
The diameter of the aperture of a Plano-convex lens is $ 6cm $ and its maximum thickness is $ 3mm $ . If the velocity of light in the material of the lens is $ 2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s $ , its focal length is (approximately)
(A) $ 10cm $
(B) $ 15cm $
(C) $ 30cm $
(D) $ 60cm $
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint
In the given questions, we have to calculate the focal length of a Plano-convex lens; we have been provided with the diameter of the aperture of the lens and the thickness of the lens. Also provided to us is the speed of light in the lens. We can find the focal length using the radius of curvature of the lens and the refractive index of the lens. The refractive index can be found using the given speed of light in the lens and the radius of curvature can be found using the diameter of the aperture and the thickness of the lens. Let’s dive right into the detailed solution.
$ \Rightarrow R=\dfrac{{{r}^{2}}}{2x} $ , $ \mu =\dfrac{c}{v} $ , $ f=\dfrac{R}{\mu -1} $
Complete step by step answer
A diagrammatic representation of the problem at hand is given below, indicating the diameter of the aperture of the lens, the thickness of the lens and a parallel ray of light that converges with the principal axis at the principal focus.
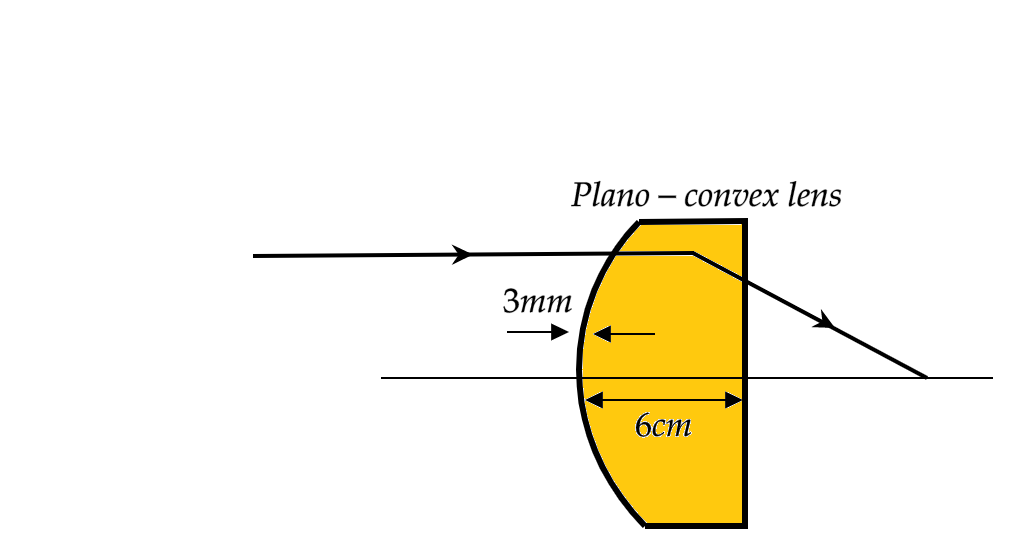
The diameter of the aperture of the lens $ (d)=6cm $
The radius of the aperture will be half of the diameter, that is $ (r)=\dfrac{d}{2}=3cm $
The thickness of the lens $ (x)=3mm=0.3cm\left[ \because 1mm=0.1cm \right] $
The radius of curvature can now be found using the relation $ R=\dfrac{{{r}^{2}}}{2x} $
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow R=\dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{2\times 0.3}=15cm $
Now that we have found the radius of curvature of the lens, we only need to find the refractive index of the lens medium
The speed of light through the lens is given as $ (v)=2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s $
We all know that the speed of light through vacuum is $ (c)=3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s $
The refractive index can now be given as $ (\mu )=\dfrac{c}{v} $
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow \mu =\dfrac{3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s}{2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s}=1.5 $
Now that we have calculated the refractive index and the radius of curvature of the lens, the focal length of the lens can be given as $ (f)=\dfrac{R}{\mu -1} $
Substituting the values once again, we get
$ \Rightarrow f=\dfrac{15cm}{1.5-1}=30cm $
Hence we can say that option (C) is the correct answer to the given question.
Note
We all know that ratios do not have any unit and are dimensionless. Instead of this fact, the units of the quantities must be taken into account while taking their ratio. The ratio is always taken of quantities having the same unit and use of dissimilar would furnish wrong answers. Note that we converted the units from millimetres to centimetres before taking the ratio and the speed of light in both numerator and denominator was in metres per second.
In the given questions, we have to calculate the focal length of a Plano-convex lens; we have been provided with the diameter of the aperture of the lens and the thickness of the lens. Also provided to us is the speed of light in the lens. We can find the focal length using the radius of curvature of the lens and the refractive index of the lens. The refractive index can be found using the given speed of light in the lens and the radius of curvature can be found using the diameter of the aperture and the thickness of the lens. Let’s dive right into the detailed solution.
$ \Rightarrow R=\dfrac{{{r}^{2}}}{2x} $ , $ \mu =\dfrac{c}{v} $ , $ f=\dfrac{R}{\mu -1} $
Complete step by step answer
A diagrammatic representation of the problem at hand is given below, indicating the diameter of the aperture of the lens, the thickness of the lens and a parallel ray of light that converges with the principal axis at the principal focus.

The diameter of the aperture of the lens $ (d)=6cm $
The radius of the aperture will be half of the diameter, that is $ (r)=\dfrac{d}{2}=3cm $
The thickness of the lens $ (x)=3mm=0.3cm\left[ \because 1mm=0.1cm \right] $
The radius of curvature can now be found using the relation $ R=\dfrac{{{r}^{2}}}{2x} $
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow R=\dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{2\times 0.3}=15cm $
Now that we have found the radius of curvature of the lens, we only need to find the refractive index of the lens medium
The speed of light through the lens is given as $ (v)=2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s $
We all know that the speed of light through vacuum is $ (c)=3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s $
The refractive index can now be given as $ (\mu )=\dfrac{c}{v} $
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow \mu =\dfrac{3\times {{10}^{8}}m/s}{2\times {{10}^{8}}m/s}=1.5 $
Now that we have calculated the refractive index and the radius of curvature of the lens, the focal length of the lens can be given as $ (f)=\dfrac{R}{\mu -1} $
Substituting the values once again, we get
$ \Rightarrow f=\dfrac{15cm}{1.5-1}=30cm $
Hence we can say that option (C) is the correct answer to the given question.
Note
We all know that ratios do not have any unit and are dimensionless. Instead of this fact, the units of the quantities must be taken into account while taking their ratio. The ratio is always taken of quantities having the same unit and use of dissimilar would furnish wrong answers. Note that we converted the units from millimetres to centimetres before taking the ratio and the speed of light in both numerator and denominator was in metres per second.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




