
The diameter of an aperture of a Plano-convex lens is 6cm and maximum thickness is 3mm. If the velocity in material is $2 \times {10^8}$ m/s, calculate focal length of the lens:
$\left( A \right)$ 10cm
$\left( B \right)$ 20cm
$\left( C \right)$ 15cm
$\left( D \right)$ 30cm
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint – In this question use the concept that that the refractive index ($\mu $) is the ratio of the velocity (C) of light in the air to the velocity of light in the medium that is $\mu = \dfrac{C}{v}$. Then the focal length can be written as $f = \dfrac{R}{{\mu - 1}}$ moreover the radius of curvature of the Plano convex lens is $R = \dfrac{{{r^2}}}{{2t}}$ where r is the radius of aperture of lens and t is the thickness of lens.
Complete step-by-step answer:
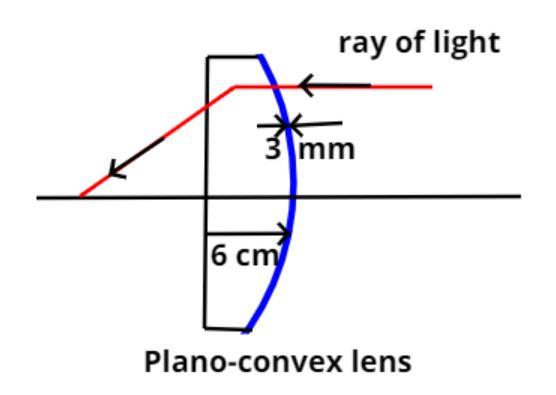
A ray of light passing through the Plano-convex lens is shown above.
It is given that the diameter of aperture of the Plano-convex lens is 6 cm as shown in the figure.
$ \Rightarrow d = 6$cm
Now as we know radius (r) is half of the diameter therefore,
r = (d/2) = (6/2) = 3cm.
Now it is also given that the thickness (t) of the lens is 3 mm as shown in the figure.
$ \Rightarrow t = 3$mm.
As we know 1mm =0.1 cm
Therefore, 3mm = 0.3 cm
$ \Rightarrow t = 0.3$cm
Now it is also given that the velocity (v) of light in material is
$ \Rightarrow v = 2 \times {10^8}$ m/s.
Now as we all know that the refractive index ($\mu $) is the ratio of the velocity (C) of light in the air to the velocity of light in the medium.
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{C}{v}$
Where C = velocity of light in the air = $3 \times {10^8}$m/s.
Now substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{3 \times {{10}^8}}}{{2 \times {{10}^8}}} = \dfrac{3}{2} = 1.5$
So the refractive index of the lens is 1.5.
Now as we know that the focal length of the lens is given as
$ \Rightarrow f = \dfrac{R}{{\mu - 1}}$............. (1)
Where, f = focal length of the lens and R = radius of the curvature of the lens.
So first find out the radius of curvature (R) of the lens.
Now radius of curvature (R) of the Plano-convex lens is given as
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{{r^2}}}{{2t}}$
Where, r = radius of the aperture of the lens and t = thickness of the lens.
Now substitute the values in above equation we have,
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{{3^2}}}{{2\left( {0.3} \right)}} = \dfrac{9}{{0.6}} = 15$cm.
Now substitute the values in equation (1) we have,
$ \Rightarrow f = \dfrac{{15}}{{1.5 - 1}} = \dfrac{{15}}{{0.5}} = 30$cm.
So the focal length of the lens is 30 cm.
Hence option (D) is the correct answer.
Note – As the name suggests Plano convex, this depicts that the lens will have a plane shape or a flat surface on one side and will be a convex lens on the other side. Generally the focal length has positive values for a Plano convex lens. The speed of light in the air medium is constant that is $3 \times {10^8}$m/s and it needs to be remembered. The application of Plano convex lenses is simply for the infinite conjugate, that is the light beams coming from infinity and which are parallel to each other.
Complete step-by-step answer:

A ray of light passing through the Plano-convex lens is shown above.
It is given that the diameter of aperture of the Plano-convex lens is 6 cm as shown in the figure.
$ \Rightarrow d = 6$cm
Now as we know radius (r) is half of the diameter therefore,
r = (d/2) = (6/2) = 3cm.
Now it is also given that the thickness (t) of the lens is 3 mm as shown in the figure.
$ \Rightarrow t = 3$mm.
As we know 1mm =0.1 cm
Therefore, 3mm = 0.3 cm
$ \Rightarrow t = 0.3$cm
Now it is also given that the velocity (v) of light in material is
$ \Rightarrow v = 2 \times {10^8}$ m/s.
Now as we all know that the refractive index ($\mu $) is the ratio of the velocity (C) of light in the air to the velocity of light in the medium.
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{C}{v}$
Where C = velocity of light in the air = $3 \times {10^8}$m/s.
Now substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{3 \times {{10}^8}}}{{2 \times {{10}^8}}} = \dfrac{3}{2} = 1.5$
So the refractive index of the lens is 1.5.
Now as we know that the focal length of the lens is given as
$ \Rightarrow f = \dfrac{R}{{\mu - 1}}$............. (1)
Where, f = focal length of the lens and R = radius of the curvature of the lens.
So first find out the radius of curvature (R) of the lens.
Now radius of curvature (R) of the Plano-convex lens is given as
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{{r^2}}}{{2t}}$
Where, r = radius of the aperture of the lens and t = thickness of the lens.
Now substitute the values in above equation we have,
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{{3^2}}}{{2\left( {0.3} \right)}} = \dfrac{9}{{0.6}} = 15$cm.
Now substitute the values in equation (1) we have,
$ \Rightarrow f = \dfrac{{15}}{{1.5 - 1}} = \dfrac{{15}}{{0.5}} = 30$cm.
So the focal length of the lens is 30 cm.
Hence option (D) is the correct answer.
Note – As the name suggests Plano convex, this depicts that the lens will have a plane shape or a flat surface on one side and will be a convex lens on the other side. Generally the focal length has positive values for a Plano convex lens. The speed of light in the air medium is constant that is $3 \times {10^8}$m/s and it needs to be remembered. The application of Plano convex lenses is simply for the infinite conjugate, that is the light beams coming from infinity and which are parallel to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




