
The dedifferentiated cells mature to form some specific cells to perform specific functions, this is referred to as:-
(A)Differentiation
(B)Dedifferentiation
(C)Redifferentiation
(D)Development
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: The cell after differentiation, can go ahead only in two ways i.e dedifferentiation and redifferentiation. All the events take place in the same manner as described after the cell is differentiated.
Complete answer:
The dedifferentiated cells mature to form some specific cells to perform specific functions, this is referred to as Redifferentiation. Differentiation occurs many times in the life span of the multicellular organism because it changes from a simple celled zygote to a very complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues even after we have reached our adulthood as adult stem cells divide and make fully differentiated daughter cells when our tissues have to be repaired and through normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure also. It was noticed that even the differentiation also changes the size of the cell, shape of the cell, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals.
Additional Information: Dedifferentiation, which is also known as integration is a cellular process that was seen in additional basal life forms like in some types of worms and amphibians during which a half or terminally differentiated cell reverts to an earlier developmental stage, usually as a part of a regenerative process. Dedifferentiation also occurs in plants. Cells that are present in cell culture can lose the properties which they originally had, like protein expression, or change form. This process is additionally termed dedifferentiation. Some believe dedifferentiation is an aberration of the traditional development cycle that leads to cancer, whereas others believe it to be a natural part of the immune reaction lost by humans which was a result of evolution.
So, the correct answer is ‘Redifferentiation’.
Note: A specialized kind of differentiation, called 'terminal differentiation', is of importance in some tissues, as an example vertebrate nervous system, skeletal muscle, epidermis, and gut. In a terminal differentiation, it was seen that the precursor cell is itself formerly capable of cellular division, it permanently leaves the cell cycle, which disturbs the cell cycle machinery and sometimes expresses a variety of genes characteristic of the cell's final function. Examples include myosin and actin of a muscle cell.
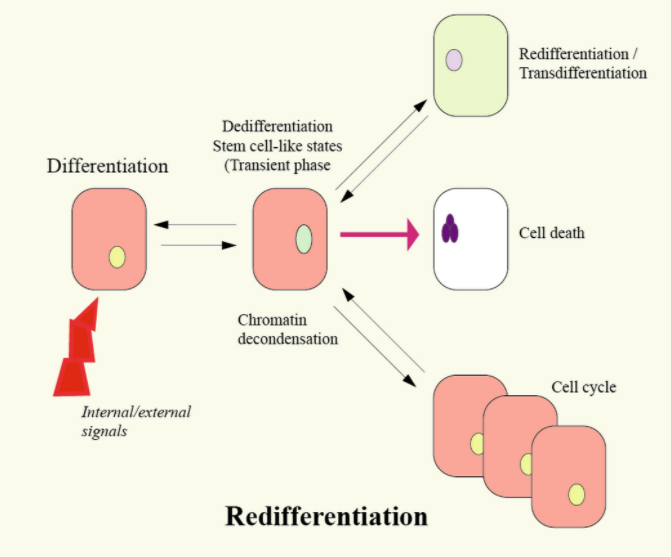
Complete answer:
The dedifferentiated cells mature to form some specific cells to perform specific functions, this is referred to as Redifferentiation. Differentiation occurs many times in the life span of the multicellular organism because it changes from a simple celled zygote to a very complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues even after we have reached our adulthood as adult stem cells divide and make fully differentiated daughter cells when our tissues have to be repaired and through normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure also. It was noticed that even the differentiation also changes the size of the cell, shape of the cell, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals.
Additional Information: Dedifferentiation, which is also known as integration is a cellular process that was seen in additional basal life forms like in some types of worms and amphibians during which a half or terminally differentiated cell reverts to an earlier developmental stage, usually as a part of a regenerative process. Dedifferentiation also occurs in plants. Cells that are present in cell culture can lose the properties which they originally had, like protein expression, or change form. This process is additionally termed dedifferentiation. Some believe dedifferentiation is an aberration of the traditional development cycle that leads to cancer, whereas others believe it to be a natural part of the immune reaction lost by humans which was a result of evolution.
So, the correct answer is ‘Redifferentiation’.
Note: A specialized kind of differentiation, called 'terminal differentiation', is of importance in some tissues, as an example vertebrate nervous system, skeletal muscle, epidermis, and gut. In a terminal differentiation, it was seen that the precursor cell is itself formerly capable of cellular division, it permanently leaves the cell cycle, which disturbs the cell cycle machinery and sometimes expresses a variety of genes characteristic of the cell's final function. Examples include myosin and actin of a muscle cell.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




