
The copolymer formed by addition polymerization of styrene and acrylonitrile in the presence of peroxide is:
A.
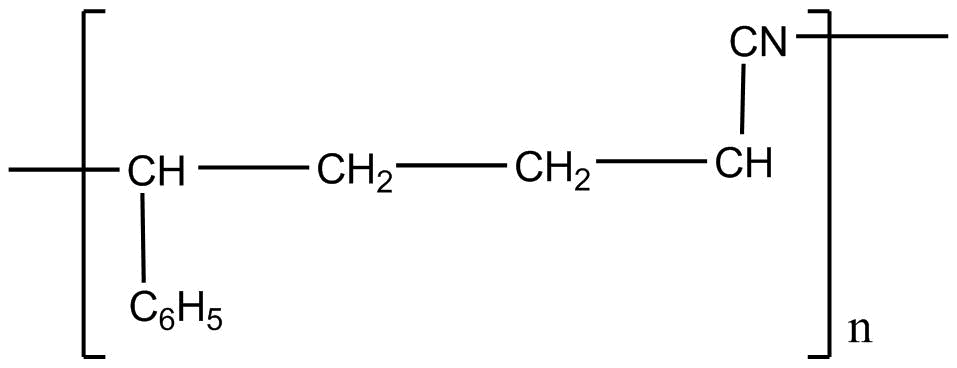
B.
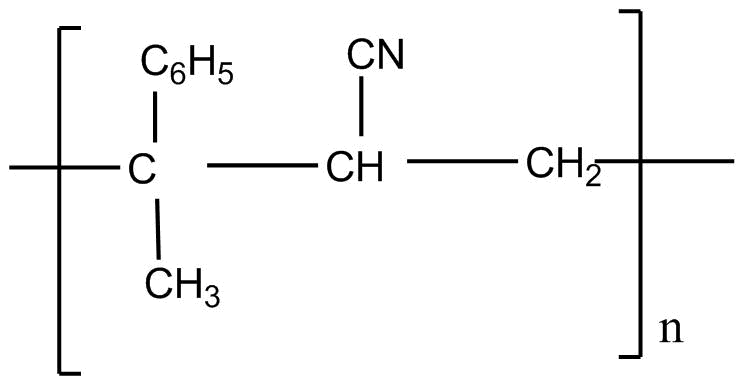
C.
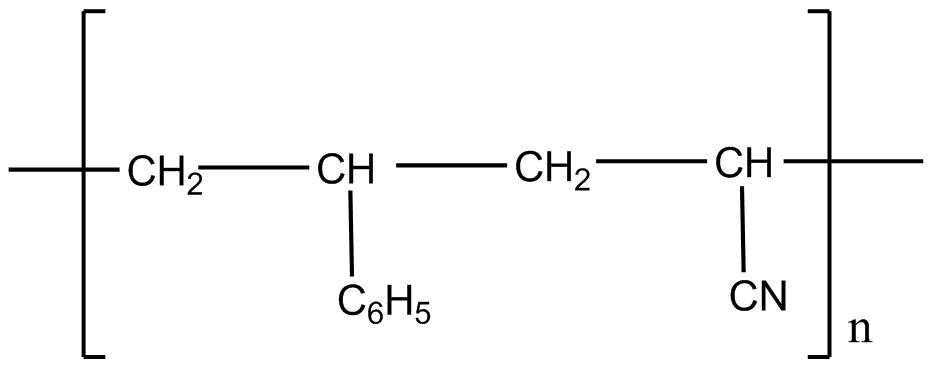
D.
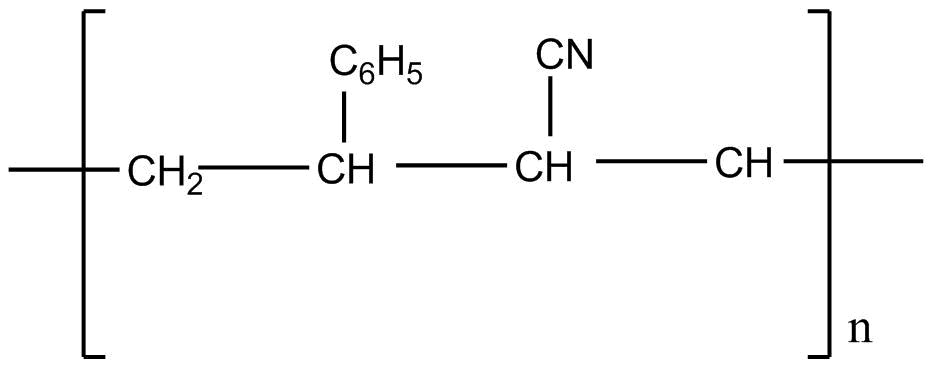




Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Addition polymerization results in forming simple links between the monomers without co-generation of other products. It also doesn’t result in formation of products such as water. Basically it creates a chain between monomers so it is also known as chain polymerization.
Complete step by step solution:
So we need to know the basic purpose of additional polymerization. Additional polymerization results in a form of link. It just adds a linkage between the monomers and doesn’t result in formation of other products during its process.
