
The diagram shows a simple circuit.
Which statement is correct?
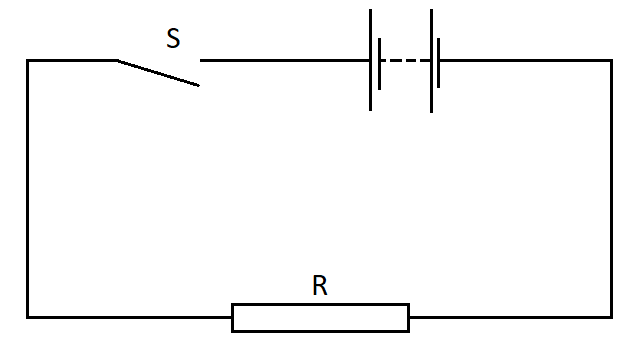
(A) When the switch S is closed, the e.m.f. of the battery falls because work is done against the internal resistance of the battery.
(B) When the switch S is closed, the e.m.f. of the battery falls because work is done against the resistance of .
(C) When the switch S is closed, the potential difference across the battery falls because work is done against the internal resistance of the battery.
(D) When the switch S is closed, the potential difference across the battery falls because work is done against the resistance of .

Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint
The e.m.f of a battery always remains constant and never changes its value. When the current flows in a circuit, then only the potential drop across the battery changes because of the work done by the current flowing across the internal resistance.
Complete step by step answer
The e.m.f or the electromotive force of a cell or a battery is the potential difference between the two electrodes of the battery. It is generally measured in volts. The e.m.f. of any battery remains constant and its value never decreases. It is also defined as the electrode potential when no current is drawn from the cell, which means the cell is in an open circuit.
As the value of e.m.f. never change, so the options A. and B. are not correct.
The potential difference between the terminals of a cell is the difference between the potentials of the two electrodes of the cell when the cell is in a closed circuit or when current is being drawn from the cell. The value of the potential difference is always less than the e.m.f. of the circuit.
When the current flows in a circuit, there is always work done against the internal resistance of the cell or the battery.
So when the circuit is switched on, then the potential difference across the battery falls to do this work against the internal resistance.
Therefore, when the switch S is closed, the potential difference across the battery falls because work is done against the internal resistance of the battery.
So the option C is correct.
Note
Hence we can say that the electromotive force of a circuit is independent of the internal resistance of the circuit. But, the potential difference of the cell changes according to the internal resistance.
The e.m.f of a battery always remains constant and never changes its value. When the current flows in a circuit, then only the potential drop across the battery changes because of the work done by the current flowing across the internal resistance.
Complete step by step answer
The e.m.f or the electromotive force of a cell or a battery is the potential difference between the two electrodes of the battery. It is generally measured in volts. The e.m.f. of any battery remains constant and its value never decreases. It is also defined as the electrode potential when no current is drawn from the cell, which means the cell is in an open circuit.
As the value of e.m.f. never change, so the options A. and B. are not correct.
The potential difference between the terminals of a cell is the difference between the potentials of the two electrodes of the cell when the cell is in a closed circuit or when current is being drawn from the cell. The value of the potential difference is always less than the e.m.f. of the circuit.
When the current flows in a circuit, there is always work done against the internal resistance of the cell or the battery.
So when the circuit is switched on, then the potential difference across the battery falls to do this work against the internal resistance.
Therefore, when the switch S is closed, the potential difference across the battery falls because work is done against the internal resistance of the battery.
So the option C is correct.
Note
Hence we can say that the electromotive force of a circuit is independent of the internal resistance of the circuit. But, the potential difference of the cell changes according to the internal resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




