
The following compounds are given to you:
$2 - $bromopentane, $2 - $bromo$ - 2 - $ methylbutane, $1 - $bromopentane,
(a) Write the compound which is most reactive towards ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction.
(b) Write the compound which is optically active.
(c) Write the compound which is most reactive towards $\beta - $ elimination reaction.
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction removal of a nucleophile and the attack of another nucleophile take place simultaneously. The compound with less steric hindrance will give the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction faster. The compound having a chiral centre will be optically active. The compounds that give more substituted alkene will be more reactive towards $\beta - $elimination reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
The structures of all the compounds are as follows:
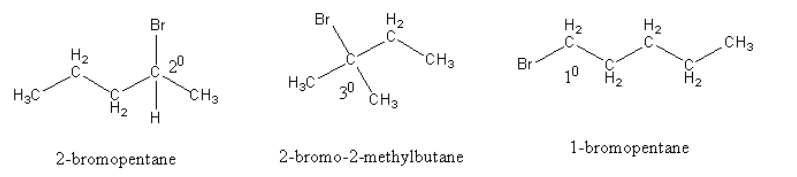
(a)
The full name of ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. In ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction, a nucleophile substitutes another nucleophile. The whole reaction takes place in one step.
The attacking nucleophile can approach the reactant easily if the reactant has less steric hindrance and thus facilitate the reaction via the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ mechanism. As the steric hindrance decreases the rate of reaction via ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ mechanism increases.
The order of increasing steric hindrance in alkyl halide is as follows:
${3^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{1^ \circ }$
The order of decreasing reactivity of alkyl halide towards the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction is as follows:
${1^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{3^ \circ }$
So, the rate of ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction will be high for $1 - $bromopentane.
(b)
The compounds in which the chiral centre is present are optically active.
$2 - $bromopentane, the carbon attached with bromine, has four different substituents ( one methyl, one bromine, one hydrogen and one propyl group). So, it is optically active.
In $2 - $bromo$ - 2 - $ methylbutane, the carbon attached with bromine, has two different substituents but two same substituents (methyl group), so it is optically inactive.
Similarly the $1 - $bromopentane, is also optically inactive.
(c)
$\beta - $elimination reactions take place in presence of a base such as alcoholic potassium hydroxide.
When an alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide reacts with an alkyl halide, the alkyl halide undergoes elimination reaction. The hydrogen halide eliminates and alkene forms.
The compound which gives more substituted alkene will be most reactive for $\beta - $elimination reaction because more substituted alkene is more stable alkene.
The product of $\beta - $elimination reaction of each compound is shown as follows;
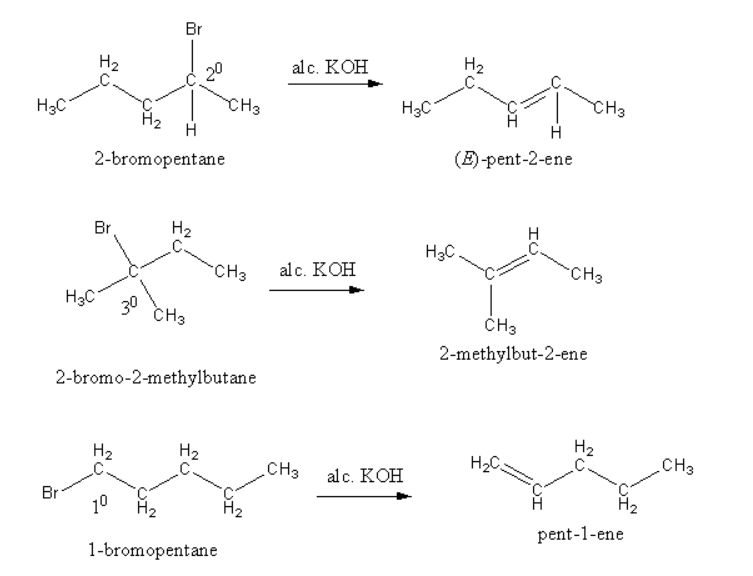
So, $2 - $bromo$ - 2 - $ methylbutane gives more substituted alkene so, $2 - $bromo$ - 2 - $ methylbutane is most reactive for $\beta - $elimination reaction.
Therefore, the compound which is most reactive towards ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$reaction is $1 - $bromopentane. The optically active compound is $2 - $bromopentane. The compound which is most reactive towards $\beta - $elimination reaction is $2 - $bromo$ - 2 - $ methylbutane.
Note:
The rate of the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction depends upon both of the reactants. In ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_1}$ mechanism, carbocation forms as intermediate. So, the reactivity depends upon the stability of the carbocation. The order of decreasing reactivity of alkyl halide towards the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_1}$ reaction is as follows: ${3^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{1^ \circ }$. The carbon having four different substituents is known as the chiral centre. The more substituted alkene means the alkene having several alkyl groups attached with a double bond.
Complete step by step answer:
The structures of all the compounds are as follows:

(a)
The full name of ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. In ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction, a nucleophile substitutes another nucleophile. The whole reaction takes place in one step.
The attacking nucleophile can approach the reactant easily if the reactant has less steric hindrance and thus facilitate the reaction via the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ mechanism. As the steric hindrance decreases the rate of reaction via ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ mechanism increases.
The order of increasing steric hindrance in alkyl halide is as follows:
${3^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{1^ \circ }$
The order of decreasing reactivity of alkyl halide towards the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction is as follows:
${1^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{3^ \circ }$
So, the rate of ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction will be high for $1 - $bromopentane.
(b)
The compounds in which the chiral centre is present are optically active.
$2 - $bromopentane, the carbon attached with bromine, has four different substituents ( one methyl, one bromine, one hydrogen and one propyl group). So, it is optically active.
In $2 - $bromo$ - 2 - $ methylbutane, the carbon attached with bromine, has two different substituents but two same substituents (methyl group), so it is optically inactive.
Similarly the $1 - $bromopentane, is also optically inactive.
(c)
$\beta - $elimination reactions take place in presence of a base such as alcoholic potassium hydroxide.
When an alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide reacts with an alkyl halide, the alkyl halide undergoes elimination reaction. The hydrogen halide eliminates and alkene forms.
The compound which gives more substituted alkene will be most reactive for $\beta - $elimination reaction because more substituted alkene is more stable alkene.
The product of $\beta - $elimination reaction of each compound is shown as follows;

So, $2 - $bromo$ - 2 - $ methylbutane gives more substituted alkene so, $2 - $bromo$ - 2 - $ methylbutane is most reactive for $\beta - $elimination reaction.
Therefore, the compound which is most reactive towards ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$reaction is $1 - $bromopentane. The optically active compound is $2 - $bromopentane. The compound which is most reactive towards $\beta - $elimination reaction is $2 - $bromo$ - 2 - $ methylbutane.
Note:
The rate of the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_2}$ reaction depends upon both of the reactants. In ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_1}$ mechanism, carbocation forms as intermediate. So, the reactivity depends upon the stability of the carbocation. The order of decreasing reactivity of alkyl halide towards the ${\text{S}}{{\text{N}}_1}$ reaction is as follows: ${3^ \circ } > \,{2^ \circ }\, > \,{1^ \circ }$. The carbon having four different substituents is known as the chiral centre. The more substituted alkene means the alkene having several alkyl groups attached with a double bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




