
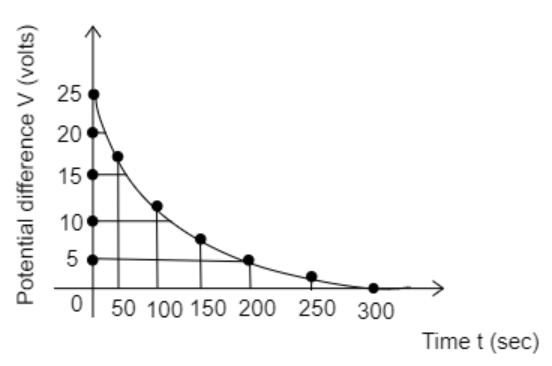
The figure represents an experiment plot for the discharging of a capacitor in an R-C circuit. Find the range of time in which the time constant lies.
The graph between potential difference and time
A) 0 sec and 50 sec
B) 50 sec and 100 sec
C) 100 sec and 150 sec
D) 150 sec and 200 sec

Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint:The figure shows that the potential difference decreases exponentially with time. The time constant in an R-C circuit refers to the time taken to charge the capacitor to 0.632 of the applied voltage. This suggests that after a time equal to the time constant the potential difference will be 0.368 of its initial voltage as the capacitor discharges.
Formula used:
-The decrease in the potential difference in an R-C circuit while discharging can be expressed as $V = {V_0}{e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{T}}}$ where ${V_0}$ is the initial voltage before the capacitor discharges, $t$ is the time taken to discharge in seconds and $T$ is the time constant of the R-C circuit.
Complete step by step answer.
Step 1: Sketch the experiment plot given in the question and identify the initial voltage ${V_0}$ from the plot.
The initial voltage ${V_0}$ is the potential difference present before the capacitor discharges i.e., the value of $V$ at $t = 0{\text{sec}}$
So, from the graph, we observe that at $t = 0{\text{sec}}$, ${V_0} = 25{\text{V}}$
Step 2: Express the decrease in the potential difference $V$ .
The decrease in the potential difference during discharging of the capacitor in an R-C circuit is given by, $V = {V_0}{e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{T}}}$ --------- (1)
where ${V_0}$ is the initial voltage before the capacitor discharges, $t$ is the time taken to discharge in seconds and $T$ is the time constant of the R-C circuit.
Here, ${V_0} = 25{\text{V}}$ then equation (1) becomes $V = 25{e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{T}}}$ -------- (2)
Step 3: Find the time constant by substituting any value of $V$ and the corresponding value of $t$ from the graph in equation (2).
Equation (2) gives us $V = 25{e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{T}}}$
Substitute the value of the potential difference $V = 5{\text{V}}$ and the time $t = 200{\text{sec}}$ in equation (2).
Then we have, $5 = 25{e^{\dfrac{{ - 200}}{T}}}$
Simplifying the above equation we get, $\dfrac{1}{5} = {e^{\dfrac{{ - 200}}{T}}}$
Taking the logarithm to the base $e$ on both sides we get, $ - {\log _e}5 = - {\log _e}{e^{\dfrac{{200}}{T}}}$
We know, ${\log _e}5 = 1.60$ so the above equation becomes $1.60 = \dfrac{{200}}{T}$ or on rearranging we get, $T = \dfrac{{200}}{{1.60}} = 125{\text{sec}}$
$\therefore $ The time constant is $T = 125{\text{sec}}$ .
Thus the time constant lies in the time range 100 sec to 150 sec. The correct option is C.
Note: After one time constant, the capacitor must have discharged to 1−0.632 of its initial voltage. We can check if the obtained time constant is correct.
According to the statement when $t = T$ the potential difference must be $V = \left( {1 - 0.632} \right){V_0}$ .
