
The cyclotrimetaphosphoric acid is:
(A) \[{\left( {HP{O_3}} \right)_3}\] and contains total \[9\] bonds.
(B) \[{H_3}{P_3}{O_6}\] and contains total \[12\] bonds.
(C) \[{\left( {HP{O_3}} \right)_3}\] and contains total \[15\] bonds.
(D) \[{H_3}{P_3}{O_9}\] and contains \[18\]σ bonds.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The question indicates that we should know the structure of given acid. It is a cyclic structure that contains the phosphorus and oxygen as the atoms linked in the hexa-cyclic form. It is a non-aromatic inorganic compound which does not have aromaticity as benzene.
Complete Step by step answer: As per the given information, we can count the number of bonds present as the options ask for the number of bonds, even though the number of atoms of hydrogen and phosphorus are same the structure changes as the number of oxygen changes as you can compare and see the structure.
The solution of this question can be concluded if we know the structure of the cyclotrimetaphosphoric acid. The structure is as shown below. The number of bonds is written on the bond and double bond and single bond is also shown in the given figure, single bond is formed between the atoms by sharing electrons in s-orbitals, double bond is formed between the atoms between the atoms by sharing the electrons in p-orbitals. Hydrogen atoms have the tendency to form single bonds, oxygen has the tendency to form double bonds and phosphorus atoms have the tendency to form four bonds. The fifth bond formed between the oxygen and phosphorus is due to electrons occupying an empty orbital in phosphorus atoms.
The structure of cyclotrimetaphosphoric acid is shown below.
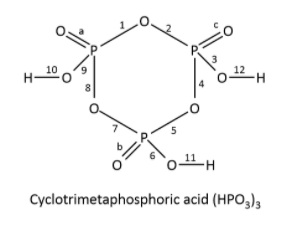
It has a total of 15 bonds.
Hence the correct option is (c).
Note: The number of double bonds in the correct option are 3 and the number of single bonds are 12 hence, in total the number of bonds are 15. The number of bonds should be counted properly by drawing the structure of acid with a hexa-cyclic non-aromatic ring.
Complete Step by step answer: As per the given information, we can count the number of bonds present as the options ask for the number of bonds, even though the number of atoms of hydrogen and phosphorus are same the structure changes as the number of oxygen changes as you can compare and see the structure.
The solution of this question can be concluded if we know the structure of the cyclotrimetaphosphoric acid. The structure is as shown below. The number of bonds is written on the bond and double bond and single bond is also shown in the given figure, single bond is formed between the atoms by sharing electrons in s-orbitals, double bond is formed between the atoms between the atoms by sharing the electrons in p-orbitals. Hydrogen atoms have the tendency to form single bonds, oxygen has the tendency to form double bonds and phosphorus atoms have the tendency to form four bonds. The fifth bond formed between the oxygen and phosphorus is due to electrons occupying an empty orbital in phosphorus atoms.
The structure of cyclotrimetaphosphoric acid is shown below.

It has a total of 15 bonds.
Hence the correct option is (c).
Note: The number of double bonds in the correct option are 3 and the number of single bonds are 12 hence, in total the number of bonds are 15. The number of bonds should be counted properly by drawing the structure of acid with a hexa-cyclic non-aromatic ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




