
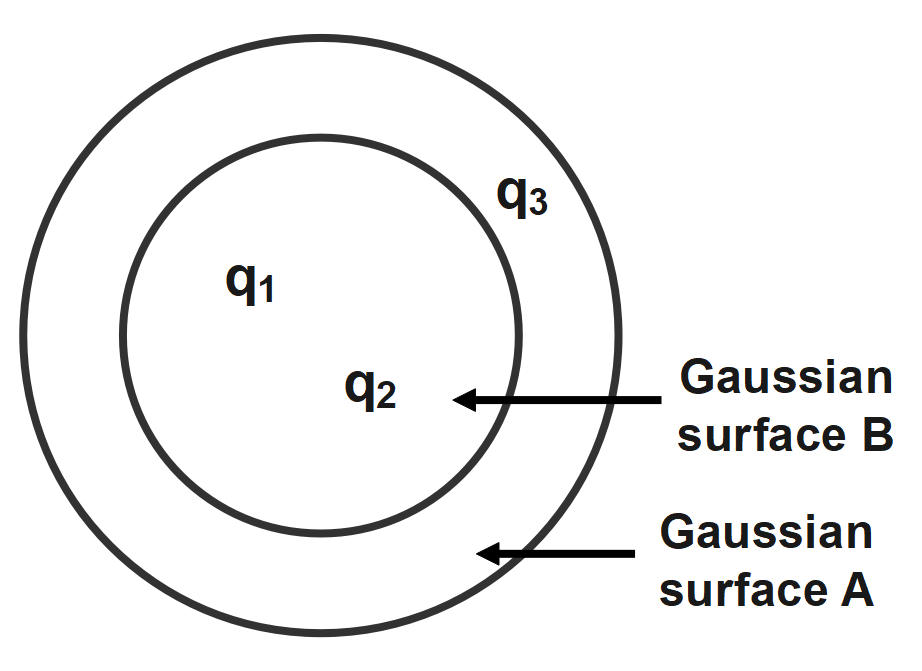
The electric flux for gaussian surface A that enclose the charged particles in free space is (given $ {{q}_{1}}=-14nC,\text{ }{{q}_{2}}=78.85nC,\text{ }{{q}_{3}}=-56nC $ ).
(A) $ {{10}^{3}}\left( N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \right) $
(B) $ {{10}^{3}}\left( C{{N}^{-1}}{{m}^{-2}} \right) $
(C) $ 6.32\times {{10}^{3}}\left( N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \right) $
(D) $ 6.32\times {{10}^{3}}\left( C{{N}^{-1}}m \right) $

Answer
497.7k+ views
Hint: We know that the electric flux passing through the point P will be dependent on the Gaussian surface and the charges it encloses, consistent with Gauss’s law. Hence, only the charges $ {{q}_{1}},\text{ }{{q}_{2}} $ and $ {{q}_{3}} $ will contribute to the electric flux in this region. The formula here for electric flux for gaussian surface used will be: $ {{\Phi }_{electric}}=\dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} $ where $ {{\Phi }_{electric}} $ is electric flux; Q is the total charges enclosed per permittivity of free space; $ {{\varepsilon }_{0}} $ is permittivity of free space $ =8.85\times {{10}^{-12}}N{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}} $ .
Complete step by step answer:
As we know, the electric flux due to the charges enclosed in a hypothetical Gaussian surface is always due to the charges enclosed within the surface. There is no contribution to the flux due to charge outside the Gaussian surface.
