
The compounds 1-butyne and 2-butyne can be distinguished by using:
A.Bromine water
B.${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ solution
C.Tollen’s reagent
D.Chlorine gas
Answer
520.8k+ views
Hint: The hydrogen atoms that are attached to the triply bonded carbon are weakly acidic in nature and hence they can form acetylides with heavy metallic salts.
Complete step by step answer:
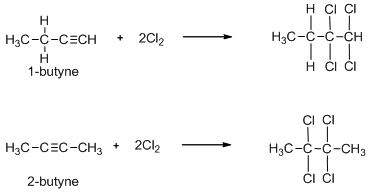
The two given alkynes are 1-butyne and 2-butyne. Their structures are shown below:
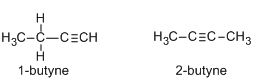
Due to the presence of two pi-bonds, alkynes can undergo a number of additional reactions in which alkynes can add two molecules of a reagent unlike alkenes which can add only one reagent molecule due to the presence of only one pi-bond.
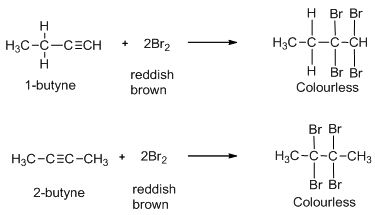
First, let us consider the reaction of both the alkynes with bromine water. Bromine water solution is a deep reddish brown colored solution. When bromine solution is added dropwise to an alkyne, the reddish brown colour disappears because the product is colourless. Thus, both 1-butyne and 2-butyne decolourise bromine water solution. Hence, bromine water tests cannot be used to distinguish between them. So, the option (A) is incorrect.
Now, let us consider the reaction of both the alkynes with ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ solution. Under neutral conditions, alkynes react with dilute ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ solution to give diketones. On the other hand, with basic ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ solution at high temperature, any alkyne will undergo oxidative cleavage. Thus, both 1-butyne and 2-butyne reacts with ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ solution and so it cannot be used to distinguish between them. So, the option (B) is incorrect.
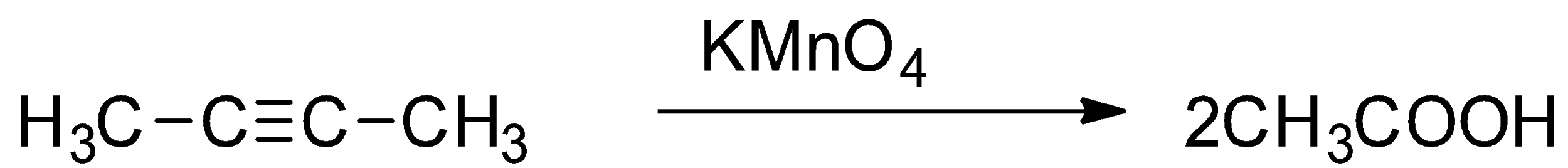
Now, consider the reaction with Tollen’s reagent. Tollen’s reagent is a chemical reagent which consists of a solution of silver nitrate, ammonia and some sodium hydroxide. Due to the acidic nature of the hydrogen atoms attached to the triply bonded carbon, terminal alkynes react with heavy metallic salts like silver nitrate. Since 1-butyne is a terminal alkyne, it will react with Tollen’s reagent while 2-butyne will not react as it is an internal alkyne.

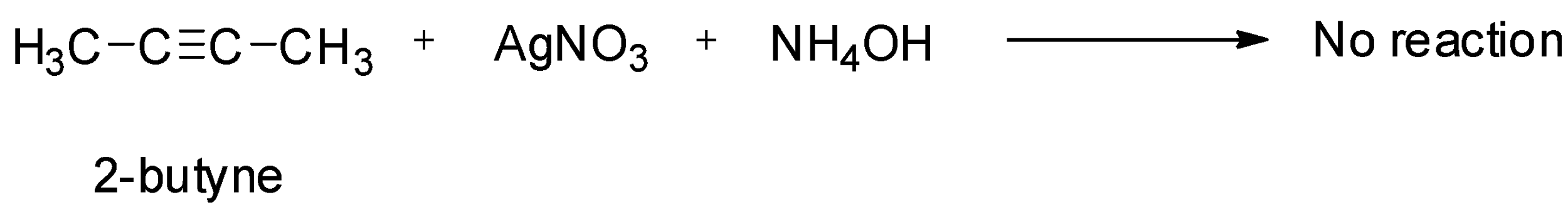
So, this test can be used to distinguish between them. So, the option (C) is correct.
Lastly, both 1-butyne and 2-butyne will undergo an addition reaction with chlorine. So, option (D) is also incorrect.
Hence option C is correct.
Note:
Alkynes having a terminal carbon-carbon triple bond when treated with ammoniacal solution of ${\text{AgN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ , forms a white precipitate of silver acetylide.
Complete step by step answer:
The two given alkynes are 1-butyne and 2-butyne. Their structures are shown below:

