
The diagram of the section of a maize grain is given below. Identify the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
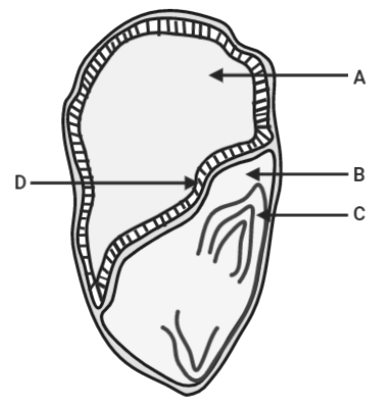
A. A-Endosperm, B-Coleoptile, C-Scutellum, D-Aleurone layer
B. A-Cotyledon, B-Coleoptile, C-Scutellum, D-Epithelium
C. A-Endosperm, B-Coleoptile, C-Scutellum, D-Epithelium
D. A-Endosperm, B-Coleorhiza, C-Scutellum, D-Epithelium

Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Maize is a monocot species, i.e. it belongs to the grass family Poaceae. It is monoecious i.e. both the male and female reproductive parts are present on the same plant. The seeds of these flowering plants have only one cotyledon hence, they are also called monocotyledonous seeds. Most monocot seeds are albuminous.
Complete answer:
Now let us study the various structures found in a maize grain.
• Externally, a maize seed is covered by a seed coat called testa. The testa is fused with the pericarp (fruit wall) and both form a single outermost layer. Internally, the seed is unequally divided into two parts by epithelium.
• The upper big part is the endosperm while the lower small part is the embryo. The starchy endosperm is covered with a proteinous aleurone layer.
• The lower part containing the embryo is opaque and whitish. It contains a single shield shaped papery cotyledon called scutellum.
• The embryonal axis is found within the scutellum. It can be differentiated into an upper plumule and a lower radicle.
• Plumule is the shoot tip and is covered by a protective sheath called coleoptile whereas, radicle is called the root tip and is also enclosed within a protective sheath called coleorhiza.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C), that is A-Endosperm, B-Coleoptile, C-Scutellum, D-Epithelium.
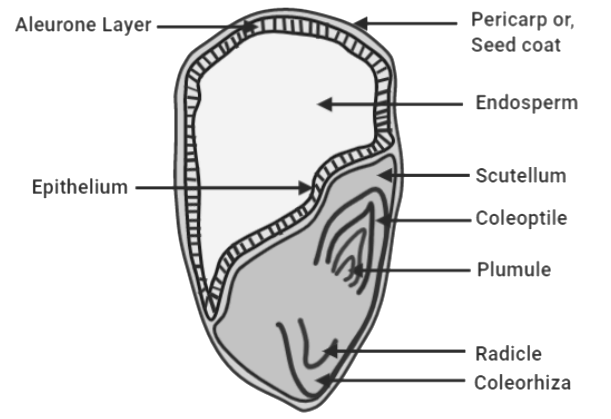
Note: Morphologically, a maize seed appears triangular with one broad end and one tapering end. It is classified as an albuminous or endospermic seed that stores food or starch. The colour of a maize seed is usually yellow, however, some other coloured varieties are also found in nature. A single grain of maize is in fact a fruit. It is called caryopsis and is found on the spadix.
Complete answer:
Now let us study the various structures found in a maize grain.
• Externally, a maize seed is covered by a seed coat called testa. The testa is fused with the pericarp (fruit wall) and both form a single outermost layer. Internally, the seed is unequally divided into two parts by epithelium.
• The upper big part is the endosperm while the lower small part is the embryo. The starchy endosperm is covered with a proteinous aleurone layer.
• The lower part containing the embryo is opaque and whitish. It contains a single shield shaped papery cotyledon called scutellum.
• The embryonal axis is found within the scutellum. It can be differentiated into an upper plumule and a lower radicle.
• Plumule is the shoot tip and is covered by a protective sheath called coleoptile whereas, radicle is called the root tip and is also enclosed within a protective sheath called coleorhiza.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C), that is A-Endosperm, B-Coleoptile, C-Scutellum, D-Epithelium.

Note: Morphologically, a maize seed appears triangular with one broad end and one tapering end. It is classified as an albuminous or endospermic seed that stores food or starch. The colour of a maize seed is usually yellow, however, some other coloured varieties are also found in nature. A single grain of maize is in fact a fruit. It is called caryopsis and is found on the spadix.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