Since ${V_0} = 25{\text{V}}$ at $t = T$, $V = \left( {1 - 0.632} \right) \times 25 = 9.05{\text{V}}$
Now, substituting $t = T$ in equation (2) we get $V = 25{e^{\dfrac{{ - T}}{T}}} = \dfrac{{25}}{e} = 9.1 \cong 9.05$
The obtained time constant is correct.
Formula used:
-The decrease in the potential difference in an R-C circuit while discharging can be expressed as $V = {V_0}{e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{T}}}$ where ${V_0}$ is the initial voltage before the capacitor discharges, $t$ is the time taken to discharge in seconds and $T$ is the time constant of the R-C circuit.
Complete step by step answer.
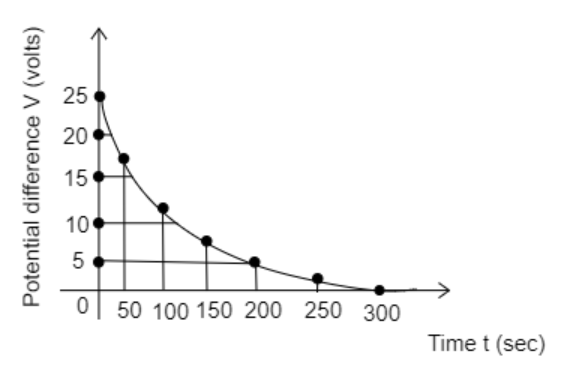
Step 1: Sketch the experiment plot given in the question and identify the initial voltage ${V_0}$ from the plot.
The graph between potential difference and time

The initial voltage ${V_0}$ is the potential difference present before the capacitor discharges i.e., the value of $V$ at $t = 0{\text{sec}}$
So, from the graph, we observe that at $t = 0{\text{sec}}$, ${V_0} = 25{\text{V}}$
Step 2: Express the decrease in the potential difference $V$ .
The decrease in the potential difference during discharging of the capacitor in an R-C circuit is given by, $V = {V_0}{e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{T}}}$ --------- (1)
where ${V_0}$ is the initial voltage before the capacitor discharges, $t$ is the time taken to discharge in seconds and $T$ is the time constant of the R-C circuit.
Here, ${V_0} = 25{\text{V}}$ then equation (1) becomes $V = 25{e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{T}}}$ -------- (2)
Step 3: Find the time constant by substituting any value of $V$ and the corresponding value of $t$ from the graph in equation (2).
Equation (2) gives us $V = 25{e^{\dfrac{{ - t}}{T}}}$
Substitute the value of the potential difference $V = 5{\text{V}}$ and the time $t = 200{\text{sec}}$ in equation (2).
Then we have, $5 = 25{e^{\dfrac{{ - 200}}{T}}}$
Simplifying the above equation we get, $\dfrac{1}{5} = {e^{\dfrac{{ - 200}}{T}}}$
Taking the logarithm to the base $e$ on both sides we get, $ - {\log _e}5 = - {\log _e}{e^{\dfrac{{200}}{T}}}$
We know, ${\log _e}5 = 1.60$ so the above equation becomes $1.60 = \dfrac{{200}}{T}$ or on rearranging we get, $T = \dfrac{{200}}{{1.60}} = 125{\text{sec}}$
$\therefore $ The time constant is $T = 125{\text{sec}}$ .
Thus the time constant lies in the time range 100 sec to 150 sec. The correct option is C.
Note: After one time constant, the capacitor must have discharged to 1−0.632 of its initial voltage. We can check if the obtained time constant is correct.
According to the statement when $t = T$ the potential difference must be $V = \left( {1 - 0.632} \right){V_0}$ .
Since ${V_0} = 25{\text{V}}$ at $t = T$, $V = \left( {1 - 0.632} \right) \times 25 = 9.05{\text{V}}$
Now, substituting $t = T$ in equation (2) we get $V = 25{e^{\dfrac{{ - T}}{T}}} = \dfrac{{25}}{e} = 9.1 \cong 9.05$
The obtained time constant is correct.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