Due to the presence of two pi-bonds, alkynes can undergo a number of additional reactions in which alkynes can add two molecules of a reagent unlike alkenes which can add only one reagent molecule due to the presence of only one pi-bond.
First, let us consider the reaction of both the alkynes with bromine water. Bromine water solution is a deep reddish brown colored solution. When bromine solution is added dropwise to an alkyne, the reddish brown colour disappears because the product is colourless. Thus, both 1-butyne and 2-butyne decolourise bromine water solution. Hence, bromine water tests cannot be used to distinguish between them. So, the option (A) is incorrect.

Now, let us consider the reaction of both the alkynes with ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ solution. Under neutral conditions, alkynes react with dilute ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ solution to give diketones. On the other hand, with basic ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ solution at high temperature, any alkyne will undergo oxidative cleavage. Thus, both 1-butyne and 2-butyne reacts with ${\text{KMn}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ solution and so it cannot be used to distinguish between them. So, the option (B) is incorrect.
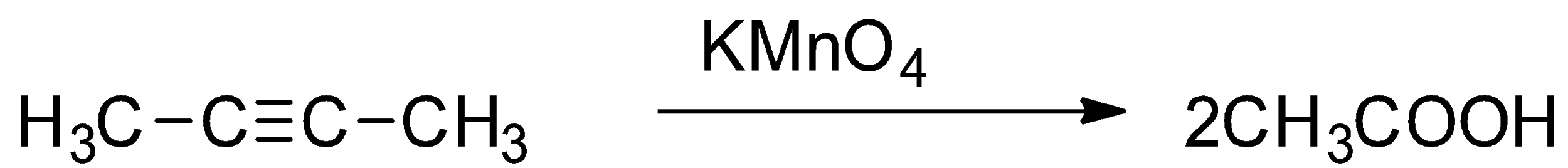
Now, consider the reaction with Tollen’s reagent. Tollen’s reagent is a chemical reagent which consists of a solution of silver nitrate, ammonia and some sodium hydroxide. Due to the acidic nature of the hydrogen atoms attached to the triply bonded carbon, terminal alkynes react with heavy metallic salts like silver nitrate. Since 1-butyne is a terminal alkyne, it will react with Tollen’s reagent while 2-butyne will not react as it is an internal alkyne.

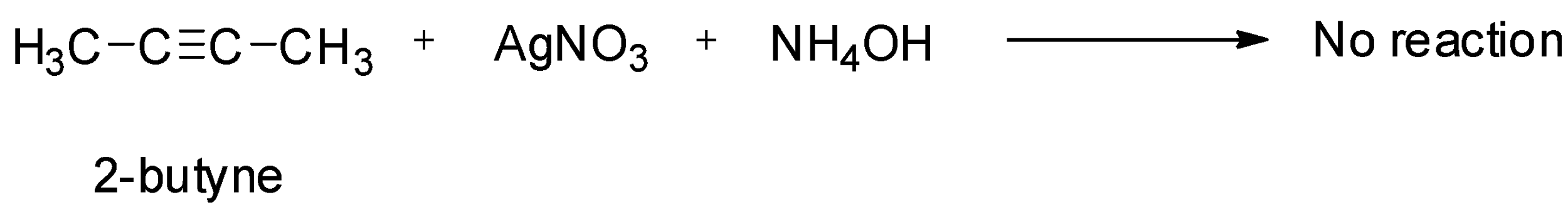
So, this test can be used to distinguish between them. So, the option (C) is correct.
Lastly, both 1-butyne and 2-butyne will undergo an addition reaction with chlorine. So, option (D) is also incorrect.

Hence option C is correct.
Note:
Alkynes having a terminal carbon-carbon triple bond when treated with ammoniacal solution of ${\text{AgN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}$ , forms a white precipitate of silver acetylide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




