepts two electrons from zinc dust and results in the formation of N-phenyl hydroxylamine.
Hence, the correct answer is A.
Note: Under mildly acidic conditions, the reaction stops at the formation of N- phenyl hydroxylamine. But when the reaction with zinc dust is carried out under acidic conditions, aniline is obtained as the product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




