
The correct decreasing order of their reactivity towards hydrolysis is:
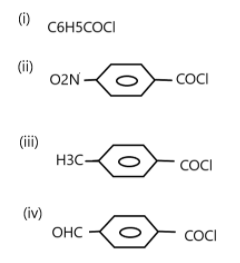
A. (ii)> (iv)> (i)> (iii)
B. (ii)> (iv)> (iii)> (i)
C. (i)> (ii)> (iii)> (iv)
D. (iv)> (ii)> (i)> (iii)

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Here, you need to know about electron withdrawing groups and electron releasing groups. Also about hydrolysis and Nucleophilic reaction. Hydrolysis is a process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrolysis is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water ruptures one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination and solvation reactions in water in the nucleophile. In simple words, it is a process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. In such reactions, one fragment of the target molecule gains a hydrogen ion which breaks a chemical bond in the compound.
Now, we need to see which compound will react most and which one will react least. Hydrolysis of carbonyl carbon is nucleophilic addition reaction. For that \[ - {C^ + }\] carbocation has to be formed. Nucleophilic addition reaction is where a chemical compound with an electrophile double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile such that the bond is broken. This reaction is considered very important as they enable the conversion of carbonyl groups into a variety of functional groups.The more easily carbocation is formed, the more reactive the compound is towards hydrolysis.
Now, \[N{O_2}\] and \[ - CHO\] are two electron withdrawing groups which favour the formation of a carbocation. \[N{O_2}\] is deactivated more than the\[ - CHO\] group hence (ii) is more reactive than (iv).
\[C{H_3}\] is an electron releasing group and hence favours less for the formation of carbonation and the first compound has no EWG or ERG (electron withdrawing and electron donating group) present, so, (i) is more reactive than (iii).
Hence the decreasing order is (ii)> (iv)> (i)> (iii), i.e. option A.
Note:
Knowing the properties of every different EWG and ERG is difficult but having knowledge is important. These types of questions can be solved by the information regarding these groups.
Complete step by step answer:
Hydrolysis is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water ruptures one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination and solvation reactions in water in the nucleophile. In simple words, it is a process in which a molecule of water is added to a substance. Sometimes this causes both the substance and water molecule to split into two parts. In such reactions, one fragment of the target molecule gains a hydrogen ion which breaks a chemical bond in the compound.
Now, we need to see which compound will react most and which one will react least. Hydrolysis of carbonyl carbon is nucleophilic addition reaction. For that \[ - {C^ + }\] carbocation has to be formed. Nucleophilic addition reaction is where a chemical compound with an electrophile double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile such that the bond is broken. This reaction is considered very important as they enable the conversion of carbonyl groups into a variety of functional groups.The more easily carbocation is formed, the more reactive the compound is towards hydrolysis.
Now, \[N{O_2}\] and \[ - CHO\] are two electron withdrawing groups which favour the formation of a carbocation. \[N{O_2}\] is deactivated more than the\[ - CHO\] group hence (ii) is more reactive than (iv).
\[C{H_3}\] is an electron releasing group and hence favours less for the formation of carbonation and the first compound has no EWG or ERG (electron withdrawing and electron donating group) present, so, (i) is more reactive than (iii).
Hence the decreasing order is (ii)> (iv)> (i)> (iii), i.e. option A.
Note:
Knowing the properties of every different EWG and ERG is difficult but having knowledge is important. These types of questions can be solved by the information regarding these groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




