
The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane shows that
(a) Quasi Fluid nature of lipid enables the lateral movement of proteins within the overall bilayer.
(b) Lateral movement within the membrane is measured as its fluidity.
(c) Fluid nature of the membrane is important for growth, the formation of intercellular junctions, secretions, endocytosis, cell division, etc.
(d) All of the above.
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: A biological membrane that separates the interior of a cell from its outside environment. To give protection to the cell from its surroundings is the primary function of the plasma membrane. It is a membrane that is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and regulates the movement of substances in and out of cells.
Complete answer:
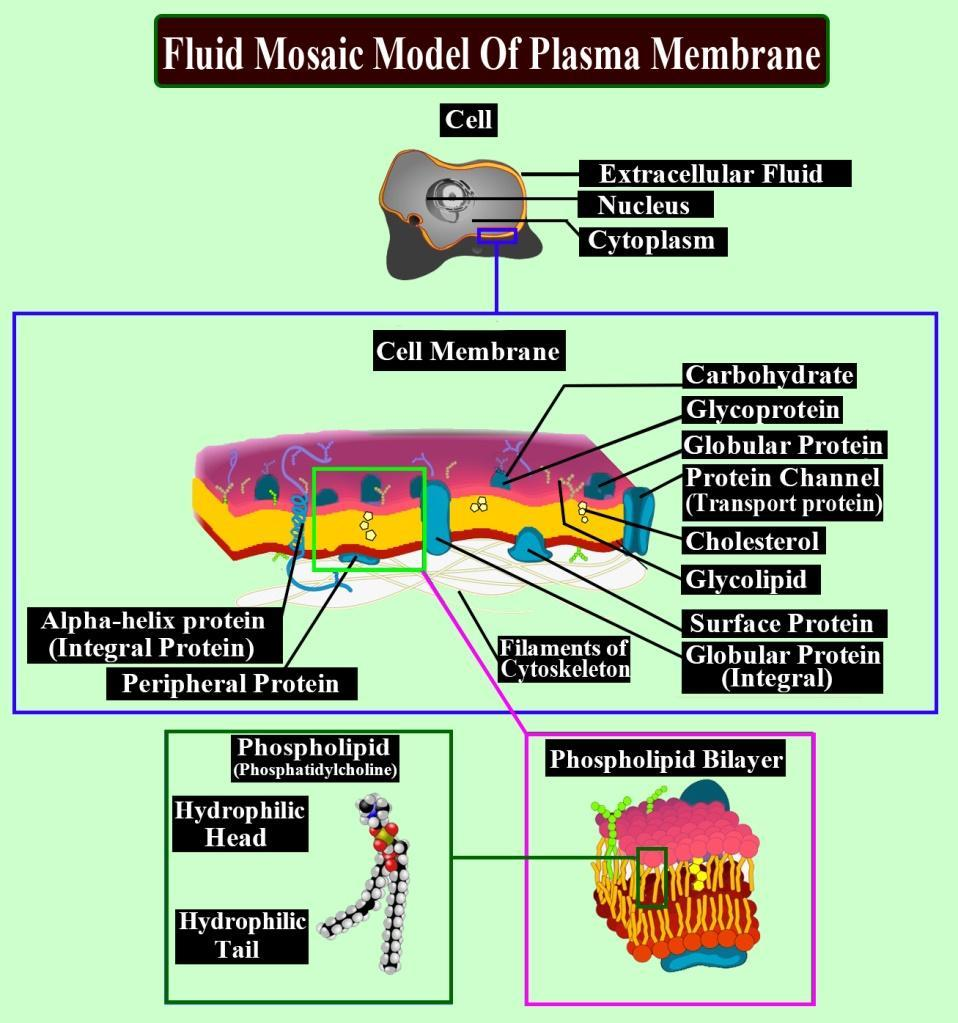
The membrane now has got a modern view of the structure, which is known as the fluid mosaic model. It was developed in the year 1972 by S. J. Singer and G. L. Nicholson. They gave three basic features of membrane structure.
