
The continuity of protoplasm from cell to cell is maintained through
A. Stomata
B. Tracheid
C. Vessels
D. Plasmodesmata
Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: Protoplasm, together cytoplasm and cell nucleus of a cell. Protoplasm is the living component of a cell-bound by a cellular membrane. This is a jelly-like, colorless, transparent, and viscous living substance present inside the cell wall.
Complete answer:
Plasmodesmata are narrow channels that link up the cytoplasm of neighboring plant cells to one another, providing living bridges among cells. Similar to the gap junctions present in animal cells, plasmodesmata, which enter both the primary and secondary cell walls, allow various molecules to move freely from one cell to the other and are essential for intercellular communication. Plasmodesmata are organized in a wholly distinct configuration than the animal cell gap junction due to a thick cell wall. Attributed to the existence of plasmodesmata, plant cells can be considered to constitute a syncytium or multinucleate mass with cytoplasmic continuity. Plasmodesmata are equipped with a plasma membrane such that all the cells associated are bound by basically one continuous cellular membrane. Most plasmodesmata often include a narrow tube-like structure called a desmotubule, which is derived from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of the cells attached.
So, the correct answer is option (D).
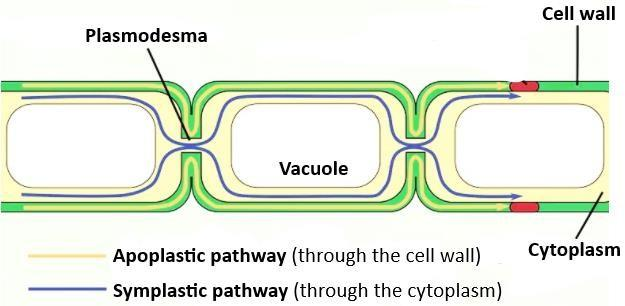
Additional information:
Stomata seem to be the small holes on the epidermis of the leaves. This is a pore located in the leaf epidermis, roots, as well as other organs that govern the rate of exchange of gas. The pore is encircled by a pair of developed parenchymal cells known as guard cells, that are otherwise responsible for managing the size of the stomatal opening. Tracheid is a basic element of xylem containing a single elongated cell with pointed ends and a supplementary, cellulose wall thickened with lignin-containing various pits however without perforation in the primary cell wall. Vessels are trachea elements of xylem, found often in angiosperms. They're also termed tracheae. Each vessel is a non-living portion of xylene and consists of a canal like a set of cells arranged from the end to end, the walls of those are absent due to dissolution.
Note: It is generally assumed that by limiting and dilating the openings at the endpoints of plasmodesmata, plant cells control the movement of small molecules, like sugars, salts, amino acids, while this mechanism is not very well known. It is acknowledged, however, that in certain cases the size constraints on the motion of molecules between cells can be resolved. By attaching to parts of the plasmodesmata, unique proteins and also some viruses are capable of increasing the diameter of the streams enough for large molecules to pass through.
Complete answer:
Plasmodesmata are narrow channels that link up the cytoplasm of neighboring plant cells to one another, providing living bridges among cells. Similar to the gap junctions present in animal cells, plasmodesmata, which enter both the primary and secondary cell walls, allow various molecules to move freely from one cell to the other and are essential for intercellular communication. Plasmodesmata are organized in a wholly distinct configuration than the animal cell gap junction due to a thick cell wall. Attributed to the existence of plasmodesmata, plant cells can be considered to constitute a syncytium or multinucleate mass with cytoplasmic continuity. Plasmodesmata are equipped with a plasma membrane such that all the cells associated are bound by basically one continuous cellular membrane. Most plasmodesmata often include a narrow tube-like structure called a desmotubule, which is derived from the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of the cells attached.
So, the correct answer is option (D).

Additional information:
Stomata seem to be the small holes on the epidermis of the leaves. This is a pore located in the leaf epidermis, roots, as well as other organs that govern the rate of exchange of gas. The pore is encircled by a pair of developed parenchymal cells known as guard cells, that are otherwise responsible for managing the size of the stomatal opening. Tracheid is a basic element of xylem containing a single elongated cell with pointed ends and a supplementary, cellulose wall thickened with lignin-containing various pits however without perforation in the primary cell wall. Vessels are trachea elements of xylem, found often in angiosperms. They're also termed tracheae. Each vessel is a non-living portion of xylene and consists of a canal like a set of cells arranged from the end to end, the walls of those are absent due to dissolution.
Note: It is generally assumed that by limiting and dilating the openings at the endpoints of plasmodesmata, plant cells control the movement of small molecules, like sugars, salts, amino acids, while this mechanism is not very well known. It is acknowledged, however, that in certain cases the size constraints on the motion of molecules between cells can be resolved. By attaching to parts of the plasmodesmata, unique proteins and also some viruses are capable of increasing the diameter of the streams enough for large molecules to pass through.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




