
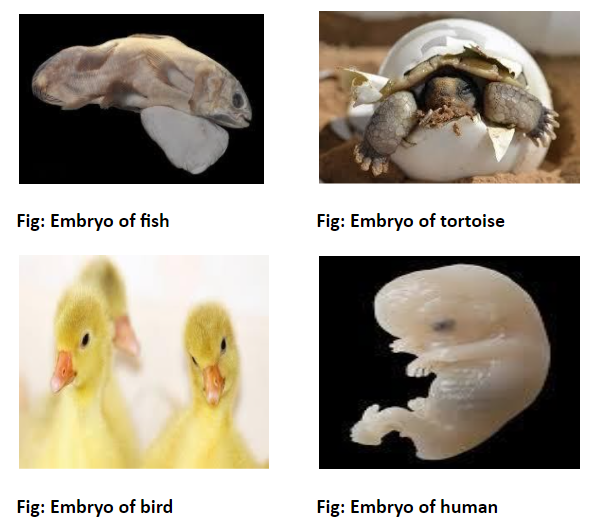
The embryos of fish, tortoise, birds, and humans at some stage resemble closely. This is an example of __________ evidence of evolution.
A. Anatomical
B.Morphological
C. Embryological
D. Paleontological
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: The study that deals with the embryological structure and function of different animals are called embryology.
Complete answer: The study of positions of body parts and body organs is known as anatomy.
The study of the shape of an organism or a cell is known as the morphological study.
The study of fossils of plants and animals is known as a planetological study.
The study of embryological development is called embryology.
Additional information: Famous scientist Ernst Hackle said ‘ontogeny repeats phylogeny’ – means the development of an organism expresses evolutionary history related to all the intermediate forms of its ancestors.
1. This study was done based on the comparative study of the embryos of related groups of animals. The adult stages of every organism are different but morphologically the embryos show similarity in the early stages of life.
2. The embryos of fish, tortoise, birds, and humans show the presence of gill slits and tails in the embryo, maybe for some organisms, the tail gets vanished (for example frog) as development commence or tail become vestigial (example human) from the embryonic condition. This is evidence of embryological evolution.
So the correct answer is option C. Embryological.
Note: Evolution is an alternation in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations.
These characteristics are the expressions of genes that are moving on from parent to offspring during reproduction.
Different characteristics tend to exist within any given population as a cause of mutation, genetic recombination, and other forms of genetic variation
Complete answer: The study of positions of body parts and body organs is known as anatomy.
The study of the shape of an organism or a cell is known as the morphological study.
The study of fossils of plants and animals is known as a planetological study.
The study of embryological development is called embryology.

Additional information: Famous scientist Ernst Hackle said ‘ontogeny repeats phylogeny’ – means the development of an organism expresses evolutionary history related to all the intermediate forms of its ancestors.
1. This study was done based on the comparative study of the embryos of related groups of animals. The adult stages of every organism are different but morphologically the embryos show similarity in the early stages of life.
2. The embryos of fish, tortoise, birds, and humans show the presence of gill slits and tails in the embryo, maybe for some organisms, the tail gets vanished (for example frog) as development commence or tail become vestigial (example human) from the embryonic condition. This is evidence of embryological evolution.
So the correct answer is option C. Embryological.
Note: Evolution is an alternation in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations.
These characteristics are the expressions of genes that are moving on from parent to offspring during reproduction.
Different characteristics tend to exist within any given population as a cause of mutation, genetic recombination, and other forms of genetic variation
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




