
The following ligands is
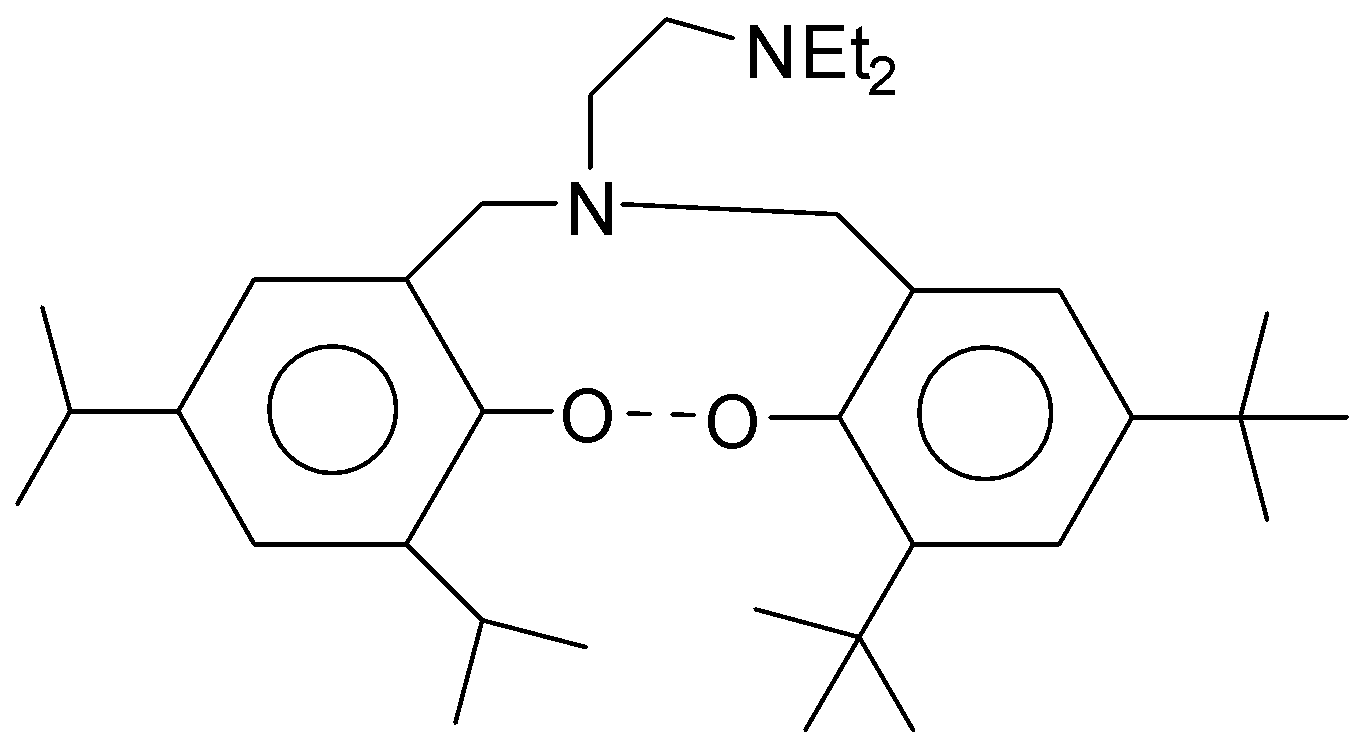
(A) Bi dentate
(B) Hexa dentate
(C) Tetra dentate
(D) Tri dentate

Answer
576k+ views
Hint:In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that bonds to a central metal atom to make a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of the electrons of the ligands donor atoms .
Complete answer:
Ligands are lewis bases whereas the central metal atom or ion is lewis acid . Ligands can be classified in various ways, like : charge, size, (bulk), the identity of the coordinating atom(s) and the number of electrons donated to the metal .
Ligands can be cations $(N{O^ + },{C_2}{H_5})$ and electron pair acceptors. Ligands can be negatively charged ions like ${F^ - },C{l^ - },B{r^ - },{I^ - },S_2^ - ,C{N^ - },NC{S^ - },O{H^ - },NH_2^ - $ or they can be neutral ligands like $N{H_3},{H_2}O,NO,{C_2}$ .
Classification of ligands on the basis of the number of binding sites with the central metal atom charge and size is as follows .
(1) Mono dentate ligands (one-toothed), the metal atom only one place. Example- $B{e^ - },{F^ - },C{l^ - },{I^ - },{H_2}O,N{H_3}$ etc.
(2) Bidentate ligands have lewis base which donates two lone pairs of electrons to the central metal atom. Ex- Ethylene di-amine(en), Acetylacetonate ion(acac).
(3) Tridentate ligands have 3 lone pairs of electrons to the central metal atom or ion.
Molecules with four donor atoms are called tetradentate, five donor atoms are called pentadentate and six donor atoms are hexadentate.
In the given question there are two nitrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms. Thus, the given ligand is tetra-dentate ligand.
Hence , option C is correct .
Additional information:-
Denticity (represented by k) refers to the number of times a ligand bonds to a metal through non-contiguous donor sites. Many ligands are capable of binding metal ions through multiple sites, usually because the ligands have lone pairs and more than one atom. Ligands that bond more than one atom are termed as chelating.
Note:
Ligand in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rate, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox ligand selection is a critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioorganic and medicinal chemistry, Homogeneous catalysis, and environmental chemistry.
Complete answer:
Ligands are lewis bases whereas the central metal atom or ion is lewis acid . Ligands can be classified in various ways, like : charge, size, (bulk), the identity of the coordinating atom(s) and the number of electrons donated to the metal .
Ligands can be cations $(N{O^ + },{C_2}{H_5})$ and electron pair acceptors. Ligands can be negatively charged ions like ${F^ - },C{l^ - },B{r^ - },{I^ - },S_2^ - ,C{N^ - },NC{S^ - },O{H^ - },NH_2^ - $ or they can be neutral ligands like $N{H_3},{H_2}O,NO,{C_2}$ .
Classification of ligands on the basis of the number of binding sites with the central metal atom charge and size is as follows .
(1) Mono dentate ligands (one-toothed), the metal atom only one place. Example- $B{e^ - },{F^ - },C{l^ - },{I^ - },{H_2}O,N{H_3}$ etc.
(2) Bidentate ligands have lewis base which donates two lone pairs of electrons to the central metal atom. Ex- Ethylene di-amine(en), Acetylacetonate ion(acac).
(3) Tridentate ligands have 3 lone pairs of electrons to the central metal atom or ion.
Molecules with four donor atoms are called tetradentate, five donor atoms are called pentadentate and six donor atoms are hexadentate.
In the given question there are two nitrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms. Thus, the given ligand is tetra-dentate ligand.
Hence , option C is correct .
Additional information:-
Denticity (represented by k) refers to the number of times a ligand bonds to a metal through non-contiguous donor sites. Many ligands are capable of binding metal ions through multiple sites, usually because the ligands have lone pairs and more than one atom. Ligands that bond more than one atom are termed as chelating.
Note:
Ligand in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rate, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox ligand selection is a critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioorganic and medicinal chemistry, Homogeneous catalysis, and environmental chemistry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




