
The figure shows a transparent sphere of radius R and refractive index $\mu$. An object O is placed at a distance $x$ from the pole of the first surface so that a real image is formed at the pole of the exactly opposite surface.
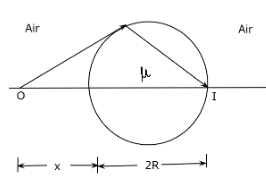
If, \[x=2R\] then the value of \[\mu \] is
A. 1.5
B. 2
C. 3
D. none of these

Answer
600k+ views
Hint: By applying the formula \[\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{v}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{\left( {{\mu }_{2}}-{{\mu }_{1}} \right)}{R}\] students can get the required refractive index \[\left( \mu \right)\] of the sphere easily. And we know the refractive index of the air is one. Considering these two refractive indices calculate the required value.
Complete step by step answer:
By applying the formula \[\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{v}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{\left( {{\mu }_{2}}-{{\mu }_{1}} \right)}{R}\] and putting the values given in question,
Refractive index of sphere is \[\left( \mu \right)\] and refractive index of the air is 1, so as per the given condition we have,
\[{{\mu }_{2}}=\mu \], \[{{\mu }_{1}}=1\], \[v=2R\], and \[u=-(x)=-\left( 2R \right)\]
Now, we have
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu }{2R}-\dfrac{1}{\left( -2R \right)}=\dfrac{\left( \mu -1 \right)}{R}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu }{2R}+\dfrac{1}{2R}=\dfrac{\left( \mu -1 \right)}{R}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu +1}{2R}=\dfrac{\left( \mu -1 \right)}{R}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu +1}{2R}=\dfrac{2\left( \mu -1 \right)}{2R}\]
Cancelling the like terms, we get
\[\Rightarrow \left( \mu +1 \right)=\left( 2\mu -2 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 2\mu -\mu =2+1\]
\[\Rightarrow \mu =3\]
So, the refractive index of the sphere will be 3.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Additional Information:
Image formation in converging lens: Converging lenses can produce both real and virtual images while diverging lenses can only produce virtual images. The process by which images are formed for lenses is the same as the process by which images are formed for plane and curved mirrors. Images are formed at locations where any observer is sighting as they view the image of the object through the lens. So, if the path of several light rays through a lens is traced, each of these light rays will intersect at a point upon refraction through the lens.
Image formation in diverging lens: Diverging lenses create virtual images since the refracted rays do not actually converge to a point. In the case of a diverging lens, the image location is located on the object's side of the lens where the refracted rays would intersect if extended backwards.
Note: Students should try to memorize the formulae of optics so that they can apply instantaneously whenever required in a question from optics, otherwise there should be a lot of waste of time in deriving that formulae.
Students often get confused about what to consider as the second medium, so remember the refractive index of air is 1.
Complete step by step answer:
By applying the formula \[\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{v}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{\left( {{\mu }_{2}}-{{\mu }_{1}} \right)}{R}\] and putting the values given in question,
Refractive index of sphere is \[\left( \mu \right)\] and refractive index of the air is 1, so as per the given condition we have,
\[{{\mu }_{2}}=\mu \], \[{{\mu }_{1}}=1\], \[v=2R\], and \[u=-(x)=-\left( 2R \right)\]
Now, we have
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu }{2R}-\dfrac{1}{\left( -2R \right)}=\dfrac{\left( \mu -1 \right)}{R}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu }{2R}+\dfrac{1}{2R}=\dfrac{\left( \mu -1 \right)}{R}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu +1}{2R}=\dfrac{\left( \mu -1 \right)}{R}\]
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{\mu +1}{2R}=\dfrac{2\left( \mu -1 \right)}{2R}\]
Cancelling the like terms, we get
\[\Rightarrow \left( \mu +1 \right)=\left( 2\mu -2 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 2\mu -\mu =2+1\]
\[\Rightarrow \mu =3\]
So, the refractive index of the sphere will be 3.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Additional Information:
Image formation in converging lens: Converging lenses can produce both real and virtual images while diverging lenses can only produce virtual images. The process by which images are formed for lenses is the same as the process by which images are formed for plane and curved mirrors. Images are formed at locations where any observer is sighting as they view the image of the object through the lens. So, if the path of several light rays through a lens is traced, each of these light rays will intersect at a point upon refraction through the lens.
Image formation in diverging lens: Diverging lenses create virtual images since the refracted rays do not actually converge to a point. In the case of a diverging lens, the image location is located on the object's side of the lens where the refracted rays would intersect if extended backwards.
Note: Students should try to memorize the formulae of optics so that they can apply instantaneously whenever required in a question from optics, otherwise there should be a lot of waste of time in deriving that formulae.
Students often get confused about what to consider as the second medium, so remember the refractive index of air is 1.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




