
The correct sequence of organelles in which glycolate and glyoxylate are produced sequentially in photorespiration is
A. Chloroplast and mitochondria
B. Chloroplast and peroxisome
C. Peroxisome and mitochondria
D. Peroxisome and chloroplast
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Photorespiration involves the movement of metabolites among chloroplasts, peroxisomes, and mitochondria in a metabolic pathway.
Complete answer: Photorespiration is an exceptional biochemical pathway.
1. Rubisco fixes molecular oxygen ($O_2$) instead of executing its intrinsic function in photosynthesis, fixation of carbon dioxide ($CO_2$), and its uptake results in the formation of two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA) that is used for biosynthetic reactions and the recycling of the acceptor molecule RuBP.
2. During $O_2$ fixation, one molecule of 3-PGA and one molecule of 2-phosphoglycolate (2-PG) are formed. The latter cannot be used by plants for biosynthetic reactions and it is a potent inhibitor of chloroplastic function.
3. Moreover, plants tend to close stomata to reduce transpiratory losses. The remaining level of $CO_2$ inside the leaf is rapidly decreased and $O_2$ is available in excess, resulting in high rates of RuBP oxygenation. The photorespiratory pathway evolved to make the best of this problematic situation. Its function is to convert 2-PG synthesized by the oxygenase activity of Rubisco back to 3-PGA recovering 75% of the carbon. It is seemingly difficult biochemically to synthesize a C3 compound or a C6 compound from a C2 compound such as 2-PG.
4. Thus, photorespiration is made up of a complex series of reactions taking place mainly in the chloroplast, the peroxisome, and the mitochondrion. 2-PG is dephosphorylated to glycolate in the chloroplast and transported to the peroxisome where it is oxidized to glyoxylate.
5. $O_2$ is the electron donor in this reaction and the resulting hydrogen peroxide (${H_2}{O_2}$) is detoxified by a peroxisomal catalase. Glyoxylate is transaminated to Gly that is transported to the mitochondrion.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: 1. In a composite biochemical reaction, two molecules of Gly are converted to one molecule of Ser, the first C3 compound in the pathway, and the remaining carbon and nitrogen are released as $CO_2$ and ammonia (NH3), respectively.
2. This reaction is the reason for the negative reputation of photorespiration as a wasteful pathway because molecules are released that had been fixed before in energy-consuming reactions.
This may limit plant biomass production dependent on the degree of RuBP oxygenation.
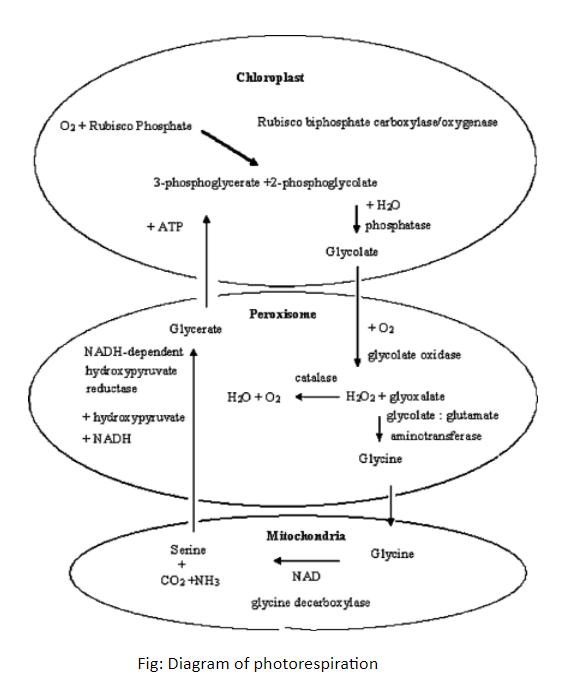
3. The Serine molecule resulting from this reaction is transported back to the peroxisome.
The amine group is used to form a new Gly molecule from glyoxylate and the resulting hydroxypyruvate is reduced to glycerate. Finally, glycerate is phosphorylated in the chloroplast to form 3-PGA, which can be fed back to the Calvin cycle.
Complete answer: Photorespiration is an exceptional biochemical pathway.
1. Rubisco fixes molecular oxygen ($O_2$) instead of executing its intrinsic function in photosynthesis, fixation of carbon dioxide ($CO_2$), and its uptake results in the formation of two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA) that is used for biosynthetic reactions and the recycling of the acceptor molecule RuBP.
2. During $O_2$ fixation, one molecule of 3-PGA and one molecule of 2-phosphoglycolate (2-PG) are formed. The latter cannot be used by plants for biosynthetic reactions and it is a potent inhibitor of chloroplastic function.
3. Moreover, plants tend to close stomata to reduce transpiratory losses. The remaining level of $CO_2$ inside the leaf is rapidly decreased and $O_2$ is available in excess, resulting in high rates of RuBP oxygenation. The photorespiratory pathway evolved to make the best of this problematic situation. Its function is to convert 2-PG synthesized by the oxygenase activity of Rubisco back to 3-PGA recovering 75% of the carbon. It is seemingly difficult biochemically to synthesize a C3 compound or a C6 compound from a C2 compound such as 2-PG.
4. Thus, photorespiration is made up of a complex series of reactions taking place mainly in the chloroplast, the peroxisome, and the mitochondrion. 2-PG is dephosphorylated to glycolate in the chloroplast and transported to the peroxisome where it is oxidized to glyoxylate.
5. $O_2$ is the electron donor in this reaction and the resulting hydrogen peroxide (${H_2}{O_2}$) is detoxified by a peroxisomal catalase. Glyoxylate is transaminated to Gly that is transported to the mitochondrion.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: 1. In a composite biochemical reaction, two molecules of Gly are converted to one molecule of Ser, the first C3 compound in the pathway, and the remaining carbon and nitrogen are released as $CO_2$ and ammonia (NH3), respectively.
2. This reaction is the reason for the negative reputation of photorespiration as a wasteful pathway because molecules are released that had been fixed before in energy-consuming reactions.
This may limit plant biomass production dependent on the degree of RuBP oxygenation.

3. The Serine molecule resulting from this reaction is transported back to the peroxisome.
The amine group is used to form a new Gly molecule from glyoxylate and the resulting hydroxypyruvate is reduced to glycerate. Finally, glycerate is phosphorylated in the chloroplast to form 3-PGA, which can be fed back to the Calvin cycle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




