
The dimerization of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ as the temperature is lowered is accompanied by
A. A decrease in pressure
B. The formation of a colloid
C. An increase in pressure
D. A decrease in paramagnetism
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: We know that dimerized means that two molecules of the same compound combine and form a dimer. When dimerization of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ occurs it leads to the formation of ${{\text{N}}_2}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$. During dimerization, new covalent bonds are formed between two molecules of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
We will first look at the structure of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$. The nitrogen atom has five valence electrons. In the structure of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$, a nitrogen atom shares two electrons and forms a coordinate bond with oxygen. Two electrons are used to form a double bond with another oxygen atom. One electron remains with the nitrogen atom.
The one unpaired electron makes the ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule highly unstable.
As ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecules are highly unstable, two molecules of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ combine with each other and form a dimer. This process is known as dimerization of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$. During dimerization, covalent bonds are formed and ${{\text{N}}_2}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is formed.
The ${{\text{N}}_2}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ molecule formed is more stable as it does not contain any unpaired electron.
The dimerization reaction of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is as follows:
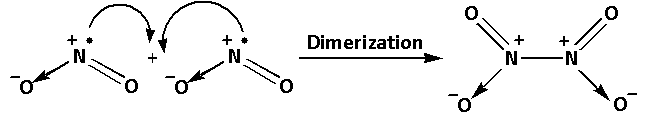
We know that the complexes having unpaired electrons are paramagnetic in nature and those having no unpaired electrons are diamagnetic in nature.${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ has an unpaired electron. Thus, ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is paramagnetic in nature. But ${{\text{N}}_2}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ does not have any unpaired electron and thus. It is diamagnetic.
Thus, we can say that when dimerization of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ occurs, the paramagnetic nature of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is lost.
Thus, the dimerization of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ as the temperature is lowered is accompanied by a decrease in paramagnetism.
Thus, the correct option is option (D).
Note:
We know that the bond formed between two atoms in which the shared pair of electrons are donated by only one atom but shared by both the atoms is known as the coordinate bond. The coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond. The coordinate bond is also known as the dative bond. The coordinate bond is represented by a single pointed arrow which goes from the atom which shares its lone pair to the other atom
Complete step by step answer:
We will first look at the structure of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$. The nitrogen atom has five valence electrons. In the structure of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$, a nitrogen atom shares two electrons and forms a coordinate bond with oxygen. Two electrons are used to form a double bond with another oxygen atom. One electron remains with the nitrogen atom.
The one unpaired electron makes the ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecule highly unstable.
As ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ molecules are highly unstable, two molecules of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ combine with each other and form a dimer. This process is known as dimerization of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$. During dimerization, covalent bonds are formed and ${{\text{N}}_2}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ is formed.
The ${{\text{N}}_2}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ molecule formed is more stable as it does not contain any unpaired electron.
The dimerization reaction of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is as follows:

We know that the complexes having unpaired electrons are paramagnetic in nature and those having no unpaired electrons are diamagnetic in nature.${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ has an unpaired electron. Thus, ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is paramagnetic in nature. But ${{\text{N}}_2}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ does not have any unpaired electron and thus. It is diamagnetic.
Thus, we can say that when dimerization of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ occurs, the paramagnetic nature of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ is lost.
Thus, the dimerization of ${\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ as the temperature is lowered is accompanied by a decrease in paramagnetism.
Thus, the correct option is option (D).
Note:
We know that the bond formed between two atoms in which the shared pair of electrons are donated by only one atom but shared by both the atoms is known as the coordinate bond. The coordinate bond is a type of covalent bond. The coordinate bond is also known as the dative bond. The coordinate bond is represented by a single pointed arrow which goes from the atom which shares its lone pair to the other atom
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




