
The fermentation of glucose by yeast normally yields
A.Lactic acid, $C{O_2}$ and $2ATP$
B.Alcohol, $C{O_2}$ and $36ATP$
C.Alcohol, $C{O_2}$ and $2ATP$
D.$C{O_2}$, ${H_2}O$ and $36ATP$
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: Glucose is a type of carbohydrate, it is made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
Fermentation is defined as the incomplete oxidation of glucose carried out in the absence of oxygen known as anaerobic condition.
Complete answer:
Fermentation of glucose is a type of metabolic reaction which involves many prokaryotic organisms and unicellular eukaryotes like yeast.
Anaerobic conditions are required for the fermentation process to complete because presence of oxygen causes complete oxidation of glucose and yields different products like pyruvate and energy.
Glucose molecules undergo a 9 step reaction to form pyruvate as in the case of glycolysis to and $2ATP$.
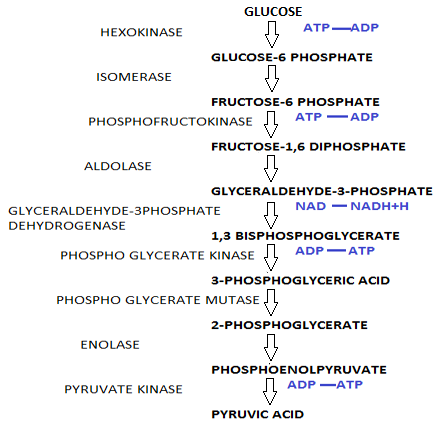
After glycolysis each molecule of glucose produced two molecules of pyruvate, $2ATP$ and $2NADH$.
After the formation of pyruvate, fermentation enzymes act on it to yield different products in the absence of oxygen.
Pyruvate molecule undergoes decarboxylation process in the presence of pyruvate decarboxylase to yield two molecules of acetaldehyde, two molecules of carbon dioxide and $NADH$.
$2{C_3}{H_4}{O_3}\underrightarrow {ez}2C{H_3}CHO + 2C{O_2} + 2NADH$
Where ${C_3}{H_4}{O_3}$ is pyruvate
$C{H_3}CHO$ Is acetaldehyde molecule
$C{O_2}$ Is carbon dioxide
$NADH$Energy molecule
$\left( {ez} \right)$ Is enzyme pyruvate decarboxylase
Acetaldehyde form in the step further undergoes chemical reaction in the presence of enzyme acetaldehyde dehydrogenase to finally form two molecules of ethanol by utilizing the energy formed in earlier step.
$2C{H_3}CHO\underrightarrow {ez}2C{H_2}OH + 2NA{D^ + }$
Where $\left( {ez} \right)$ is an enzyme acetaldehyde dehydrogenase
${C_2}{H_5}OH$ Is ethanol or alcohol
Hence, after completion of fermentation process one glucose molecule finally forms Alcohol, $C{O_2}$ and $2ATP$ so option (D) is correct .
During fermentation a very small amount of energy $\left( { < 7\% } \right)$is released from one molecule of glucose.
Note:
Glucose is commonly known as sugar because of its sweet taste. Glucose comes under the category of monosaccharide because it can not be further hydrolyzed to yield a smaller unit.
Yeast present in the reaction during fermentation undergoes self-death when concentration of alcohol reaches $\left( {13\% } \right)$
Fermentation is defined as the incomplete oxidation of glucose carried out in the absence of oxygen known as anaerobic condition.
Complete answer:
Fermentation of glucose is a type of metabolic reaction which involves many prokaryotic organisms and unicellular eukaryotes like yeast.
Anaerobic conditions are required for the fermentation process to complete because presence of oxygen causes complete oxidation of glucose and yields different products like pyruvate and energy.
Glucose molecules undergo a 9 step reaction to form pyruvate as in the case of glycolysis to and $2ATP$.

After glycolysis each molecule of glucose produced two molecules of pyruvate, $2ATP$ and $2NADH$.
After the formation of pyruvate, fermentation enzymes act on it to yield different products in the absence of oxygen.
Pyruvate molecule undergoes decarboxylation process in the presence of pyruvate decarboxylase to yield two molecules of acetaldehyde, two molecules of carbon dioxide and $NADH$.
$2{C_3}{H_4}{O_3}\underrightarrow {ez}2C{H_3}CHO + 2C{O_2} + 2NADH$
Where ${C_3}{H_4}{O_3}$ is pyruvate
$C{H_3}CHO$ Is acetaldehyde molecule
$C{O_2}$ Is carbon dioxide
$NADH$Energy molecule
$\left( {ez} \right)$ Is enzyme pyruvate decarboxylase
Acetaldehyde form in the step further undergoes chemical reaction in the presence of enzyme acetaldehyde dehydrogenase to finally form two molecules of ethanol by utilizing the energy formed in earlier step.
$2C{H_3}CHO\underrightarrow {ez}2C{H_2}OH + 2NA{D^ + }$
Where $\left( {ez} \right)$ is an enzyme acetaldehyde dehydrogenase
${C_2}{H_5}OH$ Is ethanol or alcohol
Hence, after completion of fermentation process one glucose molecule finally forms Alcohol, $C{O_2}$ and $2ATP$ so option (D) is correct .
During fermentation a very small amount of energy $\left( { < 7\% } \right)$is released from one molecule of glucose.
Note:
Glucose is commonly known as sugar because of its sweet taste. Glucose comes under the category of monosaccharide because it can not be further hydrolyzed to yield a smaller unit.
Yeast present in the reaction during fermentation undergoes self-death when concentration of alcohol reaches $\left( {13\% } \right)$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