By calculating the flux by enclosing the charge in a hypothetical surface called Gaussian surface. The Gauss law states that the electric flux is due to some charges enclosed in a Gaussian surface. Thus, the total flux due to charges enclosed per permittivity of free space $ ({{\varepsilon }_{0}}) $ and given by $ Q={{q}_{1}}+{{q}_{2}}+{{q}_{3}}=\left( -14+78.85-56 \right)nC=8.85nC. $ Since we know for Charge unit that is nC stands nano Columb and nano is $ {{10}^{-9}}. $ $ \Rightarrow Q=8.85\times {{10}^{-9}}C. $
Now that we have total charges enclosed per $ {{\varepsilon }_{0}} $ we have to calculate electric flux for gaussian surface A that enclose the charged particles in free space is given by $ {{\Phi }_{electric}}=\dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} $
On substitution the values in above equation we get;
$ {{\Phi }_{electric}}=\dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}=\dfrac{8.85\times {{10}^{-9}}\left( C \right)}{8.85\times {{10}^{-12}}\left( N{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}} \right)} $ .
On further solving and taking denominator to numerator we get;
$ {{\Phi }_{electric}}=\dfrac{{{10}^{-9}}\left( C \right)}{{{10}^{-12}}\left( N{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}} \right)}={{10}^{-9}}\left( C \right)\times {{10}^{+12}}\left( N{{C}^{-2}}{{m}^{+2}} \right) $
On simplifying we get the value of electric flux:
$ \Rightarrow {{\Phi }_{electric}}={{10}^{12-9}}\left( N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \right)={{10}^{3}}\left( N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \right). $
Therefore, correct answer is option A i.e. the electric flux for gaussian surface A that enclose the charged particles in free space is $ {{10}^{3}}\left( N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \right) $ .
Note:
Note that Coulomb's law can be derived from Gauss’s law and vice versa. It is one of Maxwell's four equations of electromagnetic interaction. It can be used to find the electric field due to discrete and continuous charge distributions.
Complete step by step answer:
As we know, the electric flux due to the charges enclosed in a hypothetical Gaussian surface is always due to the charges enclosed within the surface. There is no contribution to the flux due to charge outside the Gaussian surface.
By calculating the flux by enclosing the charge in a hypothetical surface called Gaussian surface. The Gauss law states that the electric flux is due to some charges enclosed in a Gaussian surface. Thus, the total flux due to charges enclosed per permittivity of free space $ ({{\varepsilon }_{0}}) $ and given by $ Q={{q}_{1}}+{{q}_{2}}+{{q}_{3}}=\left( -14+78.85-56 \right)nC=8.85nC. $ Since we know for Charge unit that is nC stands nano Columb and nano is $ {{10}^{-9}}. $ $ \Rightarrow Q=8.85\times {{10}^{-9}}C. $
Now that we have total charges enclosed per $ {{\varepsilon }_{0}} $ we have to calculate electric flux for gaussian surface A that enclose the charged particles in free space is given by $ {{\Phi }_{electric}}=\dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} $
On substitution the values in above equation we get;
$ {{\Phi }_{electric}}=\dfrac{Q}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}=\dfrac{8.85\times {{10}^{-9}}\left( C \right)}{8.85\times {{10}^{-12}}\left( N{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}} \right)} $ .
On further solving and taking denominator to numerator we get;
$ {{\Phi }_{electric}}=\dfrac{{{10}^{-9}}\left( C \right)}{{{10}^{-12}}\left( N{{C}^{2}}{{m}^{-2}} \right)}={{10}^{-9}}\left( C \right)\times {{10}^{+12}}\left( N{{C}^{-2}}{{m}^{+2}} \right) $
On simplifying we get the value of electric flux:
$ \Rightarrow {{\Phi }_{electric}}={{10}^{12-9}}\left( N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \right)={{10}^{3}}\left( N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \right). $
Therefore, correct answer is option A i.e. the electric flux for gaussian surface A that enclose the charged particles in free space is $ {{10}^{3}}\left( N{{C}^{-1}}{{m}^{2}} \right) $ .
Note:
Note that Coulomb's law can be derived from Gauss’s law and vice versa. It is one of Maxwell's four equations of electromagnetic interaction. It can be used to find the electric field due to discrete and continuous charge distributions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