When viewed from above one surface or the other, integral membrane proteins contribute a mosaic or 'pebbled' pattern to a membrane. In the plane of the membrane, these proteins and the membrane lipids are capable of lateral movement, it is due to the fluid nature of lipid association.
Lipid-anchored proteins are also potentially mobile as well, moving by their association with mobile lipids.
Lateral movement of proteins within the bilayer is possible, because of the quasi-fluid nature of the lipid bilayer. The fluid nature of the membrane is also important from many aspects, like cell growth, the formation of intercellular junctions, secretion, endocytosis, cell division, etc.
So, the correct answer is,’ all of the above’.
Additional information:
1) To change the shape of the membrane as some cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells can pass through narrow capillaries, the nature of the membranes must be very flexible.
2) The function of anchoring the cytoskeleton to provide shape, the cell plasma membrane plays a very important role, and in attaching to the extracellular matrix and other cells to help group cells together to form tissues. The membrane also maintains cell potential.
3) Passive osmosis and diffusion: transports gases (such as $O_2$ and $CO_2$) and other small molecules and ions.
4) Transmembrane protein channels and transporters: transports small organic molecules such as sugars or amino acids.
Note: There are restrictions on the lateral mobility of the lipid and protein components in the fluid membrane imposed by the formation of subdomains within the lipid bilayer. These subdomains arise by several processes e.g. in the extracellular matrix, the binding of membrane components, a particular biochemical composition with the nanometric membrane regions that promote the formation of lipid rafts, and protein complexes mediated by protein-protein interactions. Furthermore, protein-cytoskeleton associations mediate the formation of “cytoskeletal fences”, corrals wherein lipid and membrane proteins can diffuse freely, but that they can seldom leave. Restriction on lateral diffusion rates of membrane components is very important because it allows the functional specialization of particular regions within the cell membranes.
Complete answer:
The membrane now has got a modern view of the structure, which is known as the fluid mosaic model. It was developed in the year 1972 by S. J. Singer and G. L. Nicholson. They gave three basic features of membrane structure.
When viewed from above one surface or the other, integral membrane proteins contribute a mosaic or 'pebbled' pattern to a membrane. In the plane of the membrane, these proteins and the membrane lipids are capable of lateral movement, it is due to the fluid nature of lipid association.
Lipid-anchored proteins are also potentially mobile as well, moving by their association with mobile lipids.
Lateral movement of proteins within the bilayer is possible, because of the quasi-fluid nature of the lipid bilayer. The fluid nature of the membrane is also important from many aspects, like cell growth, the formation of intercellular junctions, secretion, endocytosis, cell division, etc.

So, the correct answer is,’ all of the above’.
Additional information:
1) To change the shape of the membrane as some cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells can pass through narrow capillaries, the nature of the membranes must be very flexible.
2) The function of anchoring the cytoskeleton to provide shape, the cell plasma membrane plays a very important role, and in attaching to the extracellular matrix and other cells to help group cells together to form tissues. The membrane also maintains cell potential.
3) Passive osmosis and diffusion: transports gases (such as $O_2$ and $CO_2$) and other small molecules and ions.
4) Transmembrane protein channels and transporters: transports small organic molecules such as sugars or amino acids.
Note: There are restrictions on the lateral mobility of the lipid and protein components in the fluid membrane imposed by the formation of subdomains within the lipid bilayer. These subdomains arise by several processes e.g. in the extracellular matrix, the binding of membrane components, a particular biochemical composition with the nanometric membrane regions that promote the formation of lipid rafts, and protein complexes mediated by protein-protein interactions. Furthermore, protein-cytoskeleton associations mediate the formation of “cytoskeletal fences”, corrals wherein lipid and membrane proteins can diffuse freely, but that they can seldom leave. Restriction on lateral diffusion rates of membrane components is very important because it allows the functional specialization of particular regions within the cell membranes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




