
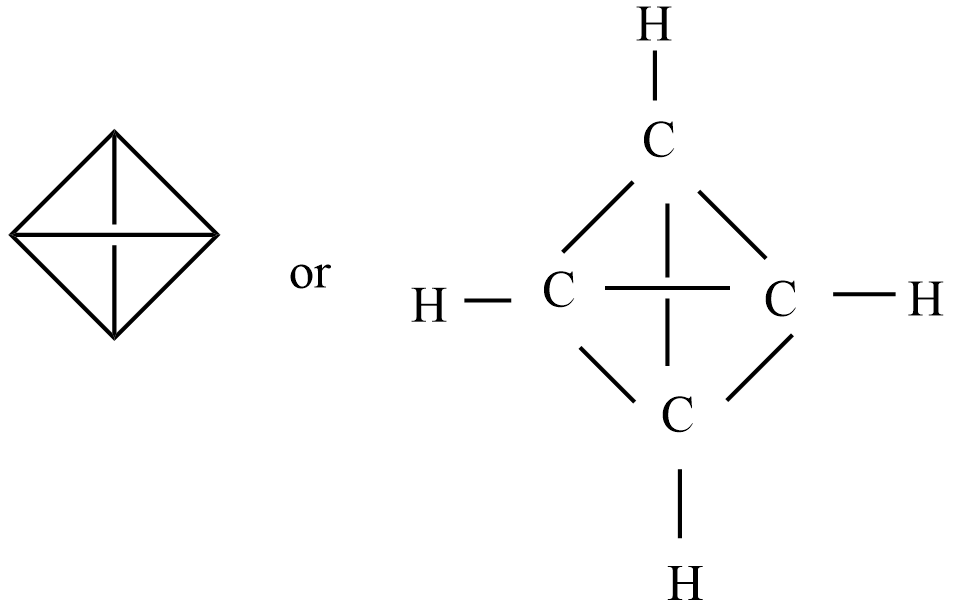
The double bond equivalent for tetrahedron
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5

Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The number of unsaturation present in the molecule is known as DBE or double bond equivalent. In a ring system or double bond referrers the term unsaturation. For example, benzene has 3 double bonds and 1 ring which gives double bond equivalent value 4. If an organic compound has the presence of an oxygen atom does not influence the double bond equivalent calculation.
Complete step by step solution:
A double bond equivalent for an organic compound can be calculated by the given formula.
$DBE=C+1-\dfrac{H}{2}-\dfrac{X}{2}+\dfrac{N}{2}$ --- (1)
DBE = double bond equivalent of unsaturation
C = number of carbon atoms present in the organic compound
H = number of hydrogen atoms present in the given organic compound
X = number of halogens atoms present like Cl, Br, or I
N = number of nitrogen atoms present in the given organic compound.
Given organic compound – tetrahedrane and chemical formula is ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{4}}$
The number of carbons present in the given organic compound = 4
Then the number of hydrogen atoms present in the given organic compound = 4
There is no number of nitrogen and halogen atoms.
From equation (1),
$DBE=4+1-\dfrac{4}{2}-\dfrac{0}{2}+\dfrac{0}{2}$= 3
Hence, the double bond equivalent for tetrahedron is 3.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: The arrangement of atoms and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together in the chemical structure of this tetrahedrane contains a total of 10 bonds. There are 4 three-membered rings, 3 four-membered rings, and 6 non-H bonds.
Complete step by step solution:
A double bond equivalent for an organic compound can be calculated by the given formula.
$DBE=C+1-\dfrac{H}{2}-\dfrac{X}{2}+\dfrac{N}{2}$ --- (1)
DBE = double bond equivalent of unsaturation
C = number of carbon atoms present in the organic compound
H = number of hydrogen atoms present in the given organic compound
X = number of halogens atoms present like Cl, Br, or I
N = number of nitrogen atoms present in the given organic compound.
Given organic compound – tetrahedrane and chemical formula is ${{C}_{4}}{{H}_{4}}$
The number of carbons present in the given organic compound = 4
Then the number of hydrogen atoms present in the given organic compound = 4
There is no number of nitrogen and halogen atoms.
From equation (1),
$DBE=4+1-\dfrac{4}{2}-\dfrac{0}{2}+\dfrac{0}{2}$= 3
Hence, the double bond equivalent for tetrahedron is 3.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: The arrangement of atoms and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together in the chemical structure of this tetrahedrane contains a total of 10 bonds. There are 4 three-membered rings, 3 four-membered rings, and 6 non-H bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