Styrene formula is \[C _6H_5CH = CH_2\]
Acrylonitrile formula is \[CH_2 = CH - CN\]
If we apply addition polymerization in presence of peroxide the following result will come:
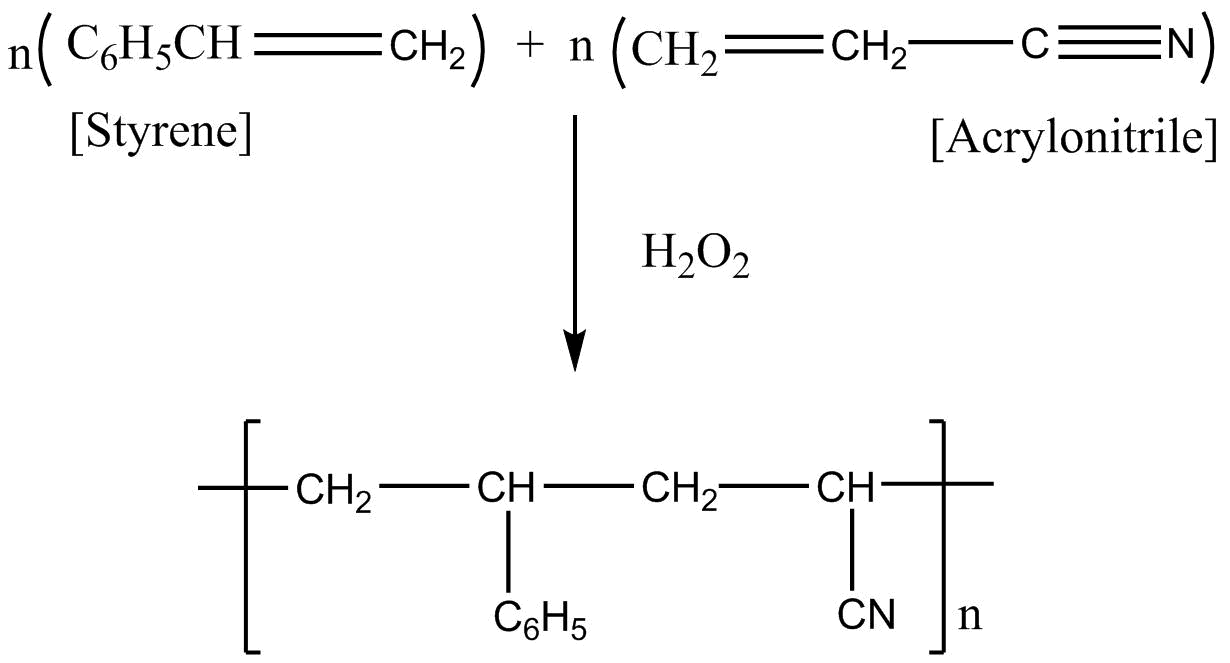
So considering all the given explanations, option C is correct.
So, the correct answer is option C.
Additional Information:
Copolymer is polymer derived from more than one kind of monomer. Styrene and acrylonitrile are the commercial copolymers. There can be types of copolymers such as linear copolymers which consist of a single main chain and include alternate, statistical and block copolymers. Second branched copolymers which consist of a single main chain with one or more polymeric side chains and look like star shaped.
Polymers are chains with an unspecified number of monomeric units. However monomers are which have capacity to form chemical bonds at least to two other monomer blocks. Types of monomer are sugars, amino acids, fatty acids and nucleotides
Additional polymers are formed by addition of simple monomers again and again. Basically it includes three steps which are initiation, chain propagation and termination of chain. So if we see these three steps as:
Chain initiation – It means it requires an initiator to start the polymerization process. It can be anion, cation, radical or metallic molecule.
Chain propagation – Monomers adds to the chain and each new monomer creates an active side for the next attachment.
Chain termination – The radical, cation or anion molecule got neutralized and stopped the chain propagation.
Note: The addition polymerization which is also known as chain polymerization describes that it only adds chains to monomers and no other product is released during the process. Copolymer also states that it is addition of different or same monomers to make a link or chain between them.
Complete step by step solution:
So we need to know the basic purpose of additional polymerization. Additional polymerization results in a form of link. It just adds a linkage between the monomers and doesn’t result in formation of other products during its process.
Styrene formula is \[C _6H_5CH = CH_2\]
Acrylonitrile formula is \[CH_2 = CH - CN\]
If we apply addition polymerization in presence of peroxide the following result will come:

So considering all the given explanations, option C is correct.
So, the correct answer is option C.
Additional Information:
Copolymer is polymer derived from more than one kind of monomer. Styrene and acrylonitrile are the commercial copolymers. There can be types of copolymers such as linear copolymers which consist of a single main chain and include alternate, statistical and block copolymers. Second branched copolymers which consist of a single main chain with one or more polymeric side chains and look like star shaped.
Polymers are chains with an unspecified number of monomeric units. However monomers are which have capacity to form chemical bonds at least to two other monomer blocks. Types of monomer are sugars, amino acids, fatty acids and nucleotides
Additional polymers are formed by addition of simple monomers again and again. Basically it includes three steps which are initiation, chain propagation and termination of chain. So if we see these three steps as:
Chain initiation – It means it requires an initiator to start the polymerization process. It can be anion, cation, radical or metallic molecule.
Chain propagation – Monomers adds to the chain and each new monomer creates an active side for the next attachment.
Chain termination – The radical, cation or anion molecule got neutralized and stopped the chain propagation.
Note: The addition polymerization which is also known as chain polymerization describes that it only adds chains to monomers and no other product is released during the process. Copolymer also states that it is addition of different or same monomers to make a link or chain between them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




