
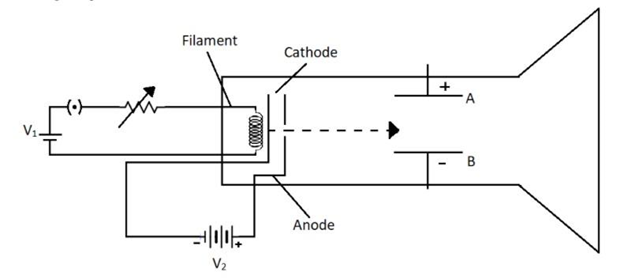
The diagram below shows a cathode ray tube in which the arrow indicates a beam of charged particles approaching an electric field between plates A and B. What will happen to the beam when it passes through the electric field?
A) Will pass undeflected
B) Will deflect towards B
C) Will have circular motion in between A and B
D) Will deflect towards A

Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) were used as a display device in televisions and computer monitors. Cathode Ray Tube are neither used in modern day television sets nor in the modern computer screens. A Cathode Ray Tube has four main parts which are mentioned below:
1. Electron Gun
2. Focussing and Accelerating Anodes
3. Horizontal and Vertical Deflection Plates
4. Evacuated Glass Envelopes
Complete step by step answer:
The Cathode Ray Tube has an electron gun. The function of the electron gun is to emit a ray of negatively charged particles into the evacuated glass tube. As the negatively charged particles also known as electrons strike the end of the tube or the screen they produce a bright spot.
Now, it is clear that the electron gun in the CRT emits a ray of electron. So when this ray will pass through plates A & B. We also know that negatively charged particles or electrons are attracted towards positively charged particles. So, a positively charged plate will attract the electron beam. When the beam will pass through the electric field the beam will be deflected towards the positively charged plate A.
Note: The evacuated glass envelope is also a very important component of a Cathode Ray Tube. Though the Cathode Ray Tubes are not used in modern day equipment, however it is necessary to know that the CRTs were not completely evacuated instead the tubes were evacuated to a low pressure since complete evacuation was hard to achieve. This evacuation was necessary for avoiding any kind of obstruction to the electron beam by air molecules.
1. Electron Gun
2. Focussing and Accelerating Anodes
3. Horizontal and Vertical Deflection Plates
4. Evacuated Glass Envelopes
Complete step by step answer:
The Cathode Ray Tube has an electron gun. The function of the electron gun is to emit a ray of negatively charged particles into the evacuated glass tube. As the negatively charged particles also known as electrons strike the end of the tube or the screen they produce a bright spot.
Now, it is clear that the electron gun in the CRT emits a ray of electron. So when this ray will pass through plates A & B. We also know that negatively charged particles or electrons are attracted towards positively charged particles. So, a positively charged plate will attract the electron beam. When the beam will pass through the electric field the beam will be deflected towards the positively charged plate A.
Note: The evacuated glass envelope is also a very important component of a Cathode Ray Tube. Though the Cathode Ray Tubes are not used in modern day equipment, however it is necessary to know that the CRTs were not completely evacuated instead the tubes were evacuated to a low pressure since complete evacuation was hard to achieve. This evacuation was necessary for avoiding any kind of obstruction to the electron beam by air molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




